Codeforces Round #329 (Div. 2)
D. Happy Tree Party
time limit per test
3 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Bogdan has a birthday today and mom gave him a tree consisting of n vertecies. For every edge of the tree i, some number *x**i* was written on it. In case you forget, a tree is a connected non-directed graph without cycles. After the present was granted, m guests consecutively come to Bogdan's party. When the i-th guest comes, he performs exactly one of the two possible operations:
- Chooses some number yi, and two vertecies ai and bi. After that, he moves along the edges of the tree from vertex ai to vertex *b**i* using the shortest path (of course, such a path is unique in the tree). Every time he moves along some edge j, he replaces his current number *y**i* by
 , that is, by the result of integer division *y**i* div *x**j*.
, that is, by the result of integer division *y**i* div *x**j*.
- Chooses some edge *p**i* and replaces the value written in it xpi by some positive integer *ci < xp**i*.
As Bogdan cares about his guests, he decided to ease the process. Write a program that performs all the operations requested by guests and outputs the resulting value *y**i* for each i of the first type.
Input
The first line of the input contains integers, n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertecies in the tree granted to Bogdan by his mom and the number of guests that came to the party respectively.
Next n - 1 lines contain the description of the edges. The i-th of these lines contains three integers ui, vi and *x**i* (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi, 1 ≤ xi ≤ 1018), denoting an edge that connects vertecies ui and vi, with the number xi initially written on it.
The following m lines describe operations, requested by Bogdan's guests. Each description contains three or four integers and has one of the two possible forms:
- 1 *a**i* *b**i* *y**i* corresponds to a guest, who chooses the operation of the first type.
- 2 *p**i* *c**i* corresponds to a guests, who chooses the operation of the second type.
It is guaranteed that all the queries are correct, namely ,1 ≤ pi ≤ n - 1 , wherexpirepresents a number written on edgepiat this particular moment of time that is not necessarily equal to the initial valuexpi
Output
For each guest who chooses the operation of the first type, print the result of processing the value *y**i* through the path from *a**i* to *b**i*.
Examples
input
Copy
6 61 2 11 3 71 4 42 5 52 6 21 4 6 172 3 21 4 6 171 5 5 202 4 11 5 1 3
output
Copy
24203
input
Copy
5 41 2 71 3 33 4 23 5 51 4 2 1001 5 4 12 2 21 1 3 4
output
Copy
202
Note
Initially the tree looks like this:
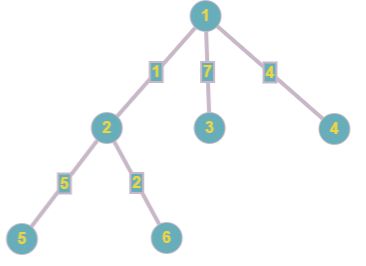
The response to the first query is:  = 2
= 2
After the third edge is changed, the tree looks like this:

The response to the second query is:  = 4
= 4
In the third query the initial and final vertex coincide, that is, the answer will be the initial number 20.
After the change in the fourth edge the tree looks like this:

In the last query the answer will be:  = 3
= 3
题意:
可以去这个链接阅读中文题意:
https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeForces-593D#author=AwayWithCorrect
思路:
1:边权转为点权建树:
确定一个root后,在dfs过程中,把边权值放在深度较大的节点的点权上。
这样建树的话,询问路径\(x->y\)的时候的边权sum和,实际求的过程中,点权只需要计算从(x到y路径的中的下一个节点z)到y节点的点权sum和。因为x的点权是root到x中的x上方的边权,并不在x到y的路径中。
2:树链剖分,同时用线段树维护连续点权的累乘积。
3:当线段树中的一个线段权值>1e18后,给该线段加个标记,或者权值定为0,因为询问是<=1e18的,那么如果询问包括了这个权值,答案一定是0.
4:更新边的权值时,直接用线段树更新那条边中深度更大的点权即可。
5:在树链剖分询问路径的过程中,别忘记1中讲到了去掉x节点点权,可以直接在最后的一个query中把id[x](x的dfs序)改为id[x]+1,因为一条链中dfs序时连续的。
判定x*y是否会超过1e18可以用这个函数的写法来求:
long long mul(long long aaa,long long bbb)
{
if(aaa==0||bbb==0)
return 0;
if(INF/aaa
## AC代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
 , that is, by the result of integer division *y**i* div *x**j*.
, that is, by the result of integer division *y**i* div *x**j*.![]() = 2
= 2![]() = 4
= 4![]() = 3
= 3

