原文链接:AFNetworking速成教程
本文是由 iOS Tutorial小组成员 ScottSherwood撰写,他是一个基于位置动态加载(DynamicallyLoaded)的软件公司(专业的混合定位)的共同创办人。
网络 — 你的程序离开了它就不能生存下去!苹果的Foundationframework中的NSURLConnection又非常难以理解, 不过这里有一个可以使用的替代品:AFNetworking.
AFNetworking 非常受开发者欢迎 – 它赢得了我们读者的青睐:2012年最佳的iOS Library奖(2012Best iOS Library Award.) 所以现在我就写这篇文章来向你介绍如何在程序中有效的使用它。
AFNetworking 包括了所有你需要与在线资源交互的内容,从webservices到文件下载。当你的程序在下载一个大文件期间,AFNetworking还能确保你的UI是可以响应的。
本文将介绍AFNetworking框架主要的组成部分。一路上,你将使用WorldWeatherOnline提供的咨询(Feeds)来创建一个天气(Weather)程序。刚开始使用的天气数据是静态的,不过在学完本文内容之后,程序将连接到实时的天气咨询。
今日预计:一个很酷的开发者学习所有关于AFNetworking知识,并在他的程序中使用AFNetworking。我们开始忙活吧!
开始
首先来这里(here)下载本文的启动项目。这个工程提供了一个基本的UI— AFNetworking相关代码还没有添加。
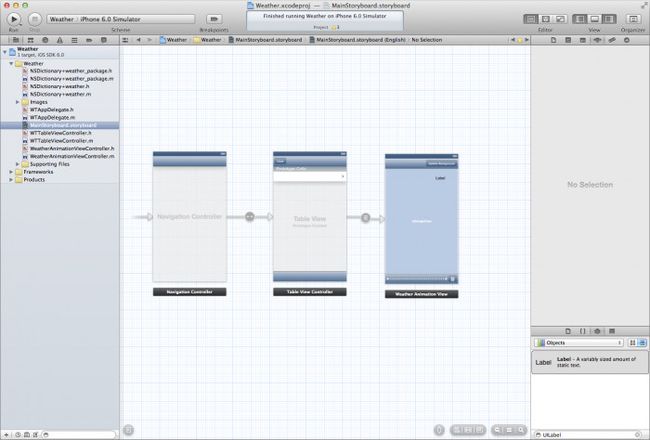
打开MainStoryboard.storyboard文件,将看到3个viewcontroller:
从左到右,分别是:
顶级(top-level)的导航控制器;
用来显示天气的一个table view controller,每天一行;
一个自定义的view controller (WeatherAnimationViewController) 当用户点击某个tableview cell时,这个view controller将显示某一天的天气咨询。
生成并运行项目,你将看到相关的UI出现,但是什么都没有实现!因为程序需要从网络中获取到所需要的数据,而相关代码还没有添加。这也是本文中你将要实现的!
首先,你需要将AFNetworking框架包含到工程中。如果你还没有AFNetworking的话,在这里下载最新的版本:GitHub.
当你解压出下载的文件后,你将看到其中有一个AFNetworking子文件夹,里面全是.h 和 .m 文件, 如下高亮显示的:
将AFNetworking拖拽到Xcode工程中.
当出现了添加文件的选项时,确保勾选上Copyitems into destination group’s folder (ifneeded)和Creategroups for any added folders.
要完成相关配置,请在工程的SupportingFiles群组中打开预编译头文件Weather-Prefix.pch.然后在别的import后面添加如下一行代码:
[objc]view plaincopy
#import "AFNetworking.h"
将AFNetworking添加到预编译头文件,意味着这个框架会被自动的添加到工程的所有源代码文件中。
很容易,不是吗?现在你已经准备好“天气”程序代码了!
操作JSON
AFNetworking通过网络来加载和处理结构化的数据是非常智能的,普通的HTTP请求也一样。尤其是它支持JSON, XML 和Property Lists (plists).
你可以下载一些JSON数据,然后用自己的解析器来解析,但这何必呢?通过AFNetworking就可以完成这些操作!
首先,你需要测试脚本(数据)所需的一个基本URL。将下面的这个静态NSString声明到WTTableViewController.m顶部,也就是所有#import下面:
[objc]view plaincopy
staticNSString*constBaseURLString =@"http://www.raywenderlich.com/downloads/weather_sample/";
这个URL是一个非常简单的“webservice”,在本文中我特意为你创建的。如果你想知道它看起来是什么样,可以来这里下载代码:downloadthe source.
这个web service以3种不同的格式(JSON, XML 和PLIST)返回天气数据。你可以使用下面的这些URL来看看返回的数据:
http://www.raywenderlich.com/downloads/weather_sample/weather.php?format=json
http://www.raywenderlich.com/downloads/weather_sample/weather.php?format=xml
http://www.raywenderlich.com/downloads/weather_sample/weather.php?format=plist (mightnot show up right in your browser)
第一个数据格式使用的是JSON.JSON 是一种常见的JavaScript派生类对象格式。看起来如下:
[objc]view plaincopy
{
"data": {
"current_condition": [
{
"cloudcover":"16",
"humidity":"59",
"observation_time":"09:09 PM",
}
]
}
}
注意:如果你想要结更多关于JSON内容,请参考:Workingwith JSON in iOS 5 Tutorial.
当用户点击程序中的JSON按钮时,你希望对从服务中获得的JSON数据进行加载并处理。在WTTableViewController.m中,找到jsonTapped:方法(现在应该是空的) ,并用下面的代码替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (IBAction)jsonTapped:(id)sender {
// 1
NSString*weatherUrl = [NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@weather.php?format=json",BaseURLString];
NSURL*url = [NSURLURLWithString:weatherUrl];
NSURLRequest*request = [NSURLRequestrequestWithURL:url];
// 2
AFJSONRequestOperation*operation =
[AFJSONRequestOperationJSONRequestOperationWithRequest:request
// 3
success:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,idJSON) {
self.weather= (NSDictionary*)JSON;
self.title=@"JSON Retrieved";
[self.tableViewreloadData];
}
// 4
failure:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,NSError*error,idJSON) {
UIAlertView*av = [[UIAlertViewalloc]initWithTitle:@"Error Retrieving Weather"
message:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@",error]
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"otherButtonTitles:nil];
[avshow];
}];
// 5
[operationstart];
}
这是你的第一个AFNetworking代码!因此,这看起来是全新的,我将对这个方法中代码进行介绍。
根据基本的URL构造出完整的一个URL。然后通过这个完整的URL获得一个NSURL对象,然后根据这个url获得一个NSURLRequest.
AFJSONRequestOperation 是一个功能完整的类(all-in-one)—整合了从网络中获取数据并对JSON进行解析。
当请求成功,则运行成功块(successblock)。在本示例中,把解析出来的天气数据从JSON变量转换为一个字典(dictionary),并将其存储在属性weather中.
如果运行出问题了,则运行失败块(failure block),比如网络不可用。如果failureblock被调用了,将会通过提示框显示出错误信息。
如上所示,AFNetworking的使用非常简单。如果要用苹果提供的APIs(如NSURLConnection)来实现同样的功能(下载和解析JSON数据),则需要许多代码才能做到。
现在天气数据已经存在于self.weather中,你需要将其显示出来。找到tableView:numberOfRowsInSection:方法,并用下面的代码替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView*)tableViewnumberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
// Return the number of rows in the section.
if(!self.weather)
return0;
switch(section) {
case0:{
return1;
}
case1:{
NSArray*upcomingWeather = [self.weatherupcomingWeather];
return[upcomingWeathercount];
}
default:
return0;
}
}
table view有两个section:第一个用来显示当前天气,第二个用来显示未来的天气。
等一分钟,你可能正在思考。这里的[self.weatherupcomingWeather]是什么? 如果self.weather是一个普通的NSDictionary,它是怎么知道 “upcomingWeather” 是什么呢?
为了更容易的解析数据,在starter工程中,有一对NSDictionary categories:
NSDictionary+weather.m
NSDictionary+weather_package.m
这些categories添加了一些方便的方法,通过这些方法可以很方便的对字典中的数据元素进行访问。这样你就可以专注于网络部分,而不是NSDictionary中数据的访问。对吧?
回到WTTableViewController.m,找到tableView:cellForRowAtIndexPath:方法,并用下面的实现替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (UITableViewCell*)tableView:(UITableView*)tableViewcellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath*)indexPath
{
staticNSString*CellIdentifier =@"WeatherCell";
UITableViewCell*cell = [tableViewdequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:CellIdentifierforIndexPath:indexPath];
NSDictionary*daysWeather;
switch(indexPath.section) {
case0:{
daysWeather = [self.weathercurrentCondition];
break;
}
case1:{
NSArray*upcomingWeather = [self.weatherupcomingWeather];
daysWeather = [upcomingWeatherobjectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
}
default:
break;
}
cell.textLabel.text= [daysWeatherweatherDescription];
// maybe some code will be added here later...
returncell;
}
跟tableView:numberOfRowsInSection: 方法一样,在这里使用了便利的NSDictionarycategories来获得数据。当前天的天气是一个字典,而未来几日的天气则存储在一个数组中。
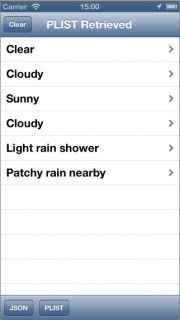
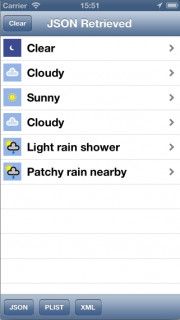
生成并运行工程,然后点击JSON按钮. 这将会动态的获得一个AFJSONOperation对象, 并看到如下画面内容:
JSON操作成功!
操作Property Lists(plists)
Property lists (或简称为 plists)是以确定的格式(苹果定义的)构成的XML文件。苹果一般将plists用在用户设置中。看起来如下:
data current_condition cloudcover 16 humidity 59
上面的意思是:
一个字典中有一个名为“data”的key,这个key对应着另外一个字典。
这个字典有一个名为 “current_condition” 的key,这个key对应着一个array.
这个数组包含着一个字典,字典中有多个key和values。比如cloudcover=16和humidity=59.
现在是时候加载plist版本的天气数据了!找到plistTapped:方法,并用下面的实现替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
-(IBAction)plistTapped:(id)sender{
NSString*weatherUrl = [NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@weather.php?format=plist",BaseURLString];
NSURL*url = [NSURLURLWithString:weatherUrl];
NSURLRequest*request = [NSURLRequestrequestWithURL:url];
AFPropertyListRequestOperation*operation =
[AFPropertyListRequestOperationpropertyListRequestOperationWithRequest:request
success:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,idpropertyList) {
self.weather= (NSDictionary*)propertyList;
self.title=@"PLIST Retrieved";
[self.tableViewreloadData];
}
failure:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,NSError*error,idpropertyList) {
UIAlertView*av = [[UIAlertViewalloc]initWithTitle:@"Error Retrieving Weather"
message:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@",error]
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"
otherButtonTitles:nil];
[avshow];
}];
[operationstart];
}
注意到,上面的代码几乎与JSON版的一致,只不过将操作(operation)的类型从AFJSONOperation 修改为AFPropertyListOperation.这非常的整齐:你才程序只需要修改一丁点代码就可以接收JSON或plist格式的数据了!
生成并运行工程,然后点击PLIST按钮。将看到如下内容:
如果你需要重置所有的内容,以重新开始操作,导航栏顶部的Clear按钮可以清除掉title和tableview中的数据。
操作XML
AFNetworking处理JSON和plist的解析使用的是类似的方法,并不需要花费太多功夫,而处理XML则要稍微复杂一点。下面,就根据XML咨询构造一个天气字典(NSDictionary)。
iOS提供了一个帮助类:NSXMLParse (如果你想了解更多内容,请看这里的链接:SAXparser).
还是在文件WTTableViewController.m,找到xmlTapped:方法,并用下面的实现替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (IBAction)xmlTapped:(id)sender{
NSString*weatherUrl = [NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@weather.php?format=xml",BaseURLString];
NSURL*url = [NSURLURLWithString:weatherUrl];
NSURLRequest*request = [NSURLRequestrequestWithURL:url];
AFXMLRequestOperation*operation =
[AFXMLRequestOperationXMLParserRequestOperationWithRequest:request
success:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,NSXMLParser*XMLParser) {
//self.xmlWeather = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
XMLParser.delegate=self;
[XMLParsersetShouldProcessNamespaces:YES];
[XMLParserparse];
}
failure:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,NSError*error,NSXMLParser*XMLParser) {
UIAlertView*av = [[UIAlertViewalloc]initWithTitle:@"Error Retrieving Weather"
message:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@",error]
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"
otherButtonTitles:nil];
[avshow];
}];
[operationstart];
}
到现在为止,这看起来跟之前处理JSON和plist很类似。最大的改动就是在成功块(success
block)中,在这里不会传递给你一个预处理好的NSDictionary对象.而是AFXMLRequestOperation实例化的NSXMLParse对象,这个对象将用来处理繁重的XML解析任务。
NSXMLParse对象有一组delegate方法是你需要实现的 —用来获得XML数据。注意,在上面的代码中我将XMLParser的delegate设置为self,因此WTTableViewController将用来处理XML的解析任务。
首先,更新一下WTTableViewController.h并修改一下类声明,如下所示:
[objc]view plaincopy
@interfaceWTTableViewController : UITableViewController
上面代码的意思是这个类将实现(遵循)NSXMLParserDelegate协议.下一步将下面的delegate方法声明添加到@implementation后面:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (void)parser:(NSXMLParser*)parserdidStartElement:(NSString*)elementNamenamespaceURI:(NSString*)namespaceURIqualifiedName:(NSString*)qNameattributes:(NSDictionary*)attributeDict;
- (void)parser:(NSXMLParser*)parserfoundCharacters:(NSString*)string;
- (void)parser:(NSXMLParser*)parserdidEndElement:(NSString*)elementNamenamespaceURI:(NSString*)namespaceURIqualifiedName:(NSString*)qName;
-(void)parserDidEndDocument:(NSXMLParser*)parser;
为了支持资讯的解析,还需要一些属性来存储相关的数据。将下面的代码添加到@implementatio后面:
[objc]view plaincopy
@property(strong)NSMutableDictionary*xmlWeather;//package containing the complete response
@property(strong)NSMutableDictionary*currentDictionary;//current section being parsed
@property(strong)NSString*previousElementName;
@property(strong)NSString*elementName;
@property(strong)NSMutableString*outstring;
接着打开WTTableViewController.m,现在你需要一个一个的实现上面所说的几个delegate方法。将下面这个方法粘贴到实现文件中:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (void)parser:(NSXMLParser*)parserdidStartElement:(NSString*)elementNamenamespaceURI:(NSString*)namespaceURIqualifiedName:(NSString*)qNameattributes:(NSDictionary*)attributeDict {
self.previousElementName=self.elementName;
if(qName) {
self.elementName= qName;
}
if([qNameisEqualToString:@"current_condition"]){
self.currentDictionary= [NSMutableDictionarydictionary];
}
elseif([qNameisEqualToString:@"weather"]){
self.currentDictionary= [NSMutableDictionarydictionary];
}
elseif([qNameisEqualToString:@"request"]){
self.currentDictionary= [NSMutableDictionarydictionary];
}
self.outstring= [NSMutableStringstring];
}
当NSXMLParser发现了新的元素开始标签时,会调用上面这个方法。在这个方法中,在构造一个新字典用来存储赋值给currentDictionary属性之前,首先保存住上一个元素名称。还要将outstring重置一下,这个字符串用来构造XML标签中的数据。
然后将下面这个方法粘贴到上一个方法的后面:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (void)parser:(NSXMLParser*)parserfoundCharacters:(NSString*)string {
if(!self.elementName){
return;
}
[self.outstringappendFormat:@"%@",string];
}
如名字一样,当NSXMLParser在一个XML标签中发现了字符数据,会调用这个方法。该方法将字符数据追加到outstring属性中,当XML标签结束的时候,这个outstring会被处理。
继续,将下面这个方法粘贴到上一个方法的后面:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (void)parser:(NSXMLParser*)parserdidEndElement:(NSString*)elementNamenamespaceURI:(NSString*)namespaceURIqualifiedName:(NSString*)qName {
// 1
if([qNameisEqualToString:@"current_condition"] ||
[qNameisEqualToString:@"request"]){
[self.xmlWeathersetObject:[NSArrayarrayWithObject:self.currentDictionary]forKey:qName];
self.currentDictionary=nil;
}
// 2
elseif([qNameisEqualToString:@"weather"]){
// Initalise the list of weather items if it dosnt exist
NSMutableArray*array = [self.xmlWeatherobjectForKey:@"weather"];
if(!array)
array = [NSMutableArrayarray];
[arrayaddObject:self.currentDictionary];
[self.xmlWeathersetObject:arrayforKey:@"weather"];
self.currentDictionary=nil;
}
// 3
elseif([qNameisEqualToString:@"value"]){
//Ignore value tags they only appear in the two conditions below
}
// 4
elseif([qNameisEqualToString:@"weatherDesc"] ||
[qNameisEqualToString:@"weatherIconUrl"]){
[self.currentDictionarysetObject:[NSArrayarrayWithObject:[NSDictionarydictionaryWithObject:self.outstringforKey:@"value"]]forKey:qName];
}
// 5
else{
[self.currentDictionarysetObject:self.outstringforKey:qName];
}
self.elementName=nil;
}
当检测到元素的结束标签时,会调用上面这个方法。在这个方法中,会查找一些标签:
urrent_condition元素表示获得了一个今天的天气。会把今天的天气直接添加到xmlWeather字典中。
weather元素表示获得了随后一天的天气。今天的天气只有一个,而后续的天气有多个,所以在此,将后续天气添加到一个数组中。
value标签出现在别的标签中,所以这里可以忽略掉这个标签。
weatherDesc和weatherIconUrl元素的值在存储之前,需要需要被放入一个数组中— 这里的结构是为了与JSON和plist版本天气咨询格式相匹配。
所有其它元素都是按照原样(as-is)进行存储的。
下面是最后一个delegate方法!将下面这个方法粘贴到上一个方法的后面:
[objc]view plaincopy
-(void)parserDidEndDocument:(NSXMLParser*)parser {
self.weather= [NSDictionarydictionaryWithObject:self.xmlWeatherforKey:@"data"];
self.title=@"XML Retrieved";
[self.tableViewreloadData];
}
当NSXMLParser解析到document的尾部时,会调用这个方法。在此,xmlWeather字典已经构造完毕,tableview可以重新加载了。
在上面代码中将xmlWeather添加到一个字典中,看起来是冗余的,不过这样可以确保与JSON和plist版本的格式完全匹配。这样所有的3种数据格式(JSON,plist和XML)都能够用相同的代码来显示!
现在所有的delegate方法和属性都搞定了,找到xmlTapped:方法,并取消注释成功块(successblock)中的一行代码:
[objc]view plaincopy
-(IBAction)xmlTapped:(id)sender{
...
success:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,NSXMLParser*XMLParser) {
// the line below used to be commented out
self.xmlWeather= [NSMutableDictionarydictionary];
XMLParser.delegate=self;
...
}
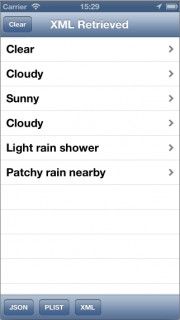
生成和运行工程,然后点击XML按钮,将看到如下内容:
一个小的天气程序
嗯, 上面的这个程序看起来体验不太友好,有点像整周都是阴雨天。如何让table view中的天气信息体验更好点呢?
再仔细看看之前的JSON格式数据:JSONformat frombefore,你会看到每个天气项里面都有一个图片URLs。 将这些天气图片显示到每个tableview cell中,这样程序看起来会更有意思。
AFNetworking给UIImageView添加了一个category,让图片能够异步加载,也就是说当图片在后台下载的时候,程序的UI界面仍然能够响应。为了使用这个功能,首先需要将这个categoryimport到WTTableViewController.m文件的顶部:
#import "UIImageView+AFNetworking.h"找到tableView:cellForRowAtIndexPath:方法,并将下面的代码粘贴到最后的return cell;代码上上面(这里应该有一个注释标记)
[objc]view plaincopy
__weakUITableViewCell*weakCell = cell;
[cell.imageViewsetImageWithURLRequest:[[NSURLRequestalloc]initWithURL:[NSURLURLWithString:daysWeather.weatherIconURL]]
placeholderImage:[UIImageimageNamed:@"placeholder.png"]
success:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,UIImage*image){
weakCell.imageView.image= image;
//only required if no placeholder is set to force the imageview on the cell to be laid out to house the new image.
//if(weakCell.imageView.frame.size.height==0 || weakCell.imageView.frame.size.width==0 ){
[weakCellsetNeedsLayout];
//}
}
failure:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,NSError*error){
}];
首先创建一个弱引用(weak)的cell,这样就可以在block中使用这个cell。如果你直接访问cell变量,Xcode会提示一个关于retain循环和内存泄露的警告。
UIImageView+AFNetworking category定义了一个setImageWithURLRequest…方法.这个方法的参数包括:一个指向图片URL的请求,一个占位符图片,一个success block和一个failure block。
当cell首次被创建的时候,cell中的UIImageView将显示一个占位符图片,直到真正的图片被下载完成。在这里你需要确保占位符的图片与实际图片尺寸大小相同。
如果尺寸不相同的话,你可以在success block中调用cell的setNeedsLayout方法.上面代码中对两行代码进行了注释,这是因为这里的占位符图片尺寸正好合适,留着注释,可能在别的程序中需要用到。
现在生成并运行工程,然后点击之前添加的3个操作中的任意一个,将看到如下内容:
很好!异步加载图片从来没有这么简单过。
一个RESTful类
到现在你已经使用类似AFJSONRequestOperation这样的类创建了一次性的HTTP请求。另外,较低级的AFHTTPClient类是用来访问单个的web
service终端。对这个AFHTTPClient一般是给它设置一个基本的URL,然后用AFHTTPClient进行多个请求(而不是像之前的那样,每次请求的时候,都创建一个AFHTTPClient)。
AFHTTPClient同样为编码参数、处理multipart表单请求body的构造、管理请求操作和批次入队列操作提供了很强的灵活性,它还处理了整套RESTful
(GET, POST, PUT, 和 DELETE), 下面我们就来试试最常用的两个:GET 和POST.
注意:对REST,GET和POST不清楚?看看这里比较有趣的介绍 – 我如何给妻子解释REST(HowI Explained REST to My Wife.)
在WTTableViewController.h顶部将类声明按照如下修改:
[objc]view plaincopy
@interfaceWTTableViewController : UITableViewController
在WTTableViewController.m中,找到httpClientTapped:方法,并用下面的实现替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (IBAction)httpClientTapped:(id)sender {
UIActionSheet*actionSheet = [[UIActionSheetalloc]initWithTitle:@"AFHTTPClient"delegate:selfcancelButtonTitle:@"Cancel"destructiveButtonTitle:nilotherButtonTitles:@"HTTP POST",@"HTTP GET",nilnil];
[actionSheetshowFromBarButtonItem:senderanimated:YES];
}
上面的方法会弹出一个action sheet,用以选择GET和POST请求。粘贴如下代码以实现actionsheet中按钮对应的操作:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (void)actionSheet:(UIActionSheet*)actionSheetclickeonAtIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex{
// 1
NSURL*baseURL = [NSURLURLWithString:[NSStringstringWithFormat:BaseURLString]];
NSDictionary*parameters = [NSDictionarydictionaryWithObject:@"json"forKey:@"format"];
// 2
AFHTTPClient*client = [[AFHTTPClientalloc]initWithBaseURL:baseURL];
[clientregisterHTTPOperationClass:[AFJSONRequestOperationclass]];
[clientsetDefaultHeader:@"Accept"value:@"application/json"];
// 3
if(buttonIndex==0) {
[clientpostPath:@"weather.php"
parameters:parameters
success:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation*operation,idresponseObject) {
self.weather= responseObject;
self.title=@"HTTP POST";
[self.tableViewreloadData];
}
failure:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation*operation,NSError*error) {
UIAlertView*av = [[UIAlertViewalloc]initWithTitle:@"Error Retrieving Weather"
message:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@",error]
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"otherButtonTitles:nil];
[avshow];
}
];
}
// 4
elseif(buttonIndex==1) {
[clientgetPath:@"weather.php"
parameters:parameters
success:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation*operation,idresponseObject) {
self.weather= responseObject;
self.title=@"HTTP GET";
[self.tableViewreloadData];
}
failure:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation*operation,NSError*error) {
UIAlertView*av = [[UIAlertViewalloc]initWithTitle:@"Error Retrieving Weather"
message:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@",error]
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"otherButtonTitles:nil];
[avshow];
}
];
}
}
上面的代码作用如下:
构建一个baseURL,以及一个参数字典,并将这两个变量传给AFHTTPClient.
将AFJSONRequestOperation注册为HTTP的操作,这样就可以跟之前的示例一样,可以获得解析好的JSON数据。
做了一个GET请求,这个请求有一对block:success和failure。
POST请求跟GET一样。
在这里,将请求一个JSON回应,当然也可以使用之前讨论过的另外两种格式来代替JSON。
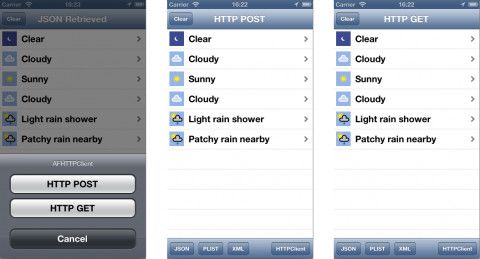
生成并运行工程,点击HTTPClient按钮,然后选择GET 或 POST按钮来初始化一个相关的请求。之后会看到如下内容:
至此,你已经知道AFHTTPClient最基本的使用方法。不过,这里还有更好的一种使用方法,它可以让代码更加干净整齐,下面我们就来学习一下吧。
连接到Live Service
到现在为止,你已经在table view controller中直接调用了AFRequestOperations 和AFHTTPClient. 实际上,大多数时候不是这样的,你的网络请求会跟某个web service或API相关。
AFHTTPClient已经具备与webAPI通讯的所有内容。AFHTTPClient在代码中已经把网络通讯部分做了解耦处理,让网络通讯的代码在整个工程中都可以重用。
下面是两个关于AFHTTPClient最佳实践的指导:
为每个webservice创建一个子类。例如,如果你在写一个社交网络聚合器,那么可能就会有Twitter的一个子类,Facebook的一个子类,Instragram的一个子类等等。
在AFHTTPClient子类中,创建一个类方法,用来返回一个共享的单例,这将会节约资源并省去必要的对象创建。
当前,你的工程中还没有一个AFHTTPClient的子类,下面就来创建一个吧。我们来处理一下,让代码清洁起来。
首先,在工程中创建一个新的文件:iOSCocoa TouchObjective-C Class. 命名为WeatherHTTPClient并让其继承自AFHTTPClient.
你希望这个类做3件事情:
A:执行HTTP请求
B:当有新的可用天气数据时,调用delegate
C:使用用户当前地理位置来获得准确的天气。
用下面的代码替换WeatherHTTPClient.h:
[objc]view plaincopy
#import "AFHTTPClient.h"
@protocolWeatherHttpClientDelegate;
@interfaceWeatherHTTPClient : AFHTTPClient
@property(weak)iddelegate;
+ (WeatherHTTPClient*)sharedWeatherHTTPClient;
- (id)initWithBaseURL:(NSURL*)url;
- (void)updateWeatherAtLocation:(CLLocation*)locationforNumberOfDays:(int)number;
@end
@protocolWeatherHttpClientDelegate
-(void)weatherHTTPClient:(WeatherHTTPClient*)clientdidUpdateWithWeather:(id)weather;
-(void)weatherHTTPClient:(WeatherHTTPClient*)clientdidFailWithError:(NSError*)error;
@end
在实现文件中,你将了解头文件中定义的更多相关内容。打开WeatherHTTPClient.m并将下面的代码添加到@implementation下面:
[objc]view plaincopy
+ (WeatherHTTPClient*)sharedWeatherHTTPClient
{
NSString*urlStr =@"http://free.worldweatheronline.com/feed/";
staticdispatch_once_t pred;
staticWeatherHTTPClient*_sharedWeatherHTTPClient =nil;
dispatch_once(&pred, ^{ _sharedWeatherHTTPClient = [[selfalloc]initWithBaseURL:[NSURLURLWithString:urlStr]]; });
return_sharedWeatherHTTPClient;
}
- (id)initWithBaseURL:(NSURL*)url
{
self= [superinitWithBaseURL:url];
if(!self) {
returnnil;
}
[selfregisterHTTPOperationClass:[AFJSONRequestOperationclass]];
[selfsetDefaultHeader:@"Accept"value:@"application/json"];
returnself;
}
sharedWeatherHTTPClient 方法使用Grand CentralDispatch(GCD)来确保这个共享的单例对象只被初始化分配一次。这里用一个base URL来初始化对象,并将其设置为期望webservice响应为JSON。
将下面的方法粘贴到上一个方法的下面:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (void)updateWeatherAtLocation:(CLLocation*)locationforNumberOfDays:(int)number{
NSMutableDictionary*parameters = [NSMutableDictionarydictionary];
[parameterssetObject:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%d",number]forKey:@"num_of_days"];
[parameterssetObject:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%f,%f",location.coordinate.latitude,location.coordinate.longitude]forKey:@"q"];
[parameterssetObject:@"json"forKey:@"format"];
[parameterssetObject:@"7f3a3480fc162445131401"forKey:@"key"];
[selfgetPath:@"weather.ashx"
parameters:parameters
success:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation*operation,idresponseObject) {
if([self.delegaterespondsToSelector:@selector(weatherHTTPClient:didUpdateWithWeather:)])
[self.delegateweatherHTTPClient:selfdidUpdateWithWeather:responseObject];
}
failure:^(AFHTTPRequestOperation*operation,NSError*error) {
if([self.delegaterespondsToSelector:@selector(weatherHTTPClient:didFailWithError:)])
[self.delegateweatherHTTPClient:selfdidFailWithError:error];
}];
}
这个方法调用World Weather Online接口,以获得具体位置的天气信息。
非常重要!本实例中的APIkey仅仅是为本文创建的。如果你创建了一个程序,请在WorldWeather Online创建一个账号,并获得你自己的APIkey!
一旦对象获得了天气数据,它需要一些方法来通知对此感兴趣的对象:数据回来了。这里要感谢WeatherHttpClientDelegate协议和它的delegate方法,在上面代码中的success
和 failureblocks可以通知一个controller:指定位置的天气已经更新了。这样,controller就可以对天气做更新显示。
现在,我们需要把这些代码片段整合到一起!WeatherHTTPClient希望接收一个位置信息,并且WeatherHTTPClient定义了一个delegate协议,现在对WTTableViewControlle类做一下更新,以使用WeatherHTTPClient.
打开WTTableViewController.h添加一个import,并用下面的代码替换@interface声明:
[objc]view plaincopy
#import "WeatherHTTPClient.h"
@interfaceWTTableViewController : UITableViewController
另外添加一个新的Core Location manager 属性:
[objc]view plaincopy
@property(strong)CLLocationManager*manager;
在WTTableViewController.m中,将下面的代码添加到viewDidLoad:的底部:
[objc]view plaincopy
self.manager= [[CLLocationManageralloc]init];
self.manager.delegate=self;
上面这两行代码初始化了Core Location manager,这样当view加载的时候,用来确定用户的当前位置。CoreLocation然后会通过delegate回调以传回位置信息。将下面的方法添加到实现文件中:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager*)managerdidUpdateToLocation:(CLLocation*)newLocationfromLocation:(CLLocation*)oldLocation{
//if the location is more than 5 minutes old ignore
if([newLocation.timestamptimeIntervalSinceNow]<300){
[self.managerstopUpdatingLocation];
WeatherHTTPClient*client = [WeatherHTTPClientsharedWeatherHTTPClient];
client.delegate=self;
[clientupdateWeatherAtLocation:newLocationforNumberOfDays:5];
}
}
现在,当用户的位置有了变化时,你就可以使用WeatherHTTPClient单例来请求当前位置的天气信息。
记住,WeatherHTTPClient有两个delegate方法需要实现。将下面两个方法添加到实现文件中:
[objc]view plaincopy
-(void)weatherHTTPClient:(WeatherHTTPClient*)clientdidUpdateWithWeather:(id)aWeather{
self.weather= aWeather;
self.title=@"API Updated";
[self.tableViewreloadData];
}
-(void)weatherHTTPClient:(WeatherHTTPClient*)clientdidFailWithError:(NSError*)error{
UIAlertView*av = [[UIAlertViewalloc]initWithTitle:@"Error Retrieving Weather"
message:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%@",error]
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"otherButtonTitles:nil];
[avshow];
}
上面的两个方法,当WeatherHTTPClient请求成功, 你就可以更新天气数据并重新加载tableview。如果网络错误,则显示一个错误信息。
找到apiTapped:方法,并用下面的方法替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
-(IBAction)apiTapped:(id)sender{
[self.managerstartUpdatingLocation];
}
生成并运行程序,点击AP按钮以初始化一个WeatherHTTPClient 请求, 然后会看到如下画面:
希望在这里你未来的天气跟我的一样:晴天!
我还没有死!
你可能注意到了,这里调用的外部webservice需要花费一些时间才能返回数据。当在进行网络操作时,给用户提供一个信息反馈是非常重要的,这样用户才知道程序是在运行中或已奔溃了。
很幸运的是,AFNetworking有一个简便的方法来提供信息反馈:AFNetworkActivityIndicatorManager.
在WTAppDelegate.m中,找到application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:方法,并用下面的方法替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication*)applicationdidFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary*)launchOptions
{
[AFNetworkActivityIndicatorManagersharedManager].enabled=YES;
returnYES;
}
让sharedManager可以自动的显示出网络活动指示器( network activityindicator)— 无论射门时候,只要有一个新的网络请求在后台运行着。 这样你就不需要每次请求的时候,都要单独进行管理。
生成并运行工程,无论什么时候,只要有网络请求,都可以在状态栏中看到一个小的网络风火轮:
现在,即使你的程序在等待一个很慢的webservice,用户都知道程序还在运行着!
下载图片
如果你在table view cell上点击,程序会切换到天气的详细画面,并且以动画的方式显示出相应的天气情况。
这非常不错,但目前动画只有一个背景图片。除了通过网络来更新背景图片,还有更好的方法吗!
下面是本文关于介绍AFNetworking的最后内容了:AFImageRequestOperation.跟AFJSONRequestOperation一样,AFImageRequestOperation封装了HTTP请求:获取图片。
在WeatherAnimationViewController.m中有两个方法需要实现.找到updateBackgroundImage:方法,并用下面的代码替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (IBAction)updateBackgroundImage:(id)sender {
//Store this image on the same server as the weather canned files
NSURLRequest*request = [NSURLRequestrequestWithURL:[NSURLURLWithString:@"http://www.scott-sherwood.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/scene.png"]];
AFImageRequestOperation*operation = [AFImageRequestOperationimageRequestOperationWithRequest:request
imageProcessingBlock:nil
success:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,UIImage*image) {
self.backgroundImageView.image= image;
[selfsaveImage:imagewithFilename:@"background.png"];
}
failure:^(NSURLRequest*request,NSHTTPURLResponse*response,NSError*error) {
NSLog(@"Error %@",error);
}];
[operationstart];
}
这个方法初始化并下载一个新的背景图片。在结束时,它将返回请求到的完整图片。
在WeatherAnimationViewController.m中,
你将看到两个辅助方法:imageWithFilename:
和saveImage:withFilename:,通过这两个辅助方法,可以对下载下来的图片进行存储和加载。updateBackgroundImage:将通过辅助方法把下载的图片存储到磁盘中。
接下来找到deleteBackgroundImage:方法,并用下面的代码替换:
[objc]view plaincopy
- (IBAction)deleteBackgroundImage:(id)sender {
NSString*path;
NSArray*paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask,YES);
path = [[pathsobjectAtIndex:0]stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"WeatherHTTPClientImages/"];
NSError*error;
[[NSFileManagerdefaultManager]removeItemAtPath:patherror:&error];
NSString*desc = [self.weatherDictionaryweatherDescription];
[selfstart:desc];
}
这个方法将删除已经下载的图片,这样在测试程序的时候,你可以再次下载图片。
最后一次:生成并运行工程,下载天气数据,并点击某个cell,以打开详细天气画面。在详细天气画面中,点击UpdateBackground 按钮. 如果你点击的是晴天cell,将会看到如下画面:
你所想到的所有方法,都可以使用AFNetworking来与外界通讯:
AFJSONOperation, AFPropertyListOperation 和AFXMLOperation用来解析结构化数据。
UIImageView+AFNetworking用来快捷的填充image view。
AFHTTPClient用来进行更底层的请求。
用自定义的AFHTTPClient子类来访问一个web service。
AFNetworkActivityIndicatorManager用来给用户做出网络访问的提示。
AFImageRequestOperation用来加载图片。
AFNetworking可以帮助你进行网络开发!