1. 概述
想必做过Android开发的同学应该都用过Service,然而有木有想过比较全面的掌握Service相关的知识点呢?看本文就对了,学姐就Service这个知识点做了下总结,希望和大家一起进步。本文从源码分析、生命周期、基本使用三个大的方面来阐述。
2. Service & IntentService源码分析
OK,还是先从源码着手吧。
(1)Service源码
public abstract class Service extends ContextWrapper implements ComponentCallbacks2 {
private static final String TAG = "Service";
public Service() {
super(null);
}
public final Application getApplication() {
return mApplication;
}
//Service创建时调用
public void onCreate() {
}
public static final int START_CONTINUATION_MASK = 0xf;
public static final int START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY = 0;
public static final int START_STICKY = 1;
public static final int START_NOT_STICKY = 2;
public static final int START_REDELIVER_INTENT = 3;
public static final int START_TASK_REMOVED_COMPLETE = 1000;
public static final int START_FLAG_REDELIVERY = 0x0001;
public static final int START_FLAG_RETRY = 0x0002;
//通过startService(intent)启动时调用。
//intent是startService(intent)启动时传入的intent意图;flags是请求的相关信息,取值为0、
//START_FLAG_REDELIVERY、或START_FLAG_RETRY;startId是请求的id唯一标识,通过stopSelfResult(int)可以停止对应服务。
//返回值描述Service被杀死后,启动的方式,取值为START_STICKY、START_NOT_STICKY、START_REDELIVER_INTENT、START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
onStart(intent, startId);
return mStartCompatibility ? START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY : START_STICKY;
}
//服务销毁时创建,通常用于清理threads、receivers等资源
public void onDestroy() {
}
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
}
public void onLowMemory() {
}
public void onTrimMemory(int level) {
}
//bindService(intent)绑定时回调。返回客户端与Service通信的IBinder通道,返回null表明客户端不能绑定到Service,该方法不一定在主线程中回调
public abstract IBinder onBind(Intent intent);
//当所有客户端都与Service断开连接时调用。默认返回false,当返回值为true时,后续有新Client绑定时会回调onRebind()
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
return false;
}
//onUnbind()返回true,且有新Client绑定时调用
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
}
public void onTaskRemoved(Intent rootIntent) {
}
//停止服务
public final void stopSelf() {
stopSelf(-1);
}
public final void stopSelf(int startId) {
if (mActivityManager == null) {
return;
}
try {
mActivityManager.stopServiceToken(
new ComponentName(this, mClassName), mToken, startId);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
//停止服务,同stopService()。当startId为onStartCommand()中传入的最近的id时,Service会立刻停止。
//若startId是无序的(如不同线程调用),则需要根据启动顺序去停止
//startId应该为onStartCommand()中的最近的id;如果是最近id,则返回值为true,且服务将被停止,否则返回false。
public final boolean stopSelfResult(int startId) {
if (mActivityManager == null) {
return false;
}
try {
return mActivityManager.stopServiceToken(
new ComponentName(this, mClassName), mToken, startId);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
return false;
}
//让服务运行在前台,同时展示通知栏。id为通知栏的标识,不为0。
public final void startForeground(int id, Notification notification) {
try {
mActivityManager.setServiceForeground(
new ComponentName(this, mClassName), mToken, id,
notification, true);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
//不让服务运行在前台。removeNotification为true表示移除通知栏;否则通知栏不会移除,除非主动移除或服务死掉
public final void stopForeground(boolean removeNotification) {
try {
mActivityManager.setServiceForeground(
new ComponentName(this, mClassName), mToken, 0, null,
removeNotification);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
}
(2)IntentService源码
public abstract class IntentService extends Service {
private volatile Looper mServiceLooper;
private volatile ServiceHandler mServiceHandler;
private String mName;
private boolean mRedelivery;
//内部Handler
private final class ServiceHandler extends Handler {
public ServiceHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
//在工作线程中处理启动请求
onHandleIntent((Intent)msg.obj);
stopSelf(msg.arg1);
}
}
public IntentService(String name) {
super();
mName = name;
}
public void setIntentRedelivery(boolean enabled) {
mRedelivery = enabled;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//服务创建时,创建一个新工作线程,启动消息循环
HandlerThread thread = new HandlerThread("IntentService[" + mName + "]");
thread.start();
mServiceLooper = thread.getLooper();
mServiceHandler = new ServiceHandler(mServiceLooper);
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
//服务启动时,将启动请求发给Handler进行处理
Message msg = mServiceHandler.obtainMessage();
msg.arg1 = startId;
msg.obj = intent;
mServiceHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
onStart(intent, startId);
return mRedelivery ? START_REDELIVER_INTENT : START_NOT_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
//服务停止时,停止消息循环
mServiceLooper.quit();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
//默认返回null,如果希望提供客户端绑定服务,可以返回自定义Binder对象
return null;
}
//工作线程中调用,用于处理启动请求,通常执行耗时任务
protected abstract void onHandleIntent(Intent intent);
}
以上源码已经对各个方法做了备注。学姐想就Service和IntentService做下对比:
(1)IntentService是Service的子类,都可以在后台执行长时间操作而不使用用户界面。
(2)IntentService内置了工作线程,可以在onHandleIntent()顺序处理客户端发送的耗时请求;而Service如果想执行耗时任务,需要在子类中添加线程。
(3)IntentService只有一个线程,只能顺序处理耗时请求;Service可以根据需要创建多个线程处理来自客户端的请求。
(4)IntentService在任务执行完后会自动停止,Service需要主动调用stopService或stopSelf停止服务。
3. Service生命周期
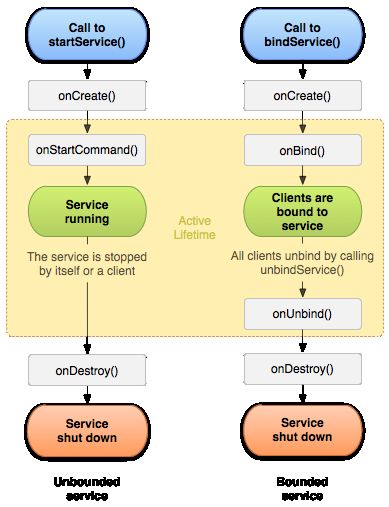
以上为Service生命周期图。分启动服务和绑定服务两种方式。
(1)启动方式
startService启动服务,stopService停止服务。
完整生命周期回调顺序为:onCreate -> onStartCommand -> onDestroy
有效生命周期为:onStartCommand和onDestroy之间
生命周期方法介绍:
onCreate 创建服务时回调。onCreate只会调用一次
onStartCommand 启动服务时回调。一旦启动,服务即可在后台运行,即使启动服务的组件已被销毁也不受影响。每次调用startService()时都会回调,允许多次调用。
传参startId是请求的id唯一标识,其返回值描述系统应该如何在服务终止的情况下继续运行服务,是对系统的要求。
返回值取值为:
START_NOT_STICKY 如果系统在 onStartCommand() 返回后终止服务,则除非有挂起 Intent 要传递,否则系统不会重建服务。这是最安全的选项,可以避免在不必要时以及应用能够轻松重启所有未完成的作业时运行服务。
START_STICKY 如果系统在 onStartCommand() 返回后终止服务,则会重建服务并调用 onStartCommand(),但绝对不会重新传递最后一个 Intent。相反,除非有挂起 Intent 要启动服务(在这种情况下,将传递这些 Intent ),否则系统会通过空 Intent 调用 onStartCommand()。这适用于不执行命令、但无限期运行并等待作业的媒体播放器(或类似服务)。
START_REDELIVER_INTENT 如果系统在 onStartCommand() 返回后终止服务,则会重建服务,并通过传递给服务的最后一个 Intent 调用 onStartCommand()。任何挂起 Intent 均依次传递。这适用于主动执行应该立即恢复的作业(例如下载文件)的服务。
onDestroy 停止服务时回调。此方法用来清理所有资源,如线程、注册的侦听器、接收器等。需要调用stopSelf(int)或stopService()停止服务。当有多个请求时,stopSelf(int) 确保服务停止请求始终基于最近的启动请求id,服务才能停止,否则服务会继续运行。
(2)绑定方式
bindService绑定服务,unbindService解绑服务。
完整生命周期回调顺序为:onCreate -> onBind -> onUnbind -> onDestroy
有效生命周期为:onBind和onUnbind之间
生命周期方法介绍:
onCreate 创建服务时回调。onCreate只会调用一次
onBind 绑定服务时回调。绑定服务提供了一个客户端-服务器接口,允许组件与服务进行交互、发送请求、获取结果,甚至是利用进程间通信 (IPC) 跨进程执行这些操作,如果不允许绑定,则应返回null。 仅当与另一个应用组件绑定时,绑定服务才会运行。 多个组件可以同时绑定到该服务,但全部取消绑定后,该服务即会被销毁。只有在第一个客户端绑定时,系统才会调用服务的 onBind() 方法来检索 IBinder,系统随后无需再次调用 onBind(),便可将同一 IBinder 传递至任何其他绑定的客户端。该方法不一定在UI线程。
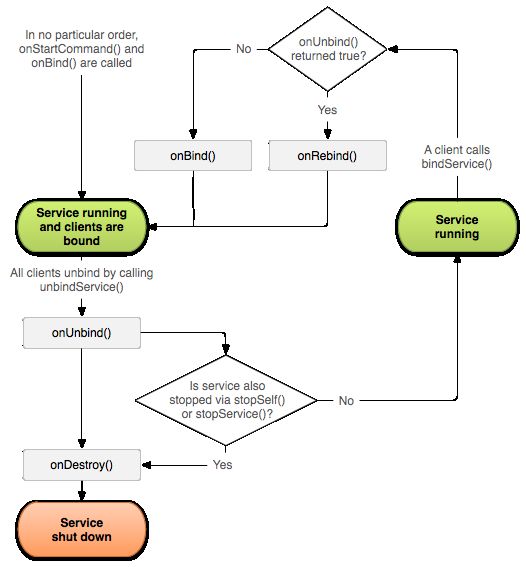
onUnbind 解绑服务时回调。当所有客户端都与Service断开连接时调用。默认返回false,当返回值为true时,后续有新Client绑定时会回调onRebind()
onRebind 重新绑定时回调。onUnbind()返回true,且有新Client绑定时调用
onDestroy 停止服务时回调。此方法用来清理所有资源,如线程、注册的侦听器、接收器等。服务与所有客户端之间的绑定全部取消时,系统便会销毁它
附录绑定方式的详细生命周期图:
ps1:所谓有效生命周期,即Service处于活跃状态的生命周期。
ps2:启动方式和绑定方式可以组合使用。同时,绑定方式可以用在同一个进程,也可以跨进程使用。跨进程可以使用Messager或AIDL方式通信。
ps3:关于使用Service还是Thread的标准是,看是否需要在后台执行耗时操作。若只需要在前台运行,则用Thread足以,否则使用Service/IntentService。
4. 基本使用
个人认为IntentService和Service两者是可以互相取代的,只不过自己需要稍微增加些代码。
下面就两个场景来描述IntentService和Service的使用。
4.1 创建后台服务
(1) 创建服务
public class RSSPullService extends IntentService {
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent workIntent) {
// Gets data from the incoming Intent
String dataString = workIntent.getDataString();
...
// Do work here, based on the contents of dataString
...
}
}
(2) 声明服务
...
//android:exported为false表示该服务只能应用内组件可以使用
(3) 发送请求
mServiceIntent = new Intent(getActivity(), RSSPullService.class);
mServiceIntent.setData(Uri.parse(dataUrl));
getActivity().startService(mServiceIntent);
(4) 结果回传
//使用LocalBroadcastManager.sendBroadcast()标明只能应用内广播可以接收
public final class Constants {
...
// Defines a custom Intent action
public static final String BROADCAST_ACTION = "com.example.android.threadsample.BROADCAST";
...
// Defines the key for the status "extra" in an Intent
public static final String EXTENDED_DATA_STATUS = "com.example.android.threadsample.STATUS";
...
}
public class RSSPullService extends IntentService {
...
/*
* Creates a new Intent containing a Uri object
* BROADCAST_ACTION is a custom Intent action
*/
Intent localIntent = new Intent(Constants.BROADCAST_ACTION)
.putExtra(Constants.EXTENDED_DATA_STATUS, status);
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).sendBroadcast(localIntent);
...
}
(5) 消息接收
// Broadcast receiver for receiving status updates from the IntentService
private class ResponseReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver
{
// Prevents instantiation
private DownloadStateReceiver() {
}
// Called when the BroadcastReceiver gets an Intent it's registered to receive
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
...
/*
* Handle Intents here.
*/
...
}
}
// Class that displays photos
public class DisplayActivity extends FragmentActivity {
...
public void onCreate(Bundle stateBundle) {
...
super.onCreate(stateBundle);
...
// The filter's action is BROADCAST_ACTION
IntentFilter mStatusIntentFilter = new IntentFilter(Constants.BROADCAST_ACTION);
// Adds a data filter for the HTTP scheme
mStatusIntentFilter.addDataScheme("http");
...
}
}
// Instantiates a new DownloadStateReceiver
DownloadStateReceiver mDownloadStateReceiver = new DownloadStateReceiver();
// Registers the DownloadStateReceiver and its intent filters
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).registerReceiver(mDownloadStateReceiver, mStatusIntentFilter);
...
4.2 绑定服务
绑定服务可以是本地服务,也可以是远程服务。
本地服务:
如果是本地服务且在同一个进程,则Service从 onBind() 返回Binder扩展实例,客户端收到 Binder 后,可利用它直接访问Binder和Service提供的方法。
远程服务:
使用Messager方式。实际是以AIDL作为其底层结构。Messenger在单一线程中创建包含所有请求的队列,无需对服务进行线程安全设计。
使用AIDL方式。服务可以同时处理多个请求,此时服务必须具备多线程处理能力,并采用线程安全式设计。
(1)本地服务
public class LocalService extends Service {
// Binder given to clients
private final IBinder mBinder = new LocalBinder();
// Random number generator
private final Random mGenerator = new Random();
/**
* Class used for the client Binder. Because we know this service always
* runs in the same process as its clients, we don't need to deal with IPC.
*/
public class LocalBinder extends Binder {
LocalService getService() {
// Return this instance of LocalService so clients can call public methods
return LocalService.this;
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
/** method for clients */
public int getRandomNumber() {
return mGenerator.nextInt(100);
}
}
public class BindingActivity extends Activity {
LocalService mService;
boolean mBound = false;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// Bind to LocalService
Intent intent = new Intent(this, LocalService.class);
bindService(intent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
// Unbind from the service
if (mBound) {
unbindService(mConnection);
mBound = false;
}
}
public void onButtonClick(View v) {
if (mBound) {
int num = mService.getRandomNumber();
Toast.makeText(this, "number: " + num, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
// We've bound to LocalService, cast the IBinder and get LocalService instance
LocalBinder binder = (LocalBinder) service;
mService = binder.getService();
mBound = true;
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) {
mBound = false;
}
};
}
(2)远程服务-Messager方式
public class MessengerService extends Service {
/** Command to the service to display a message */
static final int MSG_SAY_HELLO = 1;
/**
* Handler of incoming messages from clients.
*/
class IncomingHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_SAY_HELLO:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "hello!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
default:
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
}
}
/**
* Target we publish for clients to send messages to IncomingHandler.
*/
final Messenger mMessenger = new Messenger(new IncomingHandler());
/**
* When binding to the service, we return an interface to our messenger
* for sending messages to the service.
*/
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "binding", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return mMessenger.getBinder();
}
}
public class ActivityMessenger extends Activity {
Messenger mService = null;
boolean mBound;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
mService = new Messenger(service);
mBound = true;
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
mService = null;
mBound = false;
}
};
public void sayHello(View v) {
if (!mBound) return;
// Create and send a message to the service, using a supported 'what' value
Message msg = Message.obtain(null, MessengerService.MSG_SAY_HELLO, 0, 0);
try {
mService.send(msg);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// Bind to the service
bindService(new Intent(this, MessengerService.class), mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
// Unbind from the service
if (mBound) {
unbindService(mConnection);
mBound = false;
}
}
}
(3)远程服务-AIDL方式
由于篇幅有限,代码请参考 http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/guide/components/aidl.html
5. 总结
(1)IntentService和Service都可以后台执行耗时任务,IntentService是Service的子类,内置了线程和消息循环机制,任务执行完后自动停止服务。
(2)Service使用有两种方式:启动服务和绑定服务
(3)启动服务生命周期:onCreate -> onStartCommand -> onDestroy
(4)绑定服务生命周期:onCreate -> onBind -> onUnbind -> onDestroy
(5)启动服务适合于本地服务。绑定服务同时适合于本地服务和远程服务,远程服务可以使用Messager和AIDL实现进程间通信
6. 参考链接
http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/guide/components/services.html
http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/training/run-background-service/index.html