Netty中有一个主要的特点,就是ByteBuf的实现, 由于NIO中java.nio.ByteBuf中只有position字段来记录读写时的位置,读写切换时需要调用flip()方法。Netty自己实现一个ByteBuf来的实体, 维护两个独立的index的表示读写的位置:readerIndex 与 wirterIndex。ByteBuf又分为HeapByteBuf 与 DirectByteBuf来表示 ‘堆内内存' 与 '堆外内存', 由于Netty是基于针对网络传输,所以分配内存,释放内存,是一个很频繁的事件,Netty将ByteBuf的进行了池化,由PooledByteBufAllocator来分配ButeBuf, 由于Netty对ByteBuf进行了池化, 就需要对内存的分配与释放进行一个更有效的管理,如:分配内存空间为一个连续的空间,怎么让内存分配更快, 管理内存碎片 ... .Netty引入了 'Slab算法' 跟 'Bubby算法' 来进行对内存分配进行管理。
Slab算法:
引用Memcache中内存的分配方式相同, 将内存通过大小分为若干类,通过需要的内存大写,找第一个大于等于的类分配。Netty 中将内存的分配分为以下几类(堆外堆内相同,这里以堆外为例):
-
MemoryRegionCache:normCapacity < 512的内存分配[] tinySubPageDirectCaches -
MemoryRegionCache:normCapacity < pageSize 的内存分配 (PageSize 默认为 8KB)[] smallSubPageDirectCaches -
MemoryRegionCache:normCapacity <= chunkSize 的内存分配(chunkSize 默认值为 8KB * 2^11 = 16MB, 其直的计算方式会根据下面的Bubby算法介绍)[] normalDirectCaches -
allocateHuge(buf, reqCapacity): normCapacity > chunkSize 的内存分配
Bubby算法:
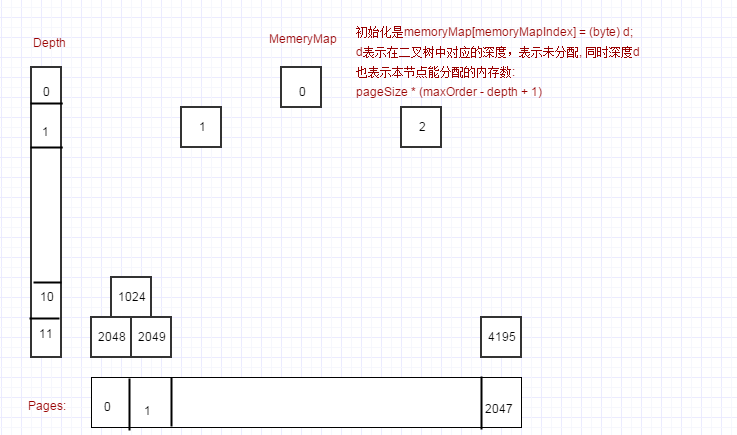
由于Netty的分配是由PoolChunk进行分配,PoolChunk是一个非常大的内存块(默认值为8KB * 2^11 = 16MB),这个内存块有一个完全平衡的二叉树来描述。
1:由一个byte[] memoryMap来对来对内存页进行管理,父节点直接管理子节点, 这里maxOrder的默认值为11, 而第一个Page(pageSize = 8KB), 由memoryMap[2^11=2048]直接管理....。这里节点是否分配油value=memoryMap[index]的值来表示,如果①:value=当前层级,表示未分配,②:unusable = (byte) (maxOrder + 1)(unusable = 12)表示节点,及节点的子节点数据都已被分配, ③: 当前层级
2:如果要分配8KB的内存,则通过开始 memoryMap[2^11=2048]——> memoryMap[2^12-1=4095]顺序查找未分配的Page。
3:需要分配大于PageSize的内存, 如16KB, 由于层级d=11每个节点管理一个pageSize=8KB的内存块,层级d=10管理两个d=11的节点,只需要分配一个层级为d=10的节点就可以分配一个16KB的内存, 则通过 memoryMap[2^10=1024]——> memoryMap[2^10-1=2047]顺序查找未分配的节点
4:小于PageSize的内存分配,直接通过对一个Page的内存分割成tinySubPageDirectCaches与smallSubPageDirectCaches进行内存的分配
补充:
1:Netty中还为了分配大内存的分配的成功率,将PoolChunk进行一个使用率的分类管理,使用率高的,自然未使用的内存数量高,分配大内存时成功率高。Netty中维护了一个PoolArena的使用率链表,每次分配的内存的时候PoolChunkList.allocate(..),会比较当前分配的PoolChunk.usage()与PoolChunkList.maxUsage比较,如果大于maxUsage,则会将此PoolChunk从当前链表中删除,添加到下一个PoolChunkList中。每次释放内存的时候PoolChunkList.free(...),会比较当前的PoolChunk.usage()与PoolChunkList.minUsage比较,如果小于minUsage,则会将此PoolChunk从当前链表中删除,添加到上一个PoolChunkList中。注意,不管是分配还是释放PoolChunkList的添加比较都是递归比较,直到找到适合自己的PoolChunkList
2:Netty中的分配为了提交并发,将会通过一个PoolArena去减少并发度,每一个线程会从PoolThreadLocalCache extends FastThreadLocal中去找到当前的PoolArena, PoolArena与线程的绑定初始化,通过最少使用算法(PoolThreadLocalCache.leastUsedArena(PoolArena)查找PoolArena。
接下来具体描述Netty中代码的实现:
分配内存的方式从PooledByteBufAllocator类开始:
public class PooledByteBufAllocator extends AbstractByteBufAllocator implements ByteBufAllocatorMetricProvider {
...
private final PoolThreadLocalCache threadCache;
...
public PooledByteBufAllocator(boolean preferDirect, int nHeapArena, int nDirectArena, int pageSize, int maxOrder,
int tinyCacheSize, int smallCacheSize, int normalCacheSize,
boolean useCacheForAllThreads, int directMemoryCacheAlignment) {
super(preferDirect);
//初始化ThreadLocal
threadCache = new PoolThreadLocalCache(useCacheForAllThreads);
...
}
...
@Override
protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
//先从ThreadLocal中查找分配的PoolArena
PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get();
PoolArena directArena = cache.directArena;
final ByteBuf buf;
if (directArena != null) {
buf = directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
} else {
buf = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ?
UnsafeByteBufUtil.newUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) :
new UnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);
}
}
我们先看一下 PoolThreadLocalCache类的定义:
//继承FastThreadLocal
final class PoolThreadLocalCache extends FastThreadLocal {
private final boolean useCacheForAllThreads;
PoolThreadLocalCache(boolean useCacheForAllThreads) {
this.useCacheForAllThreads = useCacheForAllThreads;
}
@Override
protected synchronized PoolThreadCache initialValue() {
//查找最少使用的PoolArena来作为此次分配的PoolArena
final PoolArena heapArena = leastUsedArena(heapArenas);
final PoolArena directArena = leastUsedArena(directArenas);
if (useCacheForAllThreads || Thread.currentThread() instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return new PoolThreadCache(
heapArena, directArena, tinyCacheSize, smallCacheSize, normalCacheSize,
DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_BUFFER_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_CACHE_TRIM_INTERVAL);
}
// No caching for non FastThreadLocalThreads.
return new PoolThreadCache(heapArena, directArena, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
}
@Override
protected void onRemoval(PoolThreadCache threadCache) {
threadCache.free();
}
private PoolArena leastUsedArena(PoolArena[] arenas) {
if (arenas == null || arenas.length == 0) {
return null;
}
PoolArena minArena = arenas[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arenas.length; i++) {
PoolArena arena = arenas[i];
if (arena.numThreadCaches.get() < minArena.numThreadCaches.get()) {
minArena = arena;
}
}
return minArena;
}
}
接下来查看directArena.allocate方法看一下是怎么分配的:
abstract class PoolArena implements PoolArenaMetric {
...
//Tiny类大小页数组
private final PoolSubpage[] tinySubpagePools;
//Small类大小页数组
private final PoolSubpage[] smallSubpagePools;
private final PoolChunkList q050;
private final PoolChunkList q025;
private final PoolChunkList q000;
private final PoolChunkList qInit;
private final PoolChunkList q075;
private final PoolChunkList q100;
...
protected PoolArena(PooledByteBufAllocator parent, int pageSize,
int maxOrder, int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int cacheAlignment) {
...
directMemoryCacheAlignment = cacheAlignment;
directMemoryCacheAlignmentMask = cacheAlignment - 1;
subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize - 1);
//numTinySubpagePools = 512 >>> 4;
//设置Tiny类Page页面值为2^4=16, 所以一个512大小内存块可以分配512 >>> 4 = 32个Page
tinySubpagePools = newSubpagePoolArray(numTinySubpagePools);
for (int i = 0; i < tinySubpagePools.length; i ++) {
tinySubpagePools[i] = newSubpagePoolHead(pageSize);
}
//设置Small类的Page页面值为512, 即2^9, 所以一个PageSize大小的内存块刻一个分配pageShifts - 9个Page
numSmallSubpagePools = pageShifts - 9;
smallSubpagePools = newSubpagePoolArray(numSmallSubpagePools);
for (int i = 0; i < smallSubpagePools.length; i ++) {
smallSubpagePools[i] = newSubpagePoolHead(pageSize);
}
q100 = new PoolChunkList(this, null, 100, Integer.MAX_VALUE, chunkSize);
q075 = new PoolChunkList(this, q100, 75, 100, chunkSize);
q050 = new PoolChunkList(this, q075, 50, 100, chunkSize);
q025 = new PoolChunkList(this, q050, 25, 75, chunkSize);
q000 = new PoolChunkList(this, q025, 1, 50, chunkSize);
qInit = new PoolChunkList(this, q000, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 25, chunkSize);
q100.prevList(q075);
q075.prevList(q050);
q050.prevList(q025);
q025.prevList(q000);
q000.prevList(null);
qInit.prevList(qInit);
...
}
private PoolSubpage newSubpagePoolHead(int pageSize) {
PoolSubpage head = new PoolSubpage(pageSize);
head.prev = head;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
...
PooledByteBuf allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, int reqCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
//从RECYCLER中获取
PooledByteBuf buf = newByteBuf(maxCapacity);
allocate(cache, buf, reqCapacity);
return buf;
}
/**
对分配内存大小分为 4 类:
Tiny :(0, 512)
Small: [512, PageSize)
Noraml: [PageSize, ChunkSize]
Huge: > ChunkSize
*/
private void allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf buf, final int reqCapacity) {
//获取正好大于reqCapacity的2的幂的数值
final int normCapacity = normalizeCapacity(reqCapacity);
if (isTinyOrSmall(normCapacity)) { // capacity < pageSize
int tableIdx;
PoolSubpage[] table;
boolean tiny = isTiny(normCapacity);
if (tiny) { // < 512
//首次分配缓存queue为空, 分配失败,返回false
if (cache.allocateTiny(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
//查找需要分配normCapacity大小的内存在tinySubpagePools中第一个索引值
tableIdx = tinyIdx(normCapacity);
table = tinySubpagePools;
} else {
if (cache.allocateSmall(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
//查找需要分配normCapacity大小的内存在smallSubpagePools中第一个索引值
tableIdx = smallIdx(normCapacity);
table = smallSubpagePools;
}
//将分配normCapacity在相应数组池第一个索引值对应的PoolSubpage作为head
final PoolSubpage head = table[tableIdx];
/**
* Synchronize on the head. This is needed as {@link PoolChunk#allocateSubpage(int)} and
* {@link PoolChunk#free(long)} may modify the doubly linked list as well.
*/
synchronized (head) {
//PoolSubpage 是通过 newSubpagePoolHead 方法创建
//newSubpagePoolHead方法中head.prev = head;
//初始分配是 s != head, 返回false
final PoolSubpage s = head.next;
if (s != head) {
assert s.doNotDestroy && s.elemSize == normCapacity;
long handle = s.allocate();
assert handle >= 0;
s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, handle, reqCapacity);
incTinySmallAllocation(tiny);
return;
}
}
synchronized (this) {
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
}
incTinySmallAllocation(tiny);
return;
}
//对Normal 类的内存进行分配
if (normCapacity <= chunkSize) {
if (cache.allocateNormal(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
synchronized (this) {
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
++allocationsNormal;
}
} else {
// Huge allocations are never served via the cache so just call allocateHuge
allocateHuge(buf, reqCapacity);
}
}
// Method must be called inside synchronized(this) { ... } block
private void allocateNormal(PooledByteBuf buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
if (q050.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q025.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) ||
q000.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || qInit.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) ||
q075.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
return;
}
// Add a new chunk.
PoolChunk c = newChunk(pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize);
//根据返回的handle(分配Page的位置(对与 0;
c.initBuf(buf, handle, reqCapacity);
qInit.add(c);
}
...
}
通过上面的代码,最终分配的内存方法是通过PoolChunk中的allocate(int normCapacity)方法进行内存的分配,查看一下分配逻辑:
final class PoolChunk implements PoolChunkMetric {
...
long allocate(int normCapacity) {
if ((normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0) { // >= pageSize
return allocateRun(normCapacity);
} else {
return allocateSubpage(normCapacity);
}
}
/**
* 为 normCapacity 分配 pages , pages的数量>=1
*
* @param normCapacity normalized capacity
* @return index in memoryMap
*/
private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) {
int d = maxOrder - (log2(normCapacity) - pageShifts);
int id = allocateNode(d);
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
freeBytes -= runLength(id);
return id;
}
/**
* 在memoryMap中分配一个depth d 的管理内存index 节点
*
* @param d depth
* @return index in memoryMap
*/
private int allocateNode(int d) {
int id = 1;
int initial = - (1 << d); // has last d bits = 0 and rest all = 1
byte val = value(id);
if (val > d) { // idx = 1 的节点子节点被分配,剩余内存不够,不能分配
return -1;
}
while (val < d || (id & initial) == 0) { // id & initial == 1 << d for all ids at depth d, for < d it is 0
id <<= 1;
val = value(id);
if (val > d) {
id ^= 1;
val = value(id);
}
}
byte value = value(id);
assert value == d && (id & initial) == 1 << d : String.format("val = %d, id & initial = %d, d = %d",
value, id & initial, d);
setValue(id, unusable); // 设置当前节点已被分配
updateParentsAlloc(id);//同时更新父节点的分配情况
return id;
}
private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) {
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
PoolSubpage head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity);
synchronized (head) {
//由于subpages的大小 [] subpages = this.subpages;
final int pageSize = this.pageSize;
freeBytes -= pageSize;
int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id);
PoolSubpage subpage = subpages[subpageIdx];
if (subpage == null) {
subpage = new PoolSubpage(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity);
subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage;
} else {
subpage.init(head, normCapacity);
}
return subpage.allocate();
}
}
private int runOffset(int id) {
// represents the 0-based offset in #bytes from start of the byte-array chunk
int shift = id ^ 1 << depth(id);
return shift * runLength(id);
}
...
}
对于>= pageSize内存, PoolChunk可以直接分配, 对于小于pageSize的内存, 先从PoolChunk中分配一个 pageSize的节点, 然后交给PoolSubpage进行分配:
final class PoolSubpage implements PoolSubpageMetric {
...
/** Special constructor that creates a linked list head */
PoolSubpage(int pageSize) {
chunk = null;
memoryMapIdx = -1;
runOffset = -1;
elemSize = -1;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
bitmap = null;
}
PoolSubpage(PoolSubpage head, PoolChunk chunk, int memoryMapIdx, int runOffset, int pageSize, int elemSize) {
this.chunk = chunk;
this.memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx;
this.runOffset = runOffset;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
//一个long的长度为64个字节
//分配的大小最小为16,一个Page可以划分为PageSize/16 个
//PageSize/16/64 则可以表示所有的内存段的情况
bitmap = new long[pageSize >>> 10]; // pageSize / 16 / 64
init(head, elemSize);
}
void init(PoolSubpage head, int elemSize) {
doNotDestroy = true;
this.elemSize = elemSize;
if (elemSize != 0) {
maxNumElems = numAvail = pageSize / elemSize;
nextAvail = 0;
//bitmapLength的长度为maxNumElems/64 或者长度超过有余, 则+1
bitmapLength = maxNumElems >>> 6;
if ((maxNumElems & 63) != 0) {
bitmapLength ++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapLength; i ++) {
bitmap[i] = 0;
}
}
addToPool(head);
}
/**
* Returns the bitmap index of the subpage allocation.
*/
long allocate() {
if (elemSize == 0) {
return toHandle(0);
}
if (numAvail == 0 || !doNotDestroy) {
return -1;
}
//查找可以使用下一个可以使用内存段的index
final int bitmapIdx = getNextAvail();
//根据内存段的index, 查找在bitmap中描述的idx
int q = bitmapIdx >>> 6;
//根据内存段的index,并long数据中描述位置
int r = bitmapIdx & 63;
assert (bitmap[q] >>> r & 1) == 0;
//对bitmap描述的内存段的使用情况进行更新操作
bitmap[q] |= 1L << r;
if (-- numAvail == 0) {
removeFromPool();
}
return toHandle(bitmapIdx);
}
//将bitmapIdx 放在高位, memoryMapIdx放在地位, 拼成一个long型的数据返回
private long toHandle(int bitmapIdx) {
return 0x4000000000000000L | (long) bitmapIdx << 32 | memoryMapIdx;
}
...
}
而对于内存的释放,最终会调用PooledByteBuf.deallocate()方法进行释放。
@Override
protected final void deallocate() {
if (handle >= 0) {
final long handle = this.handle;
this.handle = -1;
memory = null;
tmpNioBuf = null;
chunk.arena.free(chunk, handle, maxLength, cache);
chunk = null;
recycle();
}
}
private void recycle() {
recyclerHandle.recycle(this);
}
看一下 chunk.arena.free(chunk, handle, maxLength, cache)方法
void free(PoolChunk chunk, long handle, int normCapacity, PoolThreadCache cache) {
if (chunk.unpooled) {
int size = chunk.chunkSize();
destroyChunk(chunk);
activeBytesHuge.add(-size);
deallocationsHuge.increment();
} else {
SizeClass sizeClass = sizeClass(normCapacity);
if (cache != null && cache.add(this, chunk, handle, normCapacity, sizeClass)) {
// cached so not free it.
return;
}
freeChunk(chunk, handle, sizeClass);
}
}
可以看到调用cache.add方法,最红会把释放的内存放入Queue