一、实验总结
抽象类与接口的区别
| 区别点 | 抽象类 | 接口 |
|---|---|---|
| 定义 | 包含一个抽象方法的类 | 抽象方法和全局变量的集合 |
| 组成 | 构造方法,抽象方法,普通方法,常量,变量 | 常量,抽象方法 |
| 使用 | 子类继承抽象类 | 子类实现接口 |
| 关系 | 抽象类可以实现多个接口 | 接口不能继续抽象类,但允许继承多个接口 |
| 常见设计模式 | 模板设计 | 工厂设计,代理设计 |
| 对象 | 都通过对象的多态性产生实例化对象 | |
| 局限 | 抽象类有单继承的局限 | 接口没有此局限 |
| 实际 | 作为一个模板 | 是作为一个标准或是表示一种能力 |
| 选择 | 如果抽象类和接口都可以使用的话,优先使用接口,因为避免单继承的局限 |
实验报告
一)抽象类的使用
设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p(p-a)(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
package com.company.java;
public abstract class Shape {
public abstract void getLength();
public abstract void getArea();
}
package com.company.java;
public class Circle extends Shape {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public void getLength() {
System.out.println("该圆的周长为:"+(2*Math.PI*radius));
}
public void getArea() {
System.out.println("该圆的面积为:"+(Math.PI*Math.pow(radius,2)));
}
}
package com.company.java;
public class Rectangle extends Shape{
private double width;
private double high;
public Rectangle(double width,double high){
this.width=width;
this.high=high;
}
public double getHigh() {
return high;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setHigh(double high) {
this.high = high;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public void getLength() {
System.out.println("该矩形的周长为:"+2*(width+high));
}
public void getArea() {
System.out.println("该矩形的面积为:"+width*high);
}
}
package com.company.java;
public class Triangle extends Shape {
private double a,b,c;
double p;
public Triangle(double a,double b,double c){
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
this.c=c;
p=(a+b+c)/2;
}
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
public void setA(double a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void setB(double b) {
this.b = b;
}
public void setC(double c) {
this.c = c;
}
public void getLength() {
System.out.println("该三角形的周长为:"+(a+b+c));
}
public void getArea() {
System.out.println("该三角形的面积为:"+Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)));
}
}
package com.company.java;
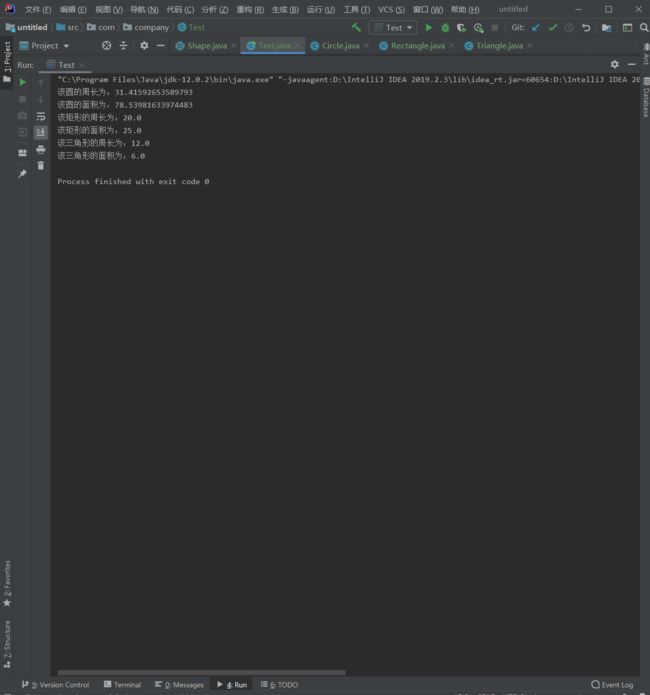
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Shape sha1=new Circle(5);
Shape sha2=new Rectangle(5,5);
Shape sha3=new Triangle(3,4,5);
sha1.getLength();
sha1.getArea();
sha2.getLength();
sha2.getArea();
sha3.getLength();
sha3.getArea();
}
}(二)使用接口技术
1定义接口Shape,其中包括一个方法size(),设计“直线”、“圆”、类实现Shape接口。分别创建一个“直线”、“圆”对象,将各类图形的大小输出。
package com.company;
interface Shape {
public abstract void size();
}
package com.company;
public class Test {
public static void plugin(Shape sha){
sha.size();
}
}
package com.company;
public class Wire implements Shape{
private double lenght;
public Wire(double lenght){
this.lenght=lenght;
}
public double getLenght() {
return lenght;
}
public void setLenght(double lenght) {
this.lenght = lenght;
}
public void size() {
System.out.println("直线的长度为:"+lenght);
}
}
package com.company;
public class Circle implements Shape {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius=radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void size() {
System.out.println("圆的半径="+radius);
System.out.println("圆的周长="+2*radius*Math.PI);
System.out.println("圆的面积="+Math.PI*Math.pow(radius,2));
}
}
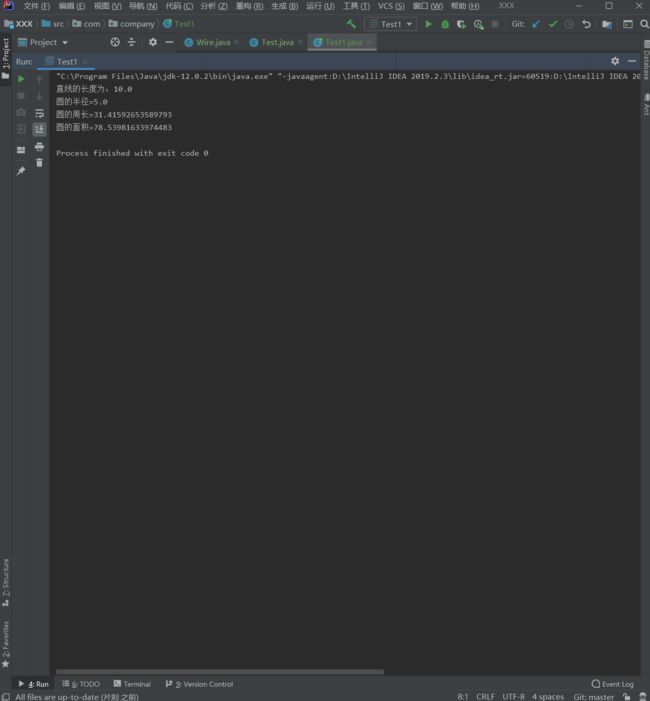
package com.company;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Test.plugin(new Wire(10));
Test.plugin(new Circle(5));
}
}