微信小程序自发布到如今已经有半年多的时间了,凭借微信平台的强大影响力,越来越多企业加入小程序开发。
小程序于M页比相比,有以下优势:
1.小程序拥有更多的能力,包括定位、录音、文件、媒体、各种硬件能力等,想象空间更大
2.运行在微信内部,体验更接近APP
3.在过度竞争的互联网行业中,获取一个有效APP用户的成本已经非常高了,小程序相比APP更加轻量、即用即走,
更容易获取用户
开发对比
从开发角度来讲,小程序官方封装了很多常用组件给开发带来很多便利性,但同时也带来很多不便:
1、小程序重新定义了DOM结构,没有window、document、div、span等,小程序只有view、text、image等
封装好的组件,页面布局只能通过这些基础组件来实现,对开发人员来讲需要一定的习惯转换成本
2、小程序不推荐直接操作DOM(仅仅从2017年7月开始才可以获取DOM和部分属性),如果不熟悉MVVM模式的开发者,
需要很高的学习成本
3、小程序没有cookie,只能通过storage来模拟各项cookie操作(包括http中的setCookie也需要自行处理)
wepy
笔者团队最近开发了多个微信小程序,为了弥补小程序各项不足和延续开发者VUE的开发习惯,团队在开发初期
就选用了wepy框架,该框架是腾讯内部基于小程序的开发框架,设计思路基本参考VUE,开发模式和编码风
格上80%以上接近VUE,开发者可以以很小的成本从VUE开发切换成小程序开发,相比于小程序,主要优点如下:
1.开发模式容易转换
wepy在原有的小程序的开发模式下进行再次封装,更贴近于现有MVVM框架开发模式。框架在开发过程中参考了
一些现在框架的一些特性,并且融入其中,以下是使用wepy前后的代码对比图。
官方DEMO代码:
/index.js
//获取应用实例
var app = getApp()
Page({
data: {
motto: 'Hello World',
userInfo: {}
},
//事件处理函数
bindViewTap: function() {
console.log('button clicked')
},
onLoad: function () {
console.log('onLoad')
}
})
基于wepy的实现:
import wepy from 'wepy';
export default class Index extends wepy.page {
data = {
motto: 'Hello World',
userInfo: {}
};
methods = {
bindViewTap () {
console.log('button clicked');
}
};
onLoad() {
console.log('onLoad');
};
}
2.真正的组件化开发
小程序虽然有
仍需在页面处理。无法实现组件化的松耦合与复用的效果。
wepy组件示例
// index.wpy
3.支持加载外部NPM包
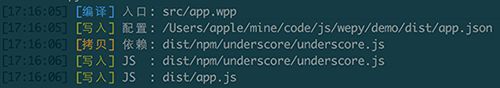
小程序较大的缺陷是不支持NPM包,导致无法直接使用大量优秀的开源内容,wepy在编译过程当中,会递归
遍历代码中的require然后将对应依赖文件从node_modules当中拷贝出来,并且修改require为相对路径,
从而实现对外部NPM包的支持。如下图:
4.单文件模式,使得目录结构更加清晰
小程序官方目录结构要求app必须有三个文件app.json,app.js,app.wxss,页面有4个文件 index.json,index.js,index.wxml,index.wxss。而且文
件必须同名。 所以使用wepy开发前后开发目录对比如下:
官方DEMO:
project
├── pages
| ├── index
| | ├── index.json index 页面配置
| | ├── index.js index 页面逻辑
| | ├── index.wxml index 页面结构
| | └── index.wxss index 页面样式表
| └── log
| ├── log.json log 页面配置
| ├── log.wxml log 页面逻辑
| ├── log.js log 页面结构
| └── log.wxss log 页面样式表
├── app.js 小程序逻辑
├── app.json 小程序公共设置
└── app.wxss 小程序公共样式表
使用wepy框架后目录结构:
project
└── src
├── pages
| ├── index.wpy index 页面配置、结构、样式、逻辑
| └── log.wpy log 页面配置、结构、样式、逻辑
└──app.wpy 小程序配置项(全局样式配置、声明钩子等)
5.默认使用babel编译,支持ES6/7的一些新特性。
6.wepy支持使用less
默认开启使用了一些新的特性如promise,async/await等等
如何开发
快速起步
安装
npm install wepy-cli -g
脚手架
wepy new myproject
切换至项目目录
cd myproject
实时编译
wepy build --watch
目录结构
├── dist 微信开发者工具指定的目录
├── node_modules
├── src 代码编写的目录
| ├── components 组件文件夹(非完整页面)
| | ├── com_a.wpy 可复用组件 a
| | └── com_b.wpy 可复用组件 b
| ├── pages 页面文件夹(完整页面)
| | ├── index.wpy 页面 index
| | └── page.wpy 页面 page
| └── app.wpy 小程序配置项(全局样式配置、声明钩子等)
└── package.json package 配置
wepy和VUE在编码风格上面非常相似,VUE开发者基本可以无缝切换,因此这里仅介绍两者的主要区别:
1.二者均支持props、data、computed、components、methods、watch(wepy中是watcher),
但wepy中的methods仅可用于页面事件绑定,其他自定义方法都要放在外层,而VUE中所有方法均放在
methods下
2.wepy中props传递需要加上.sync修饰符(类似VUE1.x)才能实现props动态更新,并且父组件再
变更传递给子组件props后要执行this.$apply()方法才能更新
3.wepy支持数据双向绑定,子组件在定义props时加上twoway:true属性值即可实现子组件修改父组
件数据
4.VUE2.x推荐使用eventBus方式进行组件通信,而在wepy中是通过$broadcast,$emit,$invoke
三种方法实现通信
· 首先事件监听需要写在events属性下:
``` bash
import wepy from 'wepy';
export default class Com extends wepy.component {
components = {};
data = {};
methods = {};
events = {
'some-event': (p1, p2, p3, $event) => {
console.log(`${this.name} receive ${$event.name} from ${$event.source.name}`);
}
};
// Other properties
}
```
· $broadcast:父组件触发所有子组件事件
· $emit:子组件触发父组件事件
· $invoke:子组件触发子组件事件
5.VUE的生命周期包括created、mounted等,wepy仅支持小程序的生命周期:onLoad、onReady等
6.wepy不支持过滤器、keep-alive、ref、transition、全局插件、路由管理、服务端渲染等VUE特性技术
wepy原理研究
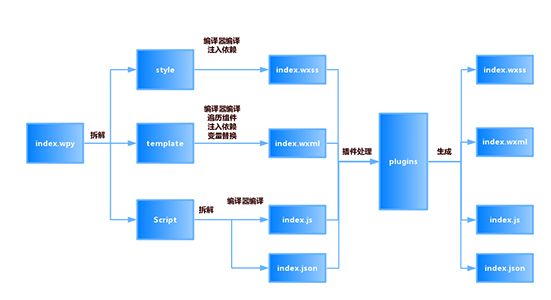
虽然wepy提升了小程序开发体验,但毕竟最终要运行在小程序环境中,归根结底wepy还是需要编译成小程序
需要的格式,因此wepy的核心在于代码解析与编译。
wepy项目文件主要有两个:
wepy-cli:用于把.wpy文件提取分析并编译成小程序所要求的wxml、wxss、js、json格式
wepy:编译后js文件中的js框架
wepy编译过程
拆解过程核心代码
//wepy自定义属性替换成小程序标准属性过程
return content.replace(/<([\w-]+)\s*[\s\S]*?(\/|<\/[\w-]+)>/ig, (tag, tagName) => {
tagName = tagName.toLowerCase();
return tag.replace(/\s+:([\w-_]*)([\.\w]*)\s*=/ig, (attr, name, type) => { // replace :param.sync => v-bind:param.sync
if (type === '.once' || type === '.sync') {
}
else
type = '.once';
return ` v-bind:${name}${type}=`;
}).replace(/\s+\@([\w-_]*)([\.\w]*)\s*=/ig, (attr, name, type) => { // replace @change => v-on:change
const prefix = type !== '.user' ? (type === '.stop' ? 'catch' : 'bind') : 'v-on:';
return ` ${prefix}${name}=`;
});
});
...
//按xml格式解析wepy文件
xml = this.createParser().parseFromString(content);
const moduleId = util.genId(filepath);
//提取后的格式
let rst = {
moduleId: moduleId,
style: [],
template: {
code: '',
src: '',
type: ''
},
script: {
code: '',
src: '',
type: ''
}
};
//循环拆解提取过程
[].slice.call(xml.childNodes || []).forEach((child) => {
const nodeName = child.nodeName;
if (nodeName === 'style' || nodeName === 'template' || nodeName === 'script') {
let rstTypeObj;
if (nodeName === 'style') {
rstTypeObj = {code: ''};
rst[nodeName].push(rstTypeObj);
} else {
rstTypeObj = rst[nodeName];
}
rstTypeObj.src = child.getAttribute('src');
rstTypeObj.type = child.getAttribute('lang') || child.getAttribute('type');
if (nodeName === 'style') {
// 针对于 style 增加是否包含 scoped 属性
rstTypeObj.scoped = child.getAttribute('scoped') ? true : false;
}
if (rstTypeObj.src) {
rstTypeObj.src = path.resolve(opath.dir, rstTypeObj.src);
}
if (rstTypeObj.src && util.isFile(rstTypeObj.src)) {
const fileCode = util.readFile(rstTypeObj.src, 'utf-8');
if (fileCode === null) {
throw '打开文件失败: ' + rstTypeObj.src;
} else {
rstTypeObj.code += fileCode;
}
} else {
[].slice.call(child.childNodes || []).forEach((c) => {
rstTypeObj.code += util.decode(c.toString());
});
}
if (!rstTypeObj.src)
rstTypeObj.src = path.join(opath.dir, opath.name + opath.ext);
}
});
...
// 拆解提取wxml过程
(() => {
if (rst.template.type !== 'wxml' && rst.template.type !== 'xml') {
let compiler = loader.loadCompiler(rst.template.type);
if (compiler && compiler.sync) {
if (rst.template.type === 'pug') { // fix indent for pug, https://github.com/wepyjs/wepy/issues/211
let indent = util.getIndent(rst.template.code);
if (indent.firstLineIndent) {
rst.template.code = util.fixIndent(rst.template.code, indent.firstLineIndent * -1, indent.char);
}
}
//调用wxml解析模块
let compilerConfig = config.compilers[rst.template.type];
// xmldom replaceNode have some issues when parsing pug minify html, so if it's not set, then default to un-minify html.
if (compilerConfig.pretty === undefined) {
compilerConfig.pretty = true;
}
rst.template.code = compiler.sync(rst.template.code, config.compilers[rst.template.type] || {});
rst.template.type = 'wxml';
}
}
if (rst.template.code)
rst.template.node = this.createParser().parseFromString(util.attrReplace(rst.template.code));
})();
// 提取import资源文件过程
(() => {
let coms = {};
rst.script.code.replace(/import\s*([\w\-\_]*)\s*from\s*['"]([\w\-\_\.\/]*)['"]/ig, (match, com, path) => {
coms[com] = path;
});
let match = rst.script.code.match(/[\s\r\n]components\s*=[\s\r\n]*/);
match = match ? match[0] : undefined;
let components = match ? this.grabConfigFromScript(rst.script.code, rst.script.code.indexOf(match) + match.length) : false;
let vars = Object.keys(coms).map((com, i) => `var ${com} = "${coms[com]}";`).join('\r\n');
try {
if (components) {
rst.template.components = new Function(`${vars}\r\nreturn ${components}`)();
} else {
rst.template.components = {};
}
} catch (e) {
util.output('错误', path.join(opath.dir, opath.base));
util.error(`解析components出错,报错信息:${e}\r\n${vars}\r\nreturn ${components}`);
}
})();
...
wepy中有专门的script、style、template、config解析模块
以template模块举例:
//compile-template.js
...
//将拆解处理好的wxml结构写入文件
getTemplate (content) {
content = `${content}`;
let doc = new DOMImplementation().createDocument();
let node = new DOMParser().parseFromString(content);
let template = [].slice.call(node.childNodes || []).filter((n) => n.nodeName === 'template');
[].slice.call(template[0].childNodes || []).forEach((n) => {
doc.appendChild(n);
});
...
return doc;
},
//处理成微信小程序所需的wxml格式
compileXML (node, template, prefix, childNodes, comAppendAttribute = {}, propsMapping = {}) {
//处理slot
this.updateSlot(node, childNodes);
//处理数据绑定bind方法
this.updateBind(node, prefix, {}, propsMapping);
//处理className
if (node && node.documentElement) {
Object.keys(comAppendAttribute).forEach((key) => {
if (key === 'class') {
let classNames = node.documentElement.getAttribute('class').split(' ').concat(comAppendAttribute[key].split(' ')).join(' ');
node.documentElement.setAttribute('class', classNames);
} else {
node.documentElement.setAttribute(key, comAppendAttribute[key]);
}
});
}
//处理repeat标签
let repeats = util.elemToArray(node.getElementsByTagName('repeat'));
...
//处理组件
let componentElements = util.elemToArray(node.getElementsByTagName('component'));
...
return node;
},
//template文件编译模块
compile (wpy){
...
//将编译好的内容写入到文件
let plg = new loader.PluginHelper(config.plugins, {
type: 'wxml',
code: util.decode(node.toString()),
file: target,
output (p) {
util.output(p.action, p.file);
},
done (rst) {
//写入操作
util.output('写入', rst.file);
rst.code = self.replaceBooleanAttr(rst.code);
util.writeFile(target, rst.code);
}
});
}
编译前后文件对比
wepy编译前的文件:
wepy编译后的文件:
{{item.title}}
¥{{item.price}}
¥{{item.originalPrice}}
{{item.cityName}}{{item.cityName&&item.businessName?' | ':''}}{{item.businessName}}
可以看到wepy将页面中所有引入的组件都直接写入页面当中,并且按照微信小程序的格式来输出
当然也从一个侧面看出,使用wepy框架后,代码风格要比原生的更加简洁优雅
以上是wepy实现原理的简要分析,有兴趣的朋友可以去阅读源码(https://github.com/wepyjs/wepy)。
综合来讲,wepy的核心在于编译环节,能够将优雅简洁的类似VUE风格的代码,编译成微信小程序所需要的繁杂代码。
wepy作为一款优秀的微信小程序框架,可以帮我们大幅提高开发效率,在为数不多的小程序框架中一枝独秀,希望有更多的团队选择wepy。
PS:wepy也在实现小程序和VUE代码同构,但目前还处在开发阶段,如果未来能实现一次开发,同时产出小程序和M页,将是一件非常爽的事情。