前言
dyld全称the dynamic link editor,即动态链接器,其本质是Mach-O文件,他是专门用来加载动态库的库。源码可以从这里下载,本文采用的是| dyld-635.2 |
源码进行分析。dyld位于/usr/lib/dyld,可以从越狱机或者mac电脑中找到。以mac为例,终端执行如下命令:
cd /usr/lib/
file dyld
输出为:
dyld: Mach-O universal binary with 2 architectures: [x86_64:Mach-O 64-bit dynamic linker x86_64] [i386:Mach-O dynamic linker i386]
dyld (for architecture x86_64): Mach-O 64-bit dynamic linker x86_64
dyld (for architecture i386): Mach-O dynamic linker i386
即,dyld是Mach-O类型的通用二进制文件,支持x86_64和i386两种架构。当然,iPhone真机对应的dyld支持的为arm系列架构。
- otool简介
otool是专门用来查看Mach-O类型文件的工具,终端输入otool可以看到很多用法:
$ otool
Usage: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/otool [-arch arch_type] [-fahlLDtdorSTMRIHGvVcXmqQjCP] [-mcpu=arg] [--version] 比如,可以通过-L来查看当前Mach-O所依赖的动态库。如,常用的gcd依赖以下这些动态库:
$ otool -L /usr/lib/system/libdispatch.dylib
/usr/lib/system/libdispatch.dylib:
/usr/lib/system/libdispatch.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1008.250.7)
/usr/lib/system/libsystem_darwin.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1.0.0)
/usr/lib/system/libdyld.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 655.1.1)
/usr/lib/system/libcompiler_rt.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 63.4.0)
/usr/lib/system/libsystem_kernel.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 4903.255.45)
/usr/lib/system/libsystem_platform.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 177.250.1)
/usr/lib/system/libsystem_pthread.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 330.250.2)
/usr/lib/system/libsystem_malloc.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 166.250.4)
/usr/lib/system/libsystem_c.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1272.250.1)
/usr/lib/system/libsystem_blocks.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 73.0.0)
/usr/lib/system/libunwind.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 35.4.0)
/usr/lib/libobjc.A.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 228.0.0)
当然,也可以通过MachOView更加直观的查看相关信息
dyld加载
动态库的加载必然在main函数之前,而load方法的调用也在main之前,因此从这里入手。新建工程,打上符号断点[NSObject load],运行程序后如图所示:
可见,load的加载是从_dyld_start这个函数开始的。_dyld_start对应汇编文件,内部调用dyldbootstrap::start,位于dyldInitialization.cpp中:
//
// This is code to bootstrap dyld. This work in normally done for a program by dyld and crt.
// In dyld we have to do this manually.
//
uintptr_t start(const struct macho_header* appsMachHeader, int argc, const char* argv[],
intptr_t slide, const struct macho_header* dyldsMachHeader,
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
// if kernel had to slide dyld, we need to fix up load sensitive locations
// we have to do this before using any global variables
slide = slideOfMainExecutable(dyldsMachHeader);
bool shouldRebase = slide != 0;
#if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls)
shouldRebase = true;
#endif
if ( shouldRebase ) {
rebaseDyld(dyldsMachHeader, slide);
}
// allow dyld to use mach messaging
mach_init();
// kernel sets up env pointer to be just past end of agv array
const char** envp = &argv[argc+1];
// kernel sets up apple pointer to be just past end of envp array
const char** apple = envp;
while(*apple != NULL) { ++apple; }
++apple;
// set up random value for stack canary
__guard_setup(apple);
#if DYLD_INITIALIZER_SUPPORT
// run all C++ initializers inside dyld
runDyldInitializers(dyldsMachHeader, slide, argc, argv, envp, apple);
#endif
// now that we are done bootstrapping dyld, call dyld's main
uintptr_t appsSlide = slideOfMainExecutable(appsMachHeader);
return dyld::_main(appsMachHeader, appsSlide, argc, argv, envp, apple, startGlue);
}
流程很简单:获取dyld对应的slide->通过slide对dyld进行rebase->mach初始化->栈溢出保护->获取应用的slide(appsSlide)->调用dyld的main函数
slide与rebase
由于apple采用了ASLR(Address space layout randomization)技术,所以Mach-O每次加载到内存中的首地址是变化的,此时想找到代码在内存中对应的地址需要重定位rebase。rebase要用到slide值,那么slide如何计算?
static uintptr_t slideOfMainExecutable(const struct macho_header* mh)
{
const uint32_t cmd_count = mh->ncmds;
const struct load_command* const cmds = (struct load_command*)(((char*)mh)+sizeof(macho_header));
const struct load_command* cmd = cmds;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cmd_count; ++i) {
if ( cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_COMMAND ) {
const struct macho_segment_command* segCmd = (struct macho_segment_command*)cmd;
if ( (segCmd->fileoff == 0) && (segCmd->filesize != 0)) {
return (uintptr_t)mh - segCmd->vmaddr;
}
}
cmd = (const struct load_command*)(((char*)cmd)+cmd->cmdsize);
}
return 0;
}
intptr_t _dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide(uint32_t imageIndex)
{
log_apis("_dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide(%d)\n", imageIndex);
const mach_header* mh = gAllImages.imageLoadAddressByIndex(imageIndex);
if ( mh != nullptr )
return dyld3::_dyld_get_image_slide(mh);
return 0;
}
intptr_t _dyld_get_image_slide(const mach_header* mh)
{
log_apis("_dyld_get_image_slide(%p)\n", mh);
const MachOLoaded* mf = (MachOLoaded*)mh;
if ( !mf->hasMachOMagic() )
return 0;
return mf->getSlide();
}
intptr_t MachOLoaded::getSlide() const
{
Diagnostics diag;
__block intptr_t slide = 0;
forEachLoadCommand(diag, ^(const load_command* cmd, bool& stop) {
if ( cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_64 ) {
const segment_command_64* seg = (segment_command_64*)cmd;
if ( strcmp(seg->segname, "__TEXT") == 0 ) {
slide = (uintptr_t)(((uint64_t)this) - seg->vmaddr);
stop = true;
}
}
else if ( cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT ) {
const segment_command* seg = (segment_command*)cmd;
if ( strcmp(seg->segname, "__TEXT") == 0 ) {
slide = (uintptr_t)(((uint64_t)this) - seg->vmaddr);
stop = true;
}
}
});
diag.assertNoError(); // any malformations in the file should have been caught by earlier validate() call
return slide;
}
由于应用本身的Mach-O及dyld的特殊性,这两个采用的是slideOfMainExecutable的方式获取slide,而动态库加载采用的是_dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide的方式获取slide。
对比后不难发现:
slide = mh首地址 - load_command中__TEXT段中vmaddr的值(slideOfMainExecutable方式中以(segCmd->fileoff == 0) && (segCmd->filesize != 0)为条件,对于应用本身Mach-O及dyld,此时也是对应__TEXT段)
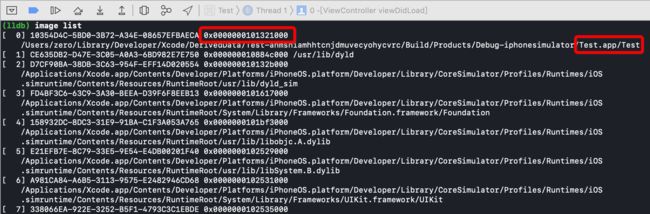
简单验证一下,以应用Mach-O为例:
可以看到,Mach-O的地址为0x101321000(16进制),VM Address的地址为4294967296(十进制,对应16进制为0x100000000)。当然,也可以通过命令行直接获取slide的值,这里为了方便理解,采用手动计算
image list -o -f
1、用Mach-O的内存地址减去对应虚拟地址,得到20058112(十进制)为slide的值
2、获取viewDidLoad函数在当前内存中的地址
3、用viewDidLoad内存地址减去slide得到Mach-O中对应的虚拟地址
4、将虚拟地址转化为16进制
可以看到,最终计算出的值0x100001750与在Mach-O中看到的值一致
dyld::_main
对ASLR有个基本认知后,接着看dyld中的main干了什么。由于内部代码过长,此处先贴出流程再逐步分析:设置运行环境->加载共享缓存->实例化主程序->加载插入的动态库->链接主程序->链接插入的动态库->执行弱符号绑定->执行初始化方法->查找入口点并返回
- 设置运行环境
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
// Grab the cdHash of the main executable from the environment
uint8_t mainExecutableCDHashBuffer[20];
const uint8_t* mainExecutableCDHash = nullptr;
if ( hexToBytes(_simple_getenv(apple, "executable_cdhash"), 40, mainExecutableCDHashBuffer) )
// 获取主程序hash
mainExecutableCDHash = mainExecutableCDHashBuffer;
// Trace dyld's load
// 告知kernel,dyld已加载
notifyKernelAboutImage((macho_header*)&__dso_handle, _simple_getenv(apple, "dyld_file"));
#if !TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// Trace the main executable's load
// 告知kernel,主程序Mach-O已加载
notifyKernelAboutImage(mainExecutableMH, _simple_getenv(apple, "executable_file"));
#endif
uintptr_t result = 0;
sMainExecutableMachHeader = mainExecutableMH;
sMainExecutableSlide = mainExecutableSlide;
#if __MAC_OS_X_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED
// if this is host dyld, check to see if iOS simulator is being run
// 获取dyld路径
const char* rootPath = _simple_getenv(envp, "DYLD_ROOT_PATH");
if ( (rootPath != NULL) ) {
// look to see if simulator has its own dyld
char simDyldPath[PATH_MAX];
strlcpy(simDyldPath, rootPath, PATH_MAX);
strlcat(simDyldPath, "/usr/lib/dyld_sim", PATH_MAX);
int fd = my_open(simDyldPath, O_RDONLY, 0);
if ( fd != -1 ) {
// 如果是模拟器,并且正确加载`dyld_sim`,则直接返回主程序地址
const char* errMessage = useSimulatorDyld(fd, mainExecutableMH, simDyldPath, argc, argv, envp, apple, startGlue, &result);
if ( errMessage != NULL )
halt(errMessage);
return result;
}
}
#endif
CRSetCrashLogMessage("dyld: launch started");
// 设置上下文
setContext(mainExecutableMH, argc, argv, envp, apple);
// Pickup the pointer to the exec path.
// 获取主程序路径
sExecPath = _simple_getenv(apple, "executable_path");
// Remove interim apple[0] transition code from dyld
if (!sExecPath) sExecPath = apple[0];
// 获取Mach-O绝对路径
if ( sExecPath[0] != '/' ) {
// have relative path, use cwd to make absolute
char cwdbuff[MAXPATHLEN];
if ( getcwd(cwdbuff, MAXPATHLEN) != NULL ) {
// maybe use static buffer to avoid calling malloc so early...
char* s = new char[strlen(cwdbuff) + strlen(sExecPath) + 2];
strcpy(s, cwdbuff);
strcat(s, "/");
strcat(s, sExecPath);
sExecPath = s;
}
}
// Remember short name of process for later logging
// 设置进程名称
sExecShortName = ::strrchr(sExecPath, '/');
if ( sExecShortName != NULL )
++sExecShortName;
else
sExecShortName = sExecPath;
// 配置进程受限模式
configureProcessRestrictions(mainExecutableMH);
// 再次检测/设置上下文环境
#if __MAC_OS_X_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED
if ( !gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsPrint && !gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsPath && !gLinkContext.allowEnvVarsSharedCache ) {
pruneEnvironmentVariables(envp, &apple);
// set again because envp and apple may have changed or moved
setContext(mainExecutableMH, argc, argv, envp, apple);
}
else
#endif
{
checkEnvironmentVariables(envp);
defaultUninitializedFallbackPaths(envp);
}
...
// 如果设置了DYLD_PRINT_OPTS,则打印参数
if ( sEnv.DYLD_PRINT_OPTS )
printOptions(argv);
// 如果设置了DYLD_PRINT_ENV,则打印环境变量
if ( sEnv.DYLD_PRINT_ENV )
printEnvironmentVariables(envp);
// 获取主程序架构信息
getHostInfo(mainExecutableMH, mainExecutableSlide);
}
通过源码可以看到,如果是模拟器运行的程序,其实是通过dyld_sim来进行后续加载工作的,与正常真机加载流程略有不同,具体实现在useSimulatorDyld这个函数中,本文不做进一步解析。不难看出,模拟器比真机多加载一个dyld_sim。
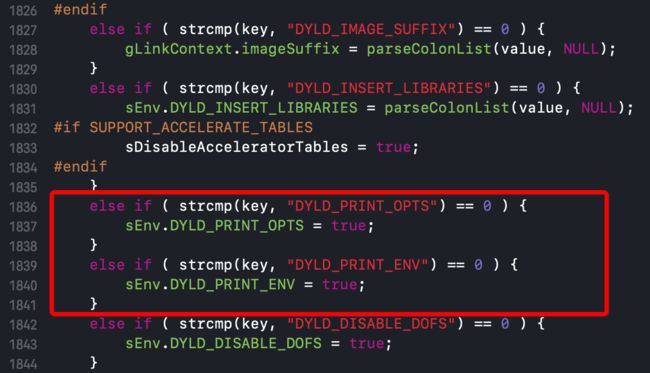
这里还有一个知识点,环境变量DYLD_PRINT_OPTS与DYLD_PRINT_ENV
添加这两个环境变量,对应的字段会被设置为true,可以看到,这里并不需要设置value
输出如下:
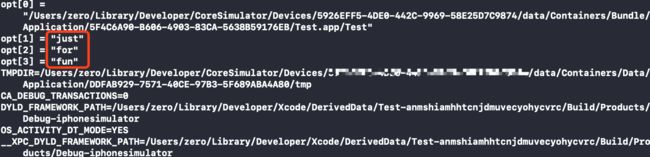
但是并非每个环境变量都不需要配置value,如:
void processDyldEnvironmentVariable(const char* key, const char* value, const char* mainExecutableDir)
{
if ( strcmp(key, "DYLD_FRAMEWORK_PATH") == 0 ) {
appendParsedColonList(value, mainExecutableDir, &sEnv.DYLD_FRAMEWORK_PATH);
}
else if ( strcmp(key, "DYLD_FALLBACK_FRAMEWORK_PATH") == 0 ) {
appendParsedColonList(value, mainExecutableDir, &sEnv.DYLD_FALLBACK_FRAMEWORK_PATH);
}
else if ( strcmp(key, "DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH") == 0 ) {
appendParsedColonList(value, mainExecutableDir, &sEnv.DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH);
}
else if ( strcmp(key, "DYLD_FALLBACK_LIBRARY_PATH") == 0 ) {
appendParsedColonList(value, mainExecutableDir, &sEnv.DYLD_FALLBACK_LIBRARY_PATH);
}
...
}
这些环境变量是需要配置value的,更多可配置的环境变量可从processDyldEnvironmentVariable函数中找到
- 加载共享缓存
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
// load shared cache
// 检测共享缓存是否可用
checkSharedRegionDisable((dyld3::MachOLoaded*)mainExecutableMH, mainExecutableSlide);
#if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// until is fixed
gLinkContext.sharedRegionMode = ImageLoader::kUsePrivateSharedRegion;
//
#endif
if ( gLinkContext.sharedRegionMode != ImageLoader::kDontUseSharedRegion ) {
// 映射共享缓存到共享区
mapSharedCache();
}
...
#if !TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
#ifdef WAIT_FOR_SYSTEM_ORDER_HANDSHAKE
// Add gating mechanism to dyld support system order file generation process
WAIT_FOR_SYSTEM_ORDER_HANDSHAKE(dyld::gProcessInfo->systemOrderFlag);
#endif
#endif
try {
// add dyld itself to UUID list
// 添加dyld的UUID到共享缓存UUID列表中
addDyldImageToUUIDList();
...
}
#endif
...
}
这部分流程也很简单:检测共享缓存是否可用->如果可用,映射共享缓存到共享区->添加dyld的UUID到缓存列表
其中,检测共享缓存是否可用checkSharedRegionDisable这个函数中有两句注释:
// if main executable has segments that overlap the shared region, then disable using the shared region
// iOS cannot run without shared region
意思是:如果主程序Mach-O有segments与共享区重叠,那么共享区不可用。并且,iOS不开启共享区无法运行。
看下是如何检测这两者是否重叠的:
...
// 调用
mainExecutableMH->intersectsRange(SHARED_REGION_BASE, SHARED_REGION_SIZE)
...
bool MachOLoaded::intersectsRange(uintptr_t start, uintptr_t length) const
{
__block bool result = false;
uintptr_t slide = getSlide();
forEachSegment(^(const SegmentInfo& info, bool& stop) {
if ( (info.vmAddr+info.vmSize+slide >= start) && (info.vmAddr+slide < start+length) )
result = true;
});
return result;
}
如果主程序segment中的虚拟地址+虚拟地址+偏移量 >= 共享区起始地址并且主程序segment中的虚拟地址 + 偏移量 < 共享区终止地址,那么认为主程序Mach-O有segments与共享区重叠,此时共享区不可用,从而动态库缓存不可用
疑问:可以看到这段检测代码在满足重叠条件后,并没有将stop设为true,所以源码其实是检测Mach-O最后一段segment与共享区是否重叠,但之前的每个segment都计算了一次。这里是否在满足重叠条件后将stop设为true跳出循环,或者只检测最后一段segment都比原方法更好?
加载共享缓存最核心的步骤在mapSharedCache中:
static void mapSharedCache()
{
dyld3::SharedCacheOptions opts;
opts.cacheDirOverride = sSharedCacheOverrideDir;
opts.forcePrivate = (gLinkContext.sharedRegionMode == ImageLoader::kUsePrivateSharedRegion);
#if __x86_64__ && !TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
opts.useHaswell = sHaswell;
#else
opts.useHaswell = false;
#endif
opts.verbose = gLinkContext.verboseMapping;
loadDyldCache(opts, &sSharedCacheLoadInfo);
// update global state
if ( sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress != nullptr ) {
gLinkContext.dyldCache = sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress;
dyld::gProcessInfo->processDetachedFromSharedRegion = opts.forcePrivate;
dyld::gProcessInfo->sharedCacheSlide = sSharedCacheLoadInfo.slide;
dyld::gProcessInfo->sharedCacheBaseAddress = (unsigned long)sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress;
sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress->getUUID(dyld::gProcessInfo->sharedCacheUUID);
dyld3::kdebug_trace_dyld_image(DBG_DYLD_UUID_SHARED_CACHE_A, (const uuid_t *)&dyld::gProcessInfo->sharedCacheUUID[0], {0,0}, {{ 0, 0 }}, (const mach_header *)sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress);
}
//#if __IPHONE_OS_VERSION_MIN_REQUIRED && !TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// RAM disk booting does not have shared cache yet
// Don't make lack of a shared cache fatal in that case
// if ( sSharedCacheLoadInfo.loadAddress == nullptr ) {
// if ( sSharedCacheLoadInfo.errorMessage != nullptr )
// halt(sSharedCacheLoadInfo.errorMessage);
// else
// halt("error loading dyld shared cache");
// }
//#endif
}
bool loadDyldCache(const SharedCacheOptions& options, SharedCacheLoadInfo* results)
{
results->loadAddress = 0;
results->slide = 0;
results->errorMessage = nullptr;
#if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// simulator only supports mmap()ing cache privately into process
return mapCachePrivate(options, results);
#else
if ( options.forcePrivate ) {
// mmap cache into this process only
return mapCachePrivate(options, results);
}
else {
// fast path: when cache is already mapped into shared region
bool hasError = false;
if ( reuseExistingCache(options, results) ) {
hasError = (results->errorMessage != nullptr);
} else {
// slow path: this is first process to load cache
hasError = mapCacheSystemWide(options, results);
}
return hasError;
}
#endif
}
可以看到,加载缓存分三种情况:
1、仅加载到当前进程,通过mapCachePrivate加载并返回错误信息
2、已经加载过的,仅获取加载错误信息并返回
3、未加载过的,通过mapCacheSystemWide加载并返回错误信息
当options.forcePrivate为true或者模拟器运行时,仅加载到当前进程。而options.forcePrivate的值是这么定义的:
opts.forcePrivate = (gLinkContext.sharedRegionMode == ImageLoader::kUsePrivateSharedRegion)
enum SharedRegionMode { kUseSharedRegion, kUsePrivateSharedRegion, kDontUseSharedRegion, kSharedRegionIsSharedCache };
gLinkContext.sharedRegionMode就是之前检测共享区是否可用的标识值,可以看到默认值为kUseSharedRegion
- 实例化主程序
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
try {
...
CRSetCrashLogMessage(sLoadingCrashMessage);
// instantiate ImageLoader for main executable
// 实例化主程序
sMainExecutable = instantiateFromLoadedImage(mainExecutableMH, mainExecutableSlide, sExecPath);
gLinkContext.mainExecutable = sMainExecutable;
gLinkContext.mainExecutableCodeSigned = hasCodeSignatureLoadCommand(mainExecutableMH);
#if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// check main executable is not too new for this OS
// 检测主程序是否支持当前设备版本
{
if ( ! isSimulatorBinary((uint8_t*)mainExecutableMH, sExecPath) ) {
throwf("program was built for a platform that is not supported by this runtime");
}
uint32_t mainMinOS = sMainExecutable->minOSVersion();
// dyld is always built for the current OS, so we can get the current OS version
// from the load command in dyld itself.
uint32_t dyldMinOS = ImageLoaderMachO::minOSVersion((const mach_header*)&__dso_handle);
if ( mainMinOS > dyldMinOS ) {
#if TARGET_OS_WATCH
throwf("app was built for watchOS %d.%d which is newer than this simulator %d.%d",
mainMinOS >> 16, ((mainMinOS >> 8) & 0xFF),
dyldMinOS >> 16, ((dyldMinOS >> 8) & 0xFF));
#elif TARGET_OS_TV
throwf("app was built for tvOS %d.%d which is newer than this simulator %d.%d",
mainMinOS >> 16, ((mainMinOS >> 8) & 0xFF),
dyldMinOS >> 16, ((dyldMinOS >> 8) & 0xFF));
#else
throwf("app was built for iOS %d.%d which is newer than this simulator %d.%d",
mainMinOS >> 16, ((mainMinOS >> 8) & 0xFF),
dyldMinOS >> 16, ((dyldMinOS >> 8) & 0xFF));
#endif
}
}
}
#endif
...
// dyld_all_image_infos image list does not contain dyld
// add it as dyldPath field in dyld_all_image_infos
// for simulator, dyld_sim is in image list, need host dyld added
#if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// get path of host dyld from table of syscall vectors in host dyld
void* addressInDyld = gSyscallHelpers;
#else
// get path of dyld itself
void* addressInDyld = (void*)&__dso_handle;
#endif
// 获取dyld路径并与gProcessInfo->dyldPath对比
// 如果不同将获取到的路径复制给gProcessInfo->dyldPath
char dyldPathBuffer[MAXPATHLEN+1];
int len = proc_regionfilename(getpid(), (uint64_t)(long)addressInDyld, dyldPathBuffer, MAXPATHLEN);
if ( len > 0 ) {
dyldPathBuffer[len] = '\0'; // proc_regionfilename() does not zero terminate returned string
if ( strcmp(dyldPathBuffer, gProcessInfo->dyldPath) != 0 )
gProcessInfo->dyldPath = strdup(dyldPathBuffer);
}
...
}
这一步流程为:实例化主程序->检测主程序是否支持当前设备版本->检测进程信息中dyld路径是否与dyld路径相符,若不符则重新赋值
源码中有这样一段注释:
// dyld_all_image_infos image list does not contain dyld
// add it as dyldPath field in dyld_all_image_infos
// for simulator, dyld_sim is in image list, need host dyld added
就是说,dyld加载的image_infos并不包含dyld本身,他被放到dyld_all_image_infos的dyldPath字段中去了。而对于模拟器,dyld加载的image_infos是包含dyld_sim的。
dyld_all_image_infos是个结构体,同样分为32位及64位两个版本,分别对应dyld_all_image_infos_32与dyld_all_image_infos_64,由于获取dyld_all_image_infos需要用到一些未开源信息,这里为了方便,从侧面验证一下这条注释信息:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < _dyld_image_count(); ++i) {
NSLog(@"%s", _dyld_get_image_name(i));
}
}
可以看到,真机打印出的加载image中并没有dyld,第0个image是主程序。同样,模拟器对应打印的image也没有dyld,第0个image是dyld_sim,第一个image才是主程序
回到最核心的instantiateFromLoadedImage函数,实例化主程序:
// The kernel maps in main executable before dyld gets control. We need to
// make an ImageLoader* for the already mapped in main executable.
static ImageLoaderMachO* instantiateFromLoadedImage(const macho_header* mh, uintptr_t slide, const char* path)
{
// try mach-o loader
if ( isCompatibleMachO((const uint8_t*)mh, path) ) {
ImageLoader* image = ImageLoaderMachO::instantiateMainExecutable(mh, slide, path, gLinkContext);
addImage(image);
return (ImageLoaderMachO*)image;
}
throw "main executable not a known format";
}
从注释及源码可以看到,kernel在dyld之前已经加载了主程序Mach-O,dyld判断Mach-O的兼容性后,实例化成ImageLoader加载到内存中交给dyld管理
// create image for main executable
ImageLoader* ImageLoaderMachO::instantiateMainExecutable(const macho_header* mh, uintptr_t slide, const char* path, const LinkContext& context)
{
//dyld::log("ImageLoader=%ld, ImageLoaderMachO=%ld, ImageLoaderMachOClassic=%ld, ImageLoaderMachOCompressed=%ld\n",
// sizeof(ImageLoader), sizeof(ImageLoaderMachO), sizeof(ImageLoaderMachOClassic), sizeof(ImageLoaderMachOCompressed));
bool compressed;
unsigned int segCount;
unsigned int libCount;
const linkedit_data_command* codeSigCmd;
const encryption_info_command* encryptCmd;
sniffLoadCommands(mh, path, false, &compressed, &segCount, &libCount, context, &codeSigCmd, &encryptCmd);
// instantiate concrete class based on content of load commands
if ( compressed )
return ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::instantiateMainExecutable(mh, slide, path, segCount, libCount, context);
else
#if SUPPORT_CLASSIC_MACHO
return ImageLoaderMachOClassic::instantiateMainExecutable(mh, slide, path, segCount, libCount, context);
#else
throw "missing LC_DYLD_INFO load command";
#endif
}
instantiateMainExecutable内部调用sniffLoadCommands,这个函数会对主程序Mach-O进行一系列的校验。从函数名也可以看出,这里的校验并不包括对主程序Mach-O的解密操作,这个操作是由xnu完成的。
可以看到,当compressed为true时,通过ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::instantiateMainExecutable初始化,否则通过ImageLoaderMachOClassic::instantiateMainExecutable初始化。其实两者内部的逻辑相同,只是返回类型一个是ImageLoaderMachOCompressed一个是ImageLoaderMachOClassic而已。
以ImageLoaderMachOCompressed为例:
// create image for main executable
ImageLoaderMachOCompressed* ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::instantiateMainExecutable(const macho_header* mh, uintptr_t slide, const char* path,
unsigned int segCount, unsigned int libCount, const LinkContext& context)
{
// 初始化image
ImageLoaderMachOCompressed* image = ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::instantiateStart(mh, path, segCount, libCount);
// set slide for PIE programs
// 设置image偏移量
image->setSlide(slide);
// for PIE record end of program, to know where to start loading dylibs
if ( slide != 0 )
// 设置动态库起始地址
fgNextPIEDylibAddress = (uintptr_t)image->getEnd();
// 禁用段覆盖检测
image->disableCoverageCheck();
// 结束image上下文
image->instantiateFinish(context);
// 设置image加载状态为dyld_image_state_mapped
image->setMapped(context);
if ( context.verboseMapping ) {
dyld::log("dyld: Main executable mapped %s\n", path);
for(unsigned int i=0, e=image->segmentCount(); i < e; ++i) {
const char* name = image->segName(i);
if ( (strcmp(name, "__PAGEZERO") == 0) || (strcmp(name, "__UNIXSTACK") == 0) )
dyld::log("%18s at 0x%08lX->0x%08lX\n", name, image->segPreferredLoadAddress(i), image->segPreferredLoadAddress(i)+image->segSize(i));
else
dyld::log("%18s at 0x%08lX->0x%08lX\n", name, image->segActualLoadAddress(i), image->segActualEndAddress(i));
}
}
return image;
}
此处流程为:初始化image->设置image偏移量->设置动态库起始地址->禁用段覆盖检测->结束image上下文->设置image加载状态为dyld_image_state_mapped,并调用notifySingle进行处理
其中,结束image上下文内部做了:解析loadCmds、设置动态库连接信息、设置符号表相关信息等
- 加载插入的动态库
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
// load any inserted libraries
// 插入动态库
if ( sEnv.DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES != NULL ) {
for (const char* const* lib = sEnv.DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES; *lib != NULL; ++lib)
loadInsertedDylib(*lib);
}
// record count of inserted libraries so that a flat search will look at
// inserted libraries, then main, then others.
// 记录插入的动态库个数
sInsertedDylibCount = sAllImages.size()-1;
...
}
如果配置了DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES环境变量,通过loadInsertedDylib插入配置的动态库。对于越狱插件而言,其实就是添加DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES这个环境变量达到加载插件的目的
static void loadInsertedDylib(const char* path)
{
ImageLoader* image = NULL;
unsigned cacheIndex;
try {
LoadContext context;
context.useSearchPaths = false;
context.useFallbackPaths = false;
context.useLdLibraryPath = false;
context.implicitRPath = false;
context.matchByInstallName = false;
context.dontLoad = false;
context.mustBeBundle = false;
context.mustBeDylib = true;
context.canBePIE = false;
context.enforceIOSMac = true;
context.origin = NULL; // can't use @loader_path with DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES
context.rpath = NULL;
image = load(path, context, cacheIndex);
}
catch (const char* msg) {
if ( gLinkContext.allowInsertFailures )
dyld::log("dyld: warning: could not load inserted library '%s' into hardened process because %s\n", path, msg);
else
halt(dyld::mkstringf("could not load inserted library '%s' because %s\n", path, msg));
}
catch (...) {
halt(dyld::mkstringf("could not load inserted library '%s'\n", path));
}
}
内部构建context后调用load函数生成image
ImageLoader* load(const char* path, const LoadContext& context, unsigned& cacheIndex)
{
...
// try all path permutations and check against existing loaded images
ImageLoader* image = loadPhase0(path, orgPath, context, cacheIndex, NULL);
if ( image != NULL ) {
CRSetCrashLogMessage2(NULL);
return image;
}
// try all path permutations and try open() until first success
std::vector exceptions;
image = loadPhase0(path, orgPath, context, cacheIndex, &exceptions);
#if !TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
// support symlinks on disk to a path in dyld shared cache
if ( image == NULL)
image = loadPhase2cache(path, orgPath, context, cacheIndex, &exceptions);
#endif
CRSetCrashLogMessage2(NULL);
if ( image != NULL ) {
// leak in dyld during dlopen when using DYLD_ variables
for (std::vector::iterator it = exceptions.begin(); it != exceptions.end(); ++it) {
free((void*)(*it));
}
// if loaded image is not from cache, but original path is in cache
// set gSharedCacheOverridden flag to disable some ObjC optimizations
if ( !gSharedCacheOverridden && !image->inSharedCache() && image->isDylib() && cacheablePath(path) && inSharedCache(path) ) {
gSharedCacheOverridden = true;
}
return image;
}
...
}
可以看到,先调用了loadPhase0查找image,如果没找到再调用loadPhase2cache查找image。其实内部有一整套loadPhase0~loadPhase6的流程来查找及加载image,如果在共享缓存中找到则直接调用instantiateFromCache 实例化image,否则通过loadPhase5open打开文件并调用loadPhase6,内部通过instantiateFromFile实例化image,最后再调用checkandAddImage将image加载进内存
- 链接主程序
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
// link main executable
gLinkContext.linkingMainExecutable = true;
#if SUPPORT_ACCELERATE_TABLES
if ( mainExcutableAlreadyRebased ) {
// previous link() on main executable has already adjusted its internal pointers for ASLR
// work around that by rebasing by inverse amount
sMainExecutable->rebase(gLinkContext, -mainExecutableSlide);
}
#endif
// 链接主程序
link(sMainExecutable, sEnv.DYLD_BIND_AT_LAUNCH, true, ImageLoader::RPathChain(NULL, NULL), -1);
sMainExecutable->setNeverUnloadRecursive();
if ( sMainExecutable->forceFlat() ) {
gLinkContext.bindFlat = true;
gLinkContext.prebindUsage = ImageLoader::kUseNoPrebinding;
}
...
}
可以看到,主程序的链接是通过link这个函数完成的:
void ImageLoader::link(const LinkContext& context, bool forceLazysBound, bool preflightOnly, bool neverUnload, const RPathChain& loaderRPaths, const char* imagePath)
{
//dyld::log("ImageLoader::link(%s) refCount=%d, neverUnload=%d\n", imagePath, fDlopenReferenceCount, fNeverUnload);
// clear error strings
(*context.setErrorStrings)(0, NULL, NULL, NULL);
uint64_t t0 = mach_absolute_time();
// 递归加载主程序依赖的库
this->recursiveLoadLibraries(context, preflightOnly, loaderRPaths, imagePath);
context.notifyBatch(dyld_image_state_dependents_mapped, preflightOnly);
// we only do the loading step for preflights
if ( preflightOnly )
return;
uint64_t t1 = mach_absolute_time();
// 清空image层级关系
context.clearAllDepths();
// 递归更新image层级关系
this->recursiveUpdateDepth(context.imageCount());
__block uint64_t t2, t3, t4, t5;
{
dyld3::ScopedTimer(DBG_DYLD_TIMING_APPLY_FIXUPS, 0, 0, 0);
t2 = mach_absolute_time();
// 递归进行rebase
this->recursiveRebase(context);
context.notifyBatch(dyld_image_state_rebased, false);
t3 = mach_absolute_time();
if ( !context.linkingMainExecutable )
// 递归绑定符号表
this->recursiveBindWithAccounting(context, forceLazysBound, neverUnload);
t4 = mach_absolute_time();
if ( !context.linkingMainExecutable )
// 绑定弱符号表
this->weakBind(context);
t5 = mach_absolute_time();
}
if ( !context.linkingMainExecutable )
context.notifyBatch(dyld_image_state_bound, false);
uint64_t t6 = mach_absolute_time();
std::vector dofs;
// 递归获取dof信息
this->recursiveGetDOFSections(context, dofs);
// 注册dofs信息
context.registerDOFs(dofs);
uint64_t t7 = mach_absolute_time();
// interpose any dynamically loaded images
if ( !context.linkingMainExecutable && (fgInterposingTuples.size() != 0) ) {
dyld3::ScopedTimer timer(DBG_DYLD_TIMING_APPLY_INTERPOSING, 0, 0, 0);
// 递归应用插入的动态库
this->recursiveApplyInterposing(context);
}
// clear error strings
(*context.setErrorStrings)(0, NULL, NULL, NULL);
fgTotalLoadLibrariesTime += t1 - t0;
fgTotalRebaseTime += t3 - t2;
fgTotalBindTime += t4 - t3;
fgTotalWeakBindTime += t5 - t4;
fgTotalDOF += t7 - t6;
// done with initial dylib loads
fgNextPIEDylibAddress = 0;
}
内部加载动态库、rebase、绑定符号表、注册dofs信息等,同时还计算各步骤的耗时。如果想获取这些耗时,只需要在环境变量中添加DYLD_PRINT_STATISTICS就可以了,同样,这个环境变量也不需要value
- 链接插入的动态库
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
// link any inserted libraries
// do this after linking main executable so that any dylibs pulled in by inserted
// dylibs (e.g. libSystem) will not be in front of dylibs the program uses
if ( sInsertedDylibCount > 0 ) {
for(unsigned int i=0; i < sInsertedDylibCount; ++i) {
ImageLoader* image = sAllImages[i+1];
link(image, sEnv.DYLD_BIND_AT_LAUNCH, true, ImageLoader::RPathChain(NULL, NULL), -1);
image->setNeverUnloadRecursive();
}
// only INSERTED libraries can interpose
// register interposing info after all inserted libraries are bound so chaining works
for(unsigned int i=0; i < sInsertedDylibCount; ++i) {
ImageLoader* image = sAllImages[i+1];
image->registerInterposing(gLinkContext);
}
}
...
// apply interposing to initial set of images
for(int i=0; i < sImageRoots.size(); ++i) {
sImageRoots[i]->applyInterposing(gLinkContext);
}
ImageLoader::applyInterposingToDyldCache(gLinkContext);
gLinkContext.linkingMainExecutable = false;
// Bind and notify for the main executable now that interposing has been registered
uint64_t bindMainExecutableStartTime = mach_absolute_time();
sMainExecutable->recursiveBindWithAccounting(gLinkContext, sEnv.DYLD_BIND_AT_LAUNCH, true);
uint64_t bindMainExecutableEndTime = mach_absolute_time();
ImageLoaderMachO::fgTotalBindTime += bindMainExecutableEndTime - bindMainExecutableStartTime;
gLinkContext.notifyBatch(dyld_image_state_bound, false);
// Bind and notify for the inserted images now interposing has been registered
if ( sInsertedDylibCount > 0 ) {
for(unsigned int i=0; i < sInsertedDylibCount; ++i) {
ImageLoader* image = sAllImages[i+1];
image->recursiveBind(gLinkContext, sEnv.DYLD_BIND_AT_LAUNCH, true);
}
}
...
}
这里很简单,从加载的images中取出image,重复前面的link操作进行连接。registerInterposing内部会加载loadCmds并查找__interpose及__DATA段,读取段信息保存到fgInterposingTuples中,然后调用applyInterposing,内部调用recursiveApplyInterposing,通过这个函数调用到doInterpose,同样以ImageLoaderMachOCompressed为例:
void ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::doInterpose(const LinkContext& context)
{
if ( context.verboseInterposing )
dyld::log("dyld: interposing %lu tuples onto image: %s\n", fgInterposingTuples.size(), this->getPath());
// update prebound symbols
eachBind(context, ^(const LinkContext& ctx, ImageLoaderMachOCompressed* image,
uintptr_t addr, uint8_t type, const char* symbolName,
uint8_t symbolFlags, intptr_t addend, long libraryOrdinal,
ExtraBindData *extraBindData,
const char* msg, LastLookup* last, bool runResolver) {
return ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::interposeAt(ctx, image, addr, type, symbolName, symbolFlags,
addend, libraryOrdinal, extraBindData,
msg, last, runResolver);
});
eachLazyBind(context, ^(const LinkContext& ctx, ImageLoaderMachOCompressed* image,
uintptr_t addr, uint8_t type, const char* symbolName,
uint8_t symbolFlags, intptr_t addend, long libraryOrdinal,
ExtraBindData *extraBindData,
const char* msg, LastLookup* last, bool runResolver) {
return ImageLoaderMachOCompressed::interposeAt(ctx, image, addr, type, symbolName, symbolFlags,
addend, libraryOrdinal, extraBindData,
msg, last, runResolver);
});
}
这里eachBind与eachLazyBind都调用了interposeAt,interposeAt通过interposedAddress在上文提到的fgInterposingTuples中找到需要替换的符号地址进行替换
- 弱符号绑定
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
// do weak binding only after all inserted images linked
sMainExecutable->weakBind(gLinkContext);
...
}
void ImageLoader::weakBind(const LinkContext& context)
{
...
// get set of ImageLoaders that participate in coalecsing
ImageLoader* imagesNeedingCoalescing[fgImagesRequiringCoalescing];
unsigned imageIndexes[fgImagesRequiringCoalescing];
// 合并所有动态库的弱符号到列表中
int count = context.getCoalescedImages(imagesNeedingCoalescing, imageIndexes);
// count how many have not already had weakbinding done
int countNotYetWeakBound = 0;
int countOfImagesWithWeakDefinitionsNotInSharedCache = 0;
for(int i=0; i < count; ++i) {
if ( ! imagesNeedingCoalescing[i]->weakSymbolsBound(imageIndexes[i]) )
// 获取未进行绑定的弱符号的个数
++countNotYetWeakBound;
if ( ! imagesNeedingCoalescing[i]->inSharedCache() )
// 获取在共享缓存中已绑定的弱符号个数
++countOfImagesWithWeakDefinitionsNotInSharedCache;
}
// don't need to do any coalescing if only one image has overrides, or all have already been done
if ( (countOfImagesWithWeakDefinitionsNotInSharedCache > 0) && (countNotYetWeakBound > 0) ) {
// make symbol iterators for each
ImageLoader::CoalIterator iterators[count];
ImageLoader::CoalIterator* sortedIts[count];
for(int i=0; i < count; ++i) {
// 对需要绑定的弱符号排序
imagesNeedingCoalescing[i]->initializeCoalIterator(iterators[i], i, imageIndexes[i]);
sortedIts[i] = &iterators[i];
if ( context.verboseWeakBind )
dyld::log("dyld: weak bind load order %d/%d for %s\n", i, count, imagesNeedingCoalescing[i]->getIndexedPath(imageIndexes[i]));
}
// walk all symbols keeping iterators in sync by
// only ever incrementing the iterator with the lowest symbol
int doneCount = 0;
while ( doneCount != count ) {
//for(int i=0; i < count; ++i)
// dyld::log("sym[%d]=%s ", sortedIts[i]->loadOrder, sortedIts[i]->symbolName);
//dyld::log("\n");
// increment iterator with lowest symbol
// 计算弱符号偏移量及大小,绑定弱符号
if ( sortedIts[0]->image->incrementCoalIterator(*sortedIts[0]) )
++doneCount;
...
}
}
主要流程:合并所有动态库的弱符号到列表中->对需要绑定的弱符号排序->计算弱符号偏移量及大小,绑定弱符号
- 初始化主程序
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
CRSetCrashLogMessage("dyld: launch, running initializers");
#if SUPPORT_OLD_CRT_INITIALIZATION
// Old way is to run initializers via a callback from crt1.o
if ( ! gRunInitializersOldWay )
initializeMainExecutable();
#else
// run all initializers
initializeMainExecutable();
#endif
// notify any montoring proccesses that this process is about to enter main()
if (dyld3::kdebug_trace_dyld_enabled(DBG_DYLD_TIMING_LAUNCH_EXECUTABLE)) {
dyld3::kdebug_trace_dyld_duration_end(launchTraceID, DBG_DYLD_TIMING_LAUNCH_EXECUTABLE, 0, 0, 2);
}
notifyMonitoringDyldMain();
...
}
void initializeMainExecutable()
{
// record that we've reached this step
gLinkContext.startedInitializingMainExecutable = true;
// run initialzers for any inserted dylibs
ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList initializerTimes[allImagesCount()];
initializerTimes[0].count = 0;
const size_t rootCount = sImageRoots.size();
if ( rootCount > 1 ) {
for(size_t i=1; i < rootCount; ++i) {
// 初始化动态库
sImageRoots[i]->runInitializers(gLinkContext, initializerTimes[0]);
}
}
// run initializers for main executable and everything it brings up
// 初始化主程序
sMainExecutable->runInitializers(gLinkContext, initializerTimes[0]);
// register cxa_atexit() handler to run static terminators in all loaded images when this process exits
if ( gLibSystemHelpers != NULL )
(*gLibSystemHelpers->cxa_atexit)(&runAllStaticTerminators, NULL, NULL);
// dump info if requested
if ( sEnv.DYLD_PRINT_STATISTICS )
ImageLoader::printStatistics((unsigned int)allImagesCount(), initializerTimes[0]);
if ( sEnv.DYLD_PRINT_STATISTICS_DETAILS )
ImageLoaderMachO::printStatisticsDetails((unsigned int)allImagesCount(), initializerTimes[0]);
}
先初始化动态库,然后初始化主程序。上文提到的DYLD_PRINT_STATISTICS环境变量在这里也出现了,除此之外还有个detail版的环境变量DYLD_PRINT_STATISTICS_DETAILS
void ImageLoader::runInitializers(const LinkContext& context, InitializerTimingList& timingInfo)
{
uint64_t t1 = mach_absolute_time();
mach_port_t thisThread = mach_thread_self();
ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards up;
up.count = 1;
up.images[0] = this;
processInitializers(context, thisThread, timingInfo, up);
context.notifyBatch(dyld_image_state_initialized, false);
mach_port_deallocate(mach_task_self(), thisThread);
uint64_t t2 = mach_absolute_time();
fgTotalInitTime += (t2 - t1);
}
void ImageLoader::processInitializers(const LinkContext& context, mach_port_t thisThread,
InitializerTimingList& timingInfo, ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards& images)
{
uint32_t maxImageCount = context.imageCount()+2;
ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards upsBuffer[maxImageCount];
ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards& ups = upsBuffer[0];
ups.count = 0;
// Calling recursive init on all images in images list, building a new list of
// uninitialized upward dependencies.
for (uintptr_t i=0; i < images.count; ++i) {
images.images[i]->recursiveInitialization(context, thisThread, images.images[i]->getPath(), timingInfo, ups);
}
// If any upward dependencies remain, init them.
if ( ups.count > 0 )
processInitializers(context, thisThread, timingInfo, ups);
}
动态库和主程序的初始化是调用runInitializers,内部通过processInitializers调用recursiveInitialization递归初始化当前image锁依赖的库
void ImageLoader::recursiveInitialization(const LinkContext& context, mach_port_t this_thread, const char* pathToInitialize,
InitializerTimingList& timingInfo, UninitedUpwards& uninitUps)
{
recursive_lock lock_info(this_thread);
recursiveSpinLock(lock_info);
if ( fState < dyld_image_state_dependents_initialized-1 ) {
uint8_t oldState = fState;
// break cycles
fState = dyld_image_state_dependents_initialized-1;
try {
// initialize lower level libraries first
for(unsigned int i=0; i < libraryCount(); ++i) {
ImageLoader* dependentImage = libImage(i);
if ( dependentImage != NULL ) {
// don't try to initialize stuff "above" me yet
if ( libIsUpward(i) ) {
uninitUps.images[uninitUps.count] = dependentImage;
uninitUps.count++;
}
else if ( dependentImage->fDepth >= fDepth ) {
dependentImage->recursiveInitialization(context, this_thread, libPath(i), timingInfo, uninitUps);
}
}
}
// record termination order
if ( this->needsTermination() )
context.terminationRecorder(this);
// let objc know we are about to initialize this image
uint64_t t1 = mach_absolute_time();
fState = dyld_image_state_dependents_initialized;
oldState = fState;
context.notifySingle(dyld_image_state_dependents_initialized, this, &timingInfo);
// initialize this image
bool hasInitializers = this->doInitialization(context);
// let anyone know we finished initializing this image
fState = dyld_image_state_initialized;
oldState = fState;
context.notifySingle(dyld_image_state_initialized, this, NULL);
if ( hasInitializers ) {
uint64_t t2 = mach_absolute_time();
timingInfo.addTime(this->getShortName(), t2-t1);
}
}
catch (const char* msg) {
// this image is not initialized
fState = oldState;
recursiveSpinUnLock();
throw;
}
}
recursiveSpinUnLock();
}
递归初始化很简单没啥好说的,注意内部有个调用context.notifySingle(dyld_image_state_initialized, this, NULL),其实每次image状态改变都会调用notifySingle这个方法:
static void notifySingle(dyld_image_states state, const ImageLoader* image, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList* timingInfo)
{
//dyld::log("notifySingle(state=%d, image=%s)\n", state, image->getPath());
std::vector* handlers = stateToHandlers(state, sSingleHandlers);
if ( handlers != NULL ) {
dyld_image_info info;
info.imageLoadAddress = image->machHeader();
info.imageFilePath = image->getRealPath();
info.imageFileModDate = image->lastModified();
for (std::vector::iterator it = handlers->begin(); it != handlers->end(); ++it) {
const char* result = (*it)(state, 1, &info);
if ( (result != NULL) && (state == dyld_image_state_mapped) ) {
//fprintf(stderr, " image rejected by handler=%p\n", *it);
// make copy of thrown string so that later catch clauses can free it
const char* str = strdup(result);
throw str;
}
}
}
if ( state == dyld_image_state_mapped ) {
// Save load addr + UUID for images from outside the shared cache
if ( !image->inSharedCache() ) {
dyld_uuid_info info;
if ( image->getUUID(info.imageUUID) ) {
info.imageLoadAddress = image->machHeader();
addNonSharedCacheImageUUID(info);
}
}
}
if ( (state == dyld_image_state_dependents_initialized) && (sNotifyObjCInit != NULL) && image->notifyObjC() ) {
uint64_t t0 = mach_absolute_time();
dyld3::ScopedTimer timer(DBG_DYLD_TIMING_OBJC_INIT, (uint64_t)image->machHeader(), 0, 0);
(*sNotifyObjCInit)(image->getRealPath(), image->machHeader());
uint64_t t1 = mach_absolute_time();
uint64_t t2 = mach_absolute_time();
uint64_t timeInObjC = t1-t0;
uint64_t emptyTime = (t2-t1)*100;
if ( (timeInObjC > emptyTime) && (timingInfo != NULL) ) {
timingInfo->addTime(image->getShortName(), timeInObjC);
}
}
// mach message csdlc about dynamically unloaded images
if ( image->addFuncNotified() && (state == dyld_image_state_terminated) ) {
notifyKernel(*image, false);
const struct mach_header* loadAddress[] = { image->machHeader() };
const char* loadPath[] = { image->getPath() };
notifyMonitoringDyld(true, 1, loadAddress, loadPath);
}
}
可见,当state == dyld_image_state_mapped时,将image对应的UUID存起来,当state == dyld_image_state_dependents_initialized并且有sNotifyObjCInit回调时调用sNotifyObjCInit函数。
搜索回调函数赋值入口:
void registerObjCNotifiers(_dyld_objc_notify_mapped mapped, _dyld_objc_notify_init init, _dyld_objc_notify_unmapped unmapped)
{
// record functions to call
sNotifyObjCMapped = mapped;
sNotifyObjCInit = init;
sNotifyObjCUnmapped = unmapped;
...
}
void _dyld_objc_notify_register(_dyld_objc_notify_mapped mapped,
_dyld_objc_notify_init init,
_dyld_objc_notify_unmapped unmapped)
{
dyld::registerObjCNotifiers(mapped, init, unmapped);
}
发现是通过_dyld_objc_notify_register这个函数注册回调的,回到文章开头符号断点[NSObject load]截图中的堆栈:
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 1.2
* frame #0: 0x000000010944f3b1 libobjc.A.dylib`+[NSObject load]
frame #1: 0x000000010943d317 libobjc.A.dylib`call_load_methods + 691
frame #2: 0x000000010943e814 libobjc.A.dylib`load_images + 77
frame #3: 0x0000000108b73b97 dyld_sim`dyld::registerObjCNotifiers(void (*)(unsigned int, char const* const*, mach_header const* const*), void (*)(char const*, mach_header const*), void (*)(char const*, mach_header const*)) + 260
frame #4: 0x000000010b779bf3 libdyld.dylib`_dyld_objc_notify_register + 113
frame #5: 0x000000010944ca12 libobjc.A.dylib`_objc_init + 115
frame #6: 0x000000010b7015c0 libdispatch.dylib`_os_object_init + 13
frame #7: 0x000000010b70f4e5 libdispatch.dylib`libdispatch_init + 300
frame #8: 0x0000000109e05a78 libSystem.B.dylib`libSystem_initializer + 164
frame #9: 0x0000000108b82b96 dyld_sim`ImageLoaderMachO::doModInitFunctions(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&) + 506
frame #10: 0x0000000108b82d9c dyld_sim`ImageLoaderMachO::doInitialization(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&) + 40
frame #11: 0x0000000108b7e3fc dyld_sim`ImageLoader::recursiveInitialization(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, unsigned int, char const*, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&, ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards&) + 324
frame #12: 0x0000000108b7e392 dyld_sim`ImageLoader::recursiveInitialization(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, unsigned int, char const*, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&, ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards&) + 218
frame #13: 0x0000000108b7d5d3 dyld_sim`ImageLoader::processInitializers(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, unsigned int, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&, ImageLoader::UninitedUpwards&) + 133
frame #14: 0x0000000108b7d665 dyld_sim`ImageLoader::runInitializers(ImageLoader::LinkContext const&, ImageLoader::InitializerTimingList&) + 73
frame #15: 0x0000000108b71333 dyld_sim`dyld::initializeMainExecutable() + 129
frame #16: 0x0000000108b75434 dyld_sim`dyld::_main(macho_header const*, unsigned long, int, char const**, char const**, char const**, unsigned long*) + 4384
frame #17: 0x0000000108b70630 dyld_sim`start_sim + 136
frame #18: 0x00000001155c1234 dyld`dyld::useSimulatorDyld(int, macho_header const*, char const*, int, char const**, char const**, char const**, unsigned long*, unsigned long*) + 2238
frame #19: 0x00000001155bf0ce dyld`dyld::_main(macho_header const*, unsigned long, int, char const**, char const**, char const**, unsigned long*) + 522
frame #20: 0x00000001155ba503 dyld`dyldbootstrap::start(macho_header const*, int, char const**, long, macho_header const*, unsigned long*) + 1167
frame #21: 0x00000001155ba036 dyld`_dyld_start + 54
可以看到,_dyld_objc_notify_register是在初始化libobjc.A.dylib这个动态库时调用的,然后_objc_init内部调用了load_images,进而调用call_load_methods,从而调用各个类中的load方法,感兴趣可以下载源码查看具体流程
notifySingle调用完毕后,开始真正初始化工作doInitialization:
bool ImageLoaderMachO::doInitialization(const LinkContext& context)
{
CRSetCrashLogMessage2(this->getPath());
// mach-o has -init and static initializers
doImageInit(context);
doModInitFunctions(context);
CRSetCrashLogMessage2(NULL);
return (fHasDashInit || fHasInitializers);
}
doImageInit执行LC_ROUTINES_COMMAND segment中保存的函数,doModInitFunctions执行__DATA,__mod_init_func section中保存的函数。这个section中保存的是C++的构造函数及带有attribute((constructor))的C函数,简单验证一下:
class Test {
public:
Test();
};
Test::Test(){
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
}
Test test;
__attribute__((constructor)) void testConstructor() {
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
}
同样,通过MachOView也可以看到:
显然,__mod_init_func中的函数在类对应的load方法之后调用。
- 查找主程序入口函数指针并返回
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue)
{
...
// find entry point for main executable
result = (uintptr_t)sMainExecutable->getEntryFromLC_MAIN();
if ( result != 0 ) {
// main executable uses LC_MAIN, we need to use helper in libdyld to call into main()
if ( (gLibSystemHelpers != NULL) && (gLibSystemHelpers->version >= 9) )
*startGlue = (uintptr_t)gLibSystemHelpers->startGlueToCallExit;
else
halt("libdyld.dylib support not present for LC_MAIN");
}
else {
// main executable uses LC_UNIXTHREAD, dyld needs to let "start" in program set up for main()
result = (uintptr_t)sMainExecutable->getEntryFromLC_UNIXTHREAD();
*startGlue = 0;
}
#if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls)
// start() calls the result pointer as a function pointer so we need to sign it.
result = (uintptr_t)__builtin_ptrauth_sign_unauthenticated((void*)result, 0, 0);
#endif
}
catch(const char* message) {
syncAllImages();
halt(message);
}
catch(...) {
dyld::log("dyld: launch failed\n");
}
CRSetCrashLogMessage("dyld2 mode");
if (sSkipMain) {
if (dyld3::kdebug_trace_dyld_enabled(DBG_DYLD_TIMING_LAUNCH_EXECUTABLE)) {
dyld3::kdebug_trace_dyld_duration_end(launchTraceID, DBG_DYLD_TIMING_LAUNCH_EXECUTABLE, 0, 0, 2);
}
result = (uintptr_t)&fake_main;
*startGlue = (uintptr_t)gLibSystemHelpers->startGlueToCallExit;
}
return result;
}
此处两步走:调用getEntryFromLC_MAIN获取入口,如果没有入口则调用getEntryFromLC_UNIXTHREAD获取入口。这个入口就是主程序main函数的地址
void* ImageLoaderMachO::getEntryFromLC_MAIN() const
{
const uint32_t cmd_count = ((macho_header*)fMachOData)->ncmds;
const struct load_command* const cmds = (struct load_command*)&fMachOData[sizeof(macho_header)];
const struct load_command* cmd = cmds;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cmd_count; ++i) {
if ( cmd->cmd == LC_MAIN ) {
entry_point_command* mainCmd = (entry_point_command*)cmd;
void* entry = (void*)(mainCmd->entryoff + (char*)fMachOData);
// verify entry point is in image
if ( this->containsAddress(entry) )
return entry;
else
throw "LC_MAIN entryoff is out of range";
}
cmd = (const struct load_command*)(((char*)cmd)+cmd->cmdsize);
}
return NULL;
}
void* ImageLoaderMachO::getEntryFromLC_UNIXTHREAD() const
{
const uint32_t cmd_count = ((macho_header*)fMachOData)->ncmds;
const struct load_command* const cmds = (struct load_command*)&fMachOData[sizeof(macho_header)];
const struct load_command* cmd = cmds;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cmd_count; ++i) {
if ( cmd->cmd == LC_UNIXTHREAD ) {
#if __i386__
const i386_thread_state_t* registers = (i386_thread_state_t*)(((char*)cmd) + 16);
void* entry = (void*)(registers->eip + fSlide);
// verify entry point is in image
if ( this->containsAddress(entry) )
return entry;
#elif __x86_64__
const x86_thread_state64_t* registers = (x86_thread_state64_t*)(((char*)cmd) + 16);
void* entry = (void*)(registers->rip + fSlide);
// verify entry point is in image
if ( this->containsAddress(entry) )
return entry;
#elif __arm64__ && !__arm64e__
// temp support until is fixed
const uint64_t* regs64 = (uint64_t*)(((char*)cmd) + 16);
void* entry = (void*)(regs64[32] + fSlide); // arm_thread_state64_t.__pc
// verify entry point is in image
if ( this->containsAddress(entry) )
return entry;
#endif
}
cmd = (const struct load_command*)(((char*)cmd)+cmd->cmdsize);
}
throw "no valid entry point";
}
可以看到,入口是在load_command的LC_MAIN或者LC_UNIXTHREAD中
受能力所限,可能存在部分理解偏差,欢迎指正。
Have fun!