零拷贝——sendfile
一、DMA
io读写有两种方式:
- 中断
- DMA
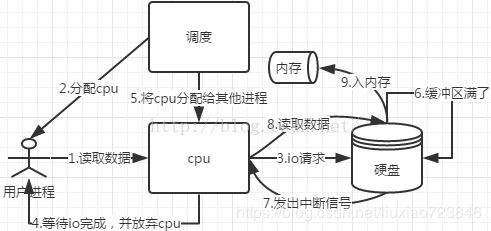
- 用户进程发起数据读取请求
- 系统调度为该进程分配cpu
- cpu向io控制器(ide,scsi)发送io请求
- 用户进程等待io完成,让出cpu
- 系统调度cpu执行其他任务
- 数据写入至io控制器的缓冲寄存器
- 缓冲寄存器满了向cpu发出中断信号
- cpu读取数据至内存
通过中断,cpu需要拷贝数据。
2、DMA
- 用户进程发起数据读取请求
- 系统调度为该进程分配cpu
- cpu向DMA发送io请求
- 用户进程等待io完成,让出cpu
- 系统调度cpu执行其他任务
- 数据写入至io控制器的缓冲寄存器
- DMA不断获取缓冲寄存器中的数据(需要cpu时钟)
- 传输至内存(需要cpu时钟)
- 所需的全部数据获取完毕后向cpu发出中断信号
减少cpu中断,不用cpu拷贝数据,把数据拷贝这类工作从cpu中解放出来。
二、数据传输1
在一个web系统中从一个文件中读出数据并将数据传输到网络上另一程序的场景,有两种方式:
1、传统方式:
读取数据后并通过网络发送 所发生的数据拷贝,java代码如下:
File.read(fileDesc, buf, len);
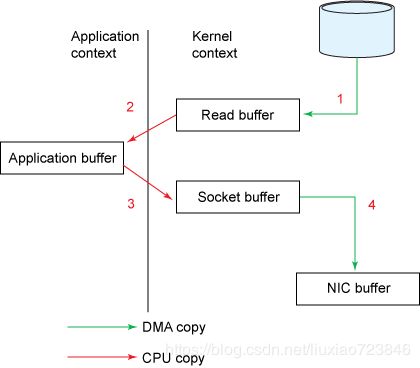
Socket.send(socket, buf, len);这里主要使用了linux底层的read()和write()两个系统调用,整个流程如下图:
- 一个read系统调用后,DMA执行了一次数据拷贝,从磁盘到内核空间
- read结束后,发生第二次数据拷贝,由cpu将数据从内核空间拷贝至用户空间
- send系统调用,cpu发生第三次数据拷贝,由cpu将数据从用户空间拷贝至内核空间(socket缓冲区)
- send系统调用结束后,DMA执行第四次数据拷贝,将数据从内核拷贝至协议引擎
整个过程有四次数据拷贝,并且每个过程都发生一次上下文切换。
2、sendfile(零拷贝):
上面的方式我们没有对文件内容做任何修改,那么在内核空间和用户空间来回拷贝数据无疑就是一种浪费,而零拷贝主要就是为了解决这种低效性。java代码如下:
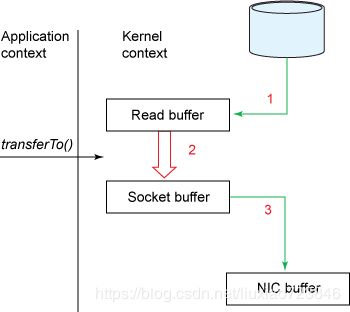
transferTo(position, count, writableChannel);这里主要依赖linux底层sendfile()调用。Linux 2.1 版本提供了sendfile函数,其基本原理如下:数据根本不经过用户态,直接从内核缓冲区进入到 Socket Buffer。流程如下:
- DMA从拷贝至内核缓冲区
- cpu将数据从内核缓冲区拷贝至内核空间(socket缓冲区)
- DMA将数据从内核拷贝至协议引擎
这三个过程中共发生三次数据拷贝,2次上下文切换,分别为发起读取文件和发送数据。
3、进一步优化:
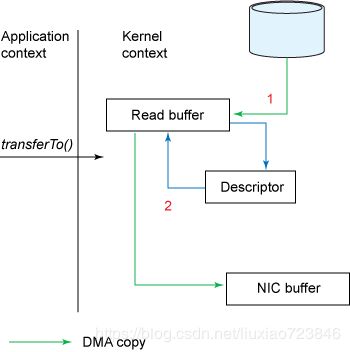
上面的方式尚未达到我们的零拷贝要求。如果底层网络接口卡支持收集操作 的话,那么我们就可以进一步减少内核的数据复制。在 Linux 内核 2.4 及后期版本中,套接字缓冲区描述符就做了相应调整,以满足该需求。这种方法不仅可以减少多个上下文切换,还可以消除需要涉及 CPU 的重复的数据拷贝。对于用户方面,用法还是一样的,整个流程如下:
- MA从拷贝至内核缓冲区
- 将数据的位置和长度的信息的描述符增加至内核空间(socket缓冲区)
- DMA将数据从内核拷贝至协议引擎
整个过程共发生两次数据拷贝。
参考:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-zerocopy/
https://www.cnblogs.com/z-sm/p/6547709.html
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaofei0859/article/details/74321216
https://www.cnblogs.com/stateis0/p/10960579.html
java零拷贝示例代码:
1、文件到文件:
class ZerocopyFile {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void transferToDemo(String from, String to) throws IOException {
FileChannel fromChannel = new RandomAccessFile(from, "rw").getChannel();
FileChannel toChannel = new RandomAccessFile(to, "rw").getChannel();
long position = 0;
long count = fromChannel.size();
fromChannel.transferTo(position, count, toChannel);
fromChannel.close();
toChannel.close();
}
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void transferFromDemo(String from, String to) throws IOException {
FileChannel fromChannel = new FileInputStream(from).getChannel();
FileChannel toChannel = new FileOutputStream(to).getChannel();
long position = 0;
long count = fromChannel.size();
toChannel.transferFrom(fromChannel, position, count);
fromChannel.close();
toChannel.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String from = "src/main/java/zerocopy/1.data";
String to = "src/main/java/zerocopy/2.data";
// transferToDemo(from,to);
transferFromDemo(from, to);
}
}2、socket:
/**
* disk-nic零拷贝
*/
class ZerocopyServer {
ServerSocketChannel listener = null;
protected void mySetup() {
InetSocketAddress listenAddr = new InetSocketAddress(9026);
try {
listener = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ServerSocket ss = listener.socket();
ss.setReuseAddress(true);
ss.bind(listenAddr);
System.out.println("监听的端口:" + listenAddr.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("端口绑定失败 : " + listenAddr.toString() + " 端口可能已经被使用,出错原因: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZerocopyServer dns = new ZerocopyServer();
dns.mySetup();
dns.readData();
}
private void readData() {
ByteBuffer dst = ByteBuffer.allocate(4096);
try {
while (true) {
SocketChannel conn = listener.accept();
System.out.println("创建的连接: " + conn);
conn.configureBlocking(true);
int nread = 0;
while (nread != -1) {
try {
nread = conn.read(dst);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
nread = -1;
}
dst.rewind();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class ZerocopyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ZerocopyClient sfc = new ZerocopyClient();
sfc.testSendfile();
}
public void testSendfile() throws IOException {
String host = "localhost";
int port = 9026;
SocketAddress sad = new InetSocketAddress(host, port);
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(sad);
sc.configureBlocking(true);
String fname = "src/main/java/zerocopy/test.data";
FileChannel fc = new FileInputStream(fname).getChannel();
long start = System.nanoTime();
long nsent = 0, curnset = 0;
curnset = fc.transferTo(0, fc.size(), sc);
System.out.println("发送的总字节数:" + curnset + " 耗时(ns):" + (System.nanoTime() - start));
try {
sc.close();
fc.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}三、数据传输2
还有一个零拷贝的例子mmap。传统方式使用read、write进行文件会产生用户态和内核态数据的拷贝,使用mmap,将文件映射到内核缓冲区,同时,用户空间可以共享内核空间的数据。
这里只做一个介绍,具体mmap的原理、使用下次再说。