原文地址
1. 背景
当有大量数据储存在磁盘时,如数据库的查找,插入, 删除等操作的实现, 如果要读取或者写入, 磁盘的寻道, 旋转时间很长, 远大于在 内存中的读取,写入时间.
平时用的二叉排序树搜索元素的时间复杂度虽然是 的, 但是底数还是太小, 树高太高.
所以就出现了 B 树(英文为B-Tree, 不是B减树), 可以理解为多叉排序树. 一个结点可以有多个孩子, 于是增大了底数, 减小了高度, 虽然比较的次数多(关键字数多), 但是由于是在内存中比较, 相较于磁盘的读取还是很快的.
2. 定义
度为 d(degree)的 B 树(阶(order) 为 2d) 定义如下,
每个结点中包含有 n 个关键字信息: 。其中:
a) 为关键字,且关键字按顺序升序排序
b) 为指向子树根的接点,
c) 关键字的数 n 满足(由此也确定了孩子结点的个数): (根节点可以少于d-1)树中每个结点最多含有 2d个孩子(d>=2);
除根结点和叶子结点外,其它每个结点至少有 d个孩子;
若根结点不是叶子结点,则至少有 2 个孩子(特殊情况:没有孩子的根结点,即根结点为叶子结点,整棵树只有一个根节点);
所有叶子结点都出现在同一层,叶子节点没有孩子和指向孩子的指针
性质:
如下是 度为2的 B 树, 每个结点可能有2,3或4 个孩子, 所以也叫 2,3,4树, 等价于红黑树
3. 查找操作
可以看成二叉排序树的扩展,二叉排序树是二路查找,B - 树是多路查找。
节点内进行查找的时候除了顺序查找之外,还可以用二分查找来提高效率。
下面是顺序查找的 python 代码
def search(self,key,withpath=False):
nd = self.root
fathers = []
while True:
i = nd.findKey(key)
if i==len(nd): fathers.append((nd,i-1,i))
else: fathers.append((nd,i,i))
if i我实现时让 fathers 记录查找的路径, 方便在实现 delete 操作时使用(虽然有种 delete 方法可以不需要, 直接 from up to down with no pass by),
4. 插入操作
自顶向下地进行插入操作, 最终插入在叶子结点,
考虑到叶子结点如果有 2t-1 个 关键字, 则需要进行分裂,
一个有 2t-1个关键字 结点分裂是这样进行的: 此结点分裂为 两个关键字为 t-1个的结点, 分别为 , , 然后再插入一个关键字到父亲结点.
注意同时要将孩子指针移动正确.
所以自顶向下地查找到叶子结点, 中间遇到 2t-1个关键字的结点就进行分裂, 这样如果其子结点进行分裂, 上升来的一个关键字可以插入到父结点而不会超过2t-1
代码如下
def insert(self,key):
if len(self.root)== self.degree*2-1:
self.root = self.root.split(node(isLeaf=False),self.degree)
self.nodeNum +=2
nd = self.root
while True:
idx = nd.findKey(key)
if idx5. 删除操作
删除操作是有点麻烦的, 有两种方法[1]
- Locate and delete the item, then restructure the tree to retain its invariants, OR
- Do a single pass down the tree, but before entering (visiting) a node, restructure the tree so that once the key to be deleted is encountered, it can be deleted without triggering the need for any further restructuring
5.1. 第一种方法
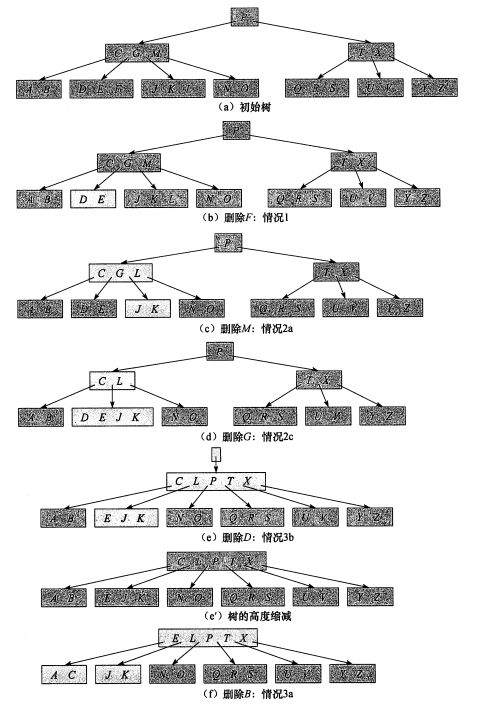
有如下情况
- 删除结点在叶子结点上
结点内的关键字个数大于d-1,可以直接删除(大于关键字个数下限,删除不影响 B - 树特性)
-
结点内的关键字个数等于d-1(等于关键字个数下限,删除后将破坏 特性),此时需观察该节点左右兄弟结点的关键字个数:
a. 旋转: 如果其左右兄弟结点中存在关键字个数大于d-1 的结点,则从关键字个数大于 d-1 的兄弟结点中借关键字:(这里看了网上的很多说法, 都是在介绍关键字的操作,而没有提到孩子结点. 我实现的时候想了很久才想出来: 借关键字时, 比如从右兄弟借一个关键字(第一个), 此时即为左旋, 将父亲结点对应关键字移到当前结点, 再将右兄弟的移动父亲结点(因为要满足排序性质, 类似二叉树的选择) 然后进行孩子操作, 将右兄弟的 插入到 当前结点的孩子指针末尾) 左兄弟类似, 而且要注意到边界条件, 比如当前结点是第0个/最后一个孩子, 则没有 左兄弟/右兄弟)b. 合并: 如果其左右兄弟结点中不存在关键字个数大于 t-1 的结点,进行结点合并:将其父结点中的关键字拿到下一层,与该节点的左右兄弟结点的所有关键字合并
同样要注意到边界条件, 比如当前结点是第0个/最后一个孩子, 则没有 左兄弟/右兄弟 自底向上地检查来到这个叶子结点的路径上的结点是否满足关键字数目的要求, 只要关键字少于d-1,则进行旋转(2a)或者合并(2b)操作
- 删除结点在非叶子结点上
- 查到到该结点, 然后转化成 上述 叶子结点中情况
- 转化过程:
a. 找到相邻关键字:即需删除关键字的左子树中的最大关键字或右子树中的最小关键字
b. 用相邻关键字来覆盖需删除的非叶子节点关键字,再删除原相邻关键字(在;叶子上,这即为上述情况)。
python 代码如下, delete函数中, 查找到结点, 用 fathers::[(父节点, 关键字指针, 孩子指针)] 记录路径, 如果不是叶子结点, 就再进行查找, 并记录结点, 转换关键字.
rebalance 就是从叶子结点自底向上到根结点, 只要遇到关键字数少于 2d-1 的,就进行平衡操作(旋转, 合并)
实现时要很仔细, 考虑边界条件, 还有当是左孩子的时候操作的是父结点的 chdIdx 的前一个, 是右孩子的时候是 chdIdx 的关键字. 具体实现完整代码见文末.
def delete(self,key):#to do
'''search the key, delete it , and form down to up to rebalance it '''
nd,idx ,fathers= self.search(key,withpath=True)
if nd is None : return
del nd[idx]
self.keyNum-=1
if not nd.isLeafNode():
chd = nd.getChd(idx) # find the predecessor key
while not chd.isLeafNode():
fathers.append((chd,len(chd)-1,len(chd)))
chd = chd.getChd(-1)
fathers.append((chd,len(chd)-1,len(chd)))
nd.insert(idx,chd[-1])
del chd[-1]
if len(fathers)>1:self.rebalance(fathers)
def rebalance(self,fathers):
nd,keyIdx,chdIdx = fathers.pop()
while len(nd)=self.degree: # rotate when only one sibling is deficient
keyIdx = chdIdx-1
nd.insert(0,prt[keyIdx]) # rotate keys
prt[keyIdx] = lbro[-1]
del lbro[-1]
if not nd.isLeafNode(): # if not leaf, move children
nd.insert(0,nd=lbro.getChd(-1))
lbro.delChd(-1)
else:
keyIdx = chdIdx
nd.insert(len(nd),prt[keyIdx]) # rotate keys
prt[keyIdx] = rbro[0]
del rbro[0]
if not nd.isLeafNode(): # if not leaf, move children
#note that insert(-1,ele) will make the ele be the last second one
nd.insert(len(nd),nd=rbro.getChd(0))
rbro.delChd(0)
if len(fathers)==1:
if len(self.root)==0:
self.root = nd
self.nodeNum -=1
break
nd,i,j = fathers.pop()
5.2. 第二种方法
这是算法导论[2]上的
例如
B-TREE-DELETE(T,k)
1 r ← root[T]
2 if n[r] = 1
3 then DISK_READ(c1[r])
4 DISK_READ(c2[r])
5 y ←c1[r]
6 z ←c2[r]
7 if n[y] = n[z] = t-1 ▹ Cases 2c or 3b
8 then B-TREE-MERGE-CHILD(r, 1, y, z)
9 root[T] ← y
10 FREE-NODE(r)
11 B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE(y, k)
12 else B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE (r, k)
13 else B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE (r, k)
考虑到根结点的特殊性,对根结点为1,并且两个子结点都是t-1的情况进行了特殊的处理:
先对两个子结点进行合并,然后把原来的根删除,把树根指向合并后的子结点y。
这样B树的高度就减少了1。这也是B树高度唯一会减少的情况。
除了这种情况以外,就直接调用子过程 B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE (x, k)。
B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE (x, k)
1 i ← 1
2 if leaf[x] ▹ Cases 1
3 then while i <= n[x] and k > keyi[x]
4 do i ← i + 1
5 if k = keyi[x]
6 then for j ← i+1 to n[x]
7 do keyj-1[x] ←keyj[x]
8 n[x] ← n[x] - 1
9 DISK-WRITE(x)
10 else error:”the key does not exist”
11 else while i <= n[x] and k > keyi[x]
12 do i ← i + 1
13 DISK-READ(ci[x])
14 y ←ci[x]
15 if i <= n[x]
16 then DISK-READ(ci+1[x])
17 z ←ci+1[x]
18 if k = keyi[x] ▹ Cases 2
19 then if n[y] > t-1 ▹ Cases 2a
20 then k′←B-TREE-SEARCH-PREDECESSOR(y)
21 B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE (y, k′)
22 keyi[x] ←k′
23 else if n[z] > t-1 ▹ Cases 2b
24 then k′←B-TREE-SEARCH-SUCCESSOR (z)
25 B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE (z, k′)
26 keyi[x] ←k′
27 else B-TREE-MERGE-CHILD(x, i, y, z)▹ Cases 2c
28 B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE (y, k)
29 else ▹ Cases 3
30 if i >1
31 then DISK-READ(ci-1[x])
32 p ←ci-1[x]
33 if n[y] = t-1
34 then if i>1 and n[p] >t-1 ▹ Cases 3a
35 then B-TREE-SHIFT-TO-RIGHT-CHILD(x,i,p,y)
36 else if i <= n[x] and n[z] > t-1 ▹ Cases 3a
37 then B-TREE-SHIFT-TO-LEFT-CHILD(x,i,y,z)
38 else if i>1 ▹ Cases 3b
39 then B-TREE-MERGE-CHILD(x, i, p, y)
40 y ← p
41 else B-TREE-MERGE-CHILD(x, i, y, z)▹ Cases 3b
42 B-TREE-DELETE-NONONE (y, k)
转移到右边的子结点
B-TREE-SHIFT-TO-RIGHT-CHILD(x,i,y,z)
1 n[z] ← n[z] +1
2 j ← n[z]
3 while j > 1
4 do keyj[z] ←keyj-1[z]
5 j ← j -1
6 key1[z] ←keyi[x]
7 keyi[x] ←keyn[y][y]
8 if not leaf[z]
9 then j ← n[z]
10 while j > 0
11 do cj+1[z] ←cj[z]
12 j ← j -1
13 c1[z] ←cn[y]+1[y]
14 n[y] ← n[y] -1
15 DISK-WRITE(y)
16 DISK-WRITE(z)
17 DISK-WRITE(x)
转移到左边的子结点
B-TREE-SHIFT-TO-LEFT-CHILD(x,i,y,z)
1 n[y] ← n[y] +1
2 keyn[y][y] ← keyi[x]
3 keyi[x] ←key1[z]
4 n[z] ← n[z] -1
5 j ← 1
6 while j <= n[z]
7 do keyj[z] ←keyj+1[z]
8 j ← j +1
9 if not leaf[z]
10 then cn[y]+1[y] ←c1[z]
11 j ← 1
12 while j <= n[z]+1
13 do cj[z] ←cj+1[z]
14 j ← j + 1
15 DISK-WRITE(y)
16 DISK-WRITE(z)
17 DISK-WRITE(x)
6. B+树
B+ 树[3]是 B- 树的变体,与B树不同的地方在于:
- 非叶子结点的子树指针与关键字个数相同;
- 非叶子结点的子树指针 指向关键字值属于 的子树(B- 树是开区间);
- 为所有叶子结点增加一个链指针;
- 所有关键字都在叶子结点出现
B+ 的搜索与 B- 树也基本相同,区别是 B+ 树只有达到叶子结点才命中(B- 树可以在非叶子结点命中),其性能也等价于在关键字全集做一次二分查找;
下面摘自 wiki[4]
查找
查找以典型的方式进行,类似于二叉查找树。起始于根节点,自顶向下遍历树,选择其分离值在要查找值的任意一边的子指针。在节点内部典型的使用是二分查找来确定这个位置。
插入
节点要处于违规状态,它必须包含在可接受范围之外数目的元素。
- 首先,查找要插入其中的节点的位置。接着把值插入这个节点中。
- 如果没有节点处于违规状态则处理结束。
- 如果某个节点有过多元素,则把它分裂为两个节点,每个都有最小数目的元素。在树上递归向上继续这个处理直到到达根节点,如果根节点被分裂,则创建一个新根节点。为了使它工作,元素的最小和最大数目典型的必须选择为使最小数不小于最大数的一半。
删除
- 首先,查找要删除的值。接着从包含它的节点中删除这个值。
- 如果没有节点处于违规状态则处理结束。
- 如果节点处于违规状态则有两种可能情况:
- 它的兄弟节点,就是同一个父节点的子节点,可以把一个或多个它的子节点转移到当前节点,而把它返回为合法状态。如果是这样,在更改父节点和两个兄弟节点的分离值之后处理结束。
- 它的兄弟节点由于处在低边界上而没有额外的子节点。在这种情况下把两个兄弟节点合并到一个单一的节点中,而且我们递归到父节点上,因为它被删除了一个子节点。持续这个处理直到当前节点是合法状态或者到达根节点,在其上根节点的子节点被合并而且合并后的节点成为新的根节点。
由于叶子结点间有指向下一个叶子的指针, 便于遍历, 以及区间查找, 所以数据库的以及操作系统文件系统的实现常用 B+树,
7. B*树
B-tree [5] 是 B+-tree 的变体,在 B+ 树的基础上 (所有的叶子结点中包含了全部关键字的信息,及指向含有这些关键字记录的指针),B * 树中非根和非叶子结点再增加指向兄弟的指针;B 树定义了非叶子结点关键字个数至少为 (2/3)*M,即块的最低使用率为 2/3(代替 B+ 树的 1/2)
8. 代码实现与测试
github地址
8.1. 测试
if __name__ =='__main__':
bt = bTree()
from random import shuffle,sample
n = 20
lst = [i for i in range(n)]
shuffle(lst)
test= sample(lst,len(lst)//4)
print(f'building b-tree with {lst}')
for i in lst:
bt.insert(i)
#print(f'inserting {i})
#print(bt)
print(bt)
print(f'serching {test}')
for i in test:
nd,idx = bt.search(i)
print(f'node: {repr(nd)}[{idx}]== {i}')
for i in test:
print(f'deleting {i}')
bt.delete(i)
print(bt)
8.2. python 实现
class node:
def __init__(self,keys=None,isLeaf = True,children=None):
if keys is None:keys=[]
if children is None: children =[]
self.keys = keys
self.isLeaf = isLeaf
self.children = []
def __getitem__(self,i):
return self.keys[i]
def __delitem__(self,i):
del self.keys[i]
def __setitem__(self,i,k):
self.keys[i] = k
def __len__(self):
return len(self.keys)
def __repr__(self):
return str(self.keys)
def __str__(self):
children = ','.join([str(nd.keys) for nd in self.children])
return f'keys: {self.keys}\nchildren: {children}\nisLeaf: {self.isLeaf}'
def getChd(self,i):
return self.children[i]
def delChd(self,i):
del self.children[i]
def setChd(self,i,chd):
self.children[i] = chd
def getChildren(self,begin=0,end=None):
if end is None:return self.children[begin:]
return self.children[begin:end]
def findKey(self,key):
for i,k in enumerate(self.keys):
if k>=key:
return i
return len(self)
def update(self,keys=None,isLeaf=None,children=None):
if keys is not None:self.keys = keys
if children is not None:self.children = children
if isLeaf is not None: self.isLeaf = isLeaf
def insert(self,i,key=None,nd=None):
if key is not None:self.keys.insert(i,key)
if not self.isLeaf and nd is not None: self.children.insert(i,nd)
def isLeafNode(self):return self.isLeaf
def split(self,prt,t):
# form new two nodes
k = self[t-1]
nd1 = node()
nd2 = node()
nd1.keys,nd2.keys = self[:t-1], self[t:] # note that t is 1 bigger than key index
nd1.isLeaf = nd2.isLeaf = self.isLeaf
if not self.isLeaf:
# note that children index is one bigger than key index, and all children included
nd1.children, nd2.children = self.children[0:t], self.children[t:]
# connect them to parent
idx = prt.findKey(k)
if prt.children !=[]: prt.children.remove(self) # remove the original node
prt.insert(idx,k,nd2)
prt.insert(idx,nd = nd1)
return prt
class bTree:
def __init__(self,degree=2):
self.root = node()
self.degree=degree
self.nodeNum = 1
self.keyNum = 0
def search(self,key,withpath=False):
nd = self.root
fathers = []
while True:
i = nd.findKey(key)
if i==len(nd): fathers.append((nd,i-1,i))
else: fathers.append((nd,i,i))
if i1:self.rebalance(fathers)
def rebalance(self,fathers):
nd,keyIdx,chdIdx = fathers.pop()
while len(nd)=self.degree: # rotate when only one sibling is deficient
keyIdx = chdIdx-1
nd.insert(0,prt[keyIdx]) # rotate keys
prt[keyIdx] = lbro[-1]
del lbro[-1]
if not nd.isLeafNode(): # if not leaf, move children
nd.insert(0,nd=lbro.getChd(-1))
lbro.delChd(-1)
else:
keyIdx = chdIdx
nd.insert(len(nd),prt[keyIdx]) # rotate keys
prt[keyIdx] = rbro[0]
del rbro[0]
if not nd.isLeafNode(): # if not leaf, move children
#note that insert(-1,ele) will make the ele be the last second one
nd.insert(len(nd),nd=rbro.getChd(0))
rbro.delChd(0)
if len(fathers)==1:
if len(self.root)==0:
self.root = nd
self.nodeNum -=1
break
nd,i,j = fathers.pop()
def __str__(self):
head= '\n'+'-'*30+'B Tree'+'-'*30
tail= '-'*30+'the end'+'-'*30+'\n'
lst = [[head],[f'node num: {self.nodeNum}, key num: {self.keyNum}']]
cur = []
ndNum =0
ndTotal= 1
que = [self.root]
while que!=[]:
nd = que.pop(0)
cur.append(repr(nd))
ndNum+=1
que+=nd.getChildren()
if ndNum==ndTotal:
lst.append(cur)
cur = []
ndNum = 0
ndTotal =len(que)
lst.append([tail])
lst = [','.join(li) for li in lst]
return '\n'.join(lst)
def __iter__(self,nd = None):
if nd is None: nd = self.root
que = [nd]
while que !=[]:
nd = que.pop(0)
yield nd
if nd.isLeafNode():continue
for i in range(len(nd)+1):
que.append(nd.getChd(i))
9. 参考资料
-
B树 ↩
-
算法导论 ↩
-
B - 树特征及插入删除操作总结 ↩
-
B+树 ↩
-
从 B 树、B + 树、B * 树谈到 R 树 ↩