ResultSetHandler是mybatis的关键类之一,用于对jdbc返回的ResultSet进行映射处理,其中包括列前缀处理,逻辑分页,鉴别器(Discriminator,基于值实现动态映射列)处理等等。
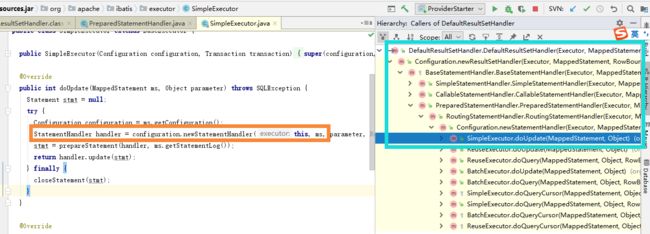
ResultSetHandler在StatementHandler执行过程中构建,如下:
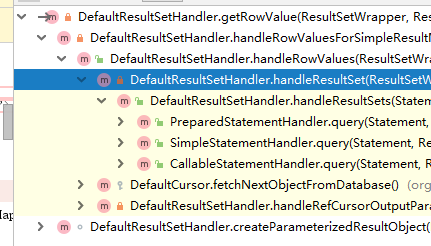
接下去来看ResultSetHandler的定义。最主要的是handleResultSets,它负责普通查询结果的处理。
public interface ResultSetHandler {List handleResultSets(Statement var1) throws SQLException; Cursor handleCursorResultSets(Statement var1) throws SQLException; void handleOutputParameters(CallableStatement var1) throws SQLException; }
handleResultSets在StatementHandler执行完成后被调用,如下:
要对结果集自定义处理的话,可以改动此处源码。因为mybatis拦截器支持对四大对象(Executor,StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,ResultSetHandler)都支持,所以也可以通过拦截器(参见mybatis自定义插件开发详解)实现,各有利弊,LZ采用后者。
逻辑分页也是在handleResultSets中处理。逻辑分页由org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds实现,mybatis内置的应用层逻辑分页实现定义,但基本上很少使用,定义如下。
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package org.apache.ibatis.session; public class RowBounds { public static final int NO_ROW_OFFSET = 0; public static final int NO_ROW_LIMIT = 2147483647; public static final RowBounds DEFAULT = new RowBounds(); private final int offset; private final int limit; public RowBounds() { this.offset = 0; this.limit = 2147483647; } public RowBounds(int offset, int limit) { this.offset = offset; this.limit = limit; } public int getOffset() { return this.offset; } public int getLimit() { return this.limit; } }
默认值为不分页。在shouldProcessMoreRows中判断,如下:
private boolean shouldProcessMoreRows(ResultContext context, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException { return !context.isStopped() && context.getResultCount() < rowBounds.getLimit(); }
在处理每一行记录的时候,先处理没有明确映射(无或不在ResultMap中)的属性,然后处理明确映射,如下:
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap) throws SQLException { ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
// 创建目标类型对象,如Pojo或Map Object rowValue = this.createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, (String)null); if (rowValue != null && !this.hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) { MetaObject metaObject = this.configuration.newMetaObject(rowValue); boolean foundValues = this.useConstructorMappings; if (this.shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) { // map就是在这里自动映射的 foundValues = this.applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, (String)null) || foundValues; } foundValues = this.applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, (String)null) || foundValues; foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues; rowValue = !foundValues && !this.configuration.isReturnInstanceForEmptyRow() ? null : rowValue; } return rowValue; }
接下去再来看ResultHandler,它用来对每行记录映射或处理,典型的比如二次过滤或脱敏处理,都可以在这里处理,当然也可以通过插件,只不过在这里处理从性能上看最佳。其定义比较简单:
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package org.apache.ibatis.session; public interface ResultHandler{ void handleResult(ResultContextextends T> var1); }
相对来说,ResultHandler的实现很简单,这里就不详解了,真的想了解的可以参考https://www.cnblogs.com/51life/p/9633002.html。