python之命令行可以做的事儿
-
前言
说起python,大家都知道可以做很多有趣的事儿。知乎、CSDN上很多大牛做过很多或高大上或实用的事儿。参见这篇文章Python趣味代码整合之提升学生编程兴趣,
另外,我发现命令行也可以做很多事。以下是我的一些想法,欢迎大家补充!
-
环境配置与模块安装
- 运行环境:Python3.6+cmd命令行
- 依赖模块:requests,bs4,numpy,PIL,webbrowser,subprocess
模块具体安装方法参见网上教程
-
实现功能
- 查询天气
早上起来,想看今天的天气,打开电脑,百度搜索地点,简直太麻烦。不妨命令行输入指令快速获取。(请忽略手机查看等其他更快捷方式,虽然相比较而言前者有些不足,但,存在即有意义,命令行也可以做很多事。)
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#获取www.tianqi.com的天气,参数:地名拼音
def data_of_tianqi(addr):
response = requests.get("https://www.tianqi.com/"+addr+"/")
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
tag_dd = soup.find_all(name='dd')
tag_span = soup.find_all(name='span')[0]
temp = str(soup.find_all(name='b')[0])[3:-4]#温度
city_html = BeautifulSoup(str(tag_dd[0]), 'html.parser')
city = str(city_html.find_all(name='h2'))[5:-6]#城市
if str(tag_dd[1])[41:43]=='')
weather = weather_and_temp[0]#天气
temp = str(soup.find_all(name='b')[0])[3:-4]#实时温度
temp_from_to = weather_and_temp[1]#温度范围
shidu = str(tag_dd[3]).replace("","").replace("","").split("")[1]#湿度
fengxaing = str(tag_dd[3]).replace("","").replace("","").split("")[2]#风向
ziwaixian = str(tag_dd[3]).replace("","").replace("","").split("")[3]#紫外线
other_info = str(tag_dd[4])[57:-12].replace('','
').replace('
','
').split('
')#空气质量、PM、日出、日落
print('城市:'+city)
print('时间:'+time)
print('天气:'+weather)
print('实时温度:'+temp+' '+'温度范围:'+temp_from_to)
print(shidu+' '+fengxaing+' '+ziwaixian)
print(other_info[0]+' '+other_info[1])
print(other_info[2]+' '+other_info[3])代码参考了一些网上资料(表示感谢),再做了相应修改,展示更美观一些。
在命令行输入python start.py weather chengdu,便得到的成都天气信息:
- .浏览器操作
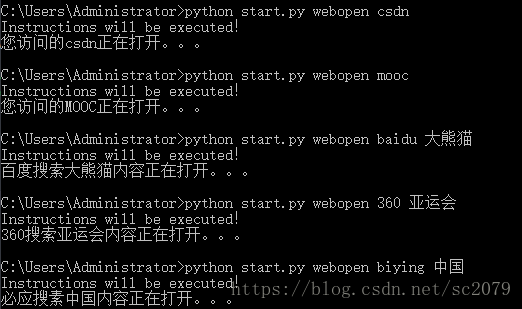
想在命令行百度搜索、360搜索、必应搜索?想快速打开指定网页?没关系,这些都可以实现!
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Aug 7 11:06:53 2018
快速搜索(百度、360、必应)&快速打开常用网站
csdn 百度 MOOC 新华社
@author: Administrator
"""
import webbrowser
def search(word):
if word[0]=='baidu':
print('百度搜索'+word[1]+'内容正在打开。。。')
webbrowser.open('https://www.baidu.com/s?wd='+word[1])
if word[0]=='360':
print('360搜索'+word[1]+'内容正在打开。。。')
webbrowser.open('https://www.so.com/s?q='+word[1])
if word[0]=='biying':
print('必应搜索'+word[1]+'内容正在打开。。。')
webbrowser.open('http://global.bing.com/search?q='+word[1])
def webopen(word):
name=['csdn','百度','MOOC','新华社']
words=['csdn','baidu','mooc','xhs']
if type(word)==list:
search(word)
elif word not in words:
print('访问失败!')
else:
for i in range(len(words)):
if word==words[i]:
print('您访问的'+name[i]+'正在打开。。。')
break
if i==0:
webbrowser.open('https://download.csdn.net/my')
elif i==1:
webbrowser.open('https://www.baidu.com/')
elif i==2:
webbrowser.open('http://www.icourse163.org/home.htm?userId=7816710#/home/course')
elif i==3:
webbrowser.open('http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/home.htm')
由于一些隐私原因,我删除了部分我常去的一些网站,你当然也可以按照格式添加属于你的网站访问快捷方式。
- 启动应用程序
同样,用subprocess模块可以打开计算机上的应用程序。虽然现在电脑软件大多有快捷方式,但是用命令行打开其实也挺不错的。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Aug 8 10:59:15 2018
命令行启动应用程序
@author: Administrator
"""
import subprocess
def setup(word):
words=['excel','word','ppt','visio','pycharm']
if word not in words:
print('打开失败!')
else:
for i in range(len(words)):
if word==words[i]:
print(word+'应用程序正在打开中。。。')
break
if i==0:
subprocess.Popen('C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office16\\EXCEL.exe')
if i==1:
subprocess.Popen('C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office16\\WINWORD.exe')
if i==2:
subprocess.Popen('C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office16\\POWERPNT.exe')
if i==3:
subprocess.Popen('C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office16\\VISIO.exe')
if i==4:
subprocess.Popen('C:\\Program Files\\JetBrains\\PyCharm Community Edition 2017.2.4\\bin\\pycharm64')
- 图片转字符
参考《python 极客项目编程》这本书有关于ASCII文本图形的代码,并做相应修改。如下:
"""
ascii.py
A python program that convert images to ASCII art.
Author: Mahesh Venkitachalam
"""
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
# gray scale level values from:
# http://paulbourke.net/dataformats/asciiart/
# 70 levels of gray
gscale1 = "$@B%8&WM#*oahkbdpqwmZO0QLCJUYXzcvunxrjft/\|()1{}[]?-_+~<>i!lI;:,\"^`'. "
# 10 levels of gray
gscale2 = '@%#*+=-:. '
def getAverageL(image):
"""
Given PIL Image, return average value of grayscale value
"""
# get image as numpy array
im = np.array(image)
# get shape
w,h = im.shape
# get average
return np.average(im.reshape(w*h))
def covertImageToAscii(fileName, cols, scale, moreLevels):
"""
Given Image and dims (rows, cols) returns an m*n list of Images
"""
# declare globals
global gscale1, gscale2
# open image and convert to grayscale
image = Image.open(fileName).convert('L')
# store dimensions
W, H = image.size[0], image.size[1]
print("input image dims: %d x %d" % (W, H))
# compute width of tile
cols=int(cols)
w = W/cols
# compute tile height based on aspect ratio and scale
h = w/scale
# compute number of rows
rows = int(H/h)
print("cols: %d, rows: %d" % (cols, rows))
print("tile dims: %d x %d" % (w, h))
# check if image size is too small
if cols > W or rows > H:
print("Image too small for specified cols!")
exit(0)
# ascii image is a list of character strings
aimg = []
# generate list of dimensions
for j in range(rows):
y1 = int(j*h)
y2 = int((j+1)*h)
# correct last tile
if j == rows-1:
y2 = H
# append an empty string
aimg.append("")
for i in range(cols):
# crop image to tile
x1 = int(i*w)
x2 = int((i+1)*w)
# correct last tile
if i == cols-1:
x2 = W
# crop image to extract tile
img = image.crop((x1, y1, x2, y2))
# get average luminance
avg = int(getAverageL(img))
# look up ascii char
if moreLevels:
gsval = gscale1[int((avg*69)/255)]
else:
gsval = gscale2[int((avg*9)/255)]
# append ascii char to string
aimg[j] += gsval
# return txt image
return aimg
# main() function
def ascii_write(word):
word=['D:\\pycodes\\命令行快速访问\\asc_data\\'+word[0],word[1]]
imgFile = word[0]
# set output file
outFile = 'D:\\pycodes\\命令行快速访问\\asc_data\\out.txt'
# set scale default as 0.43 which suits a Courier font
scale = 0.43
# set cols
cols = word[1]
print('generating ASCII art...')
# convert image to ascii txt
aimg = covertImageToAscii(imgFile, cols, scale,0)
# open file
f = open(outFile, 'w')
# write to file
for row in aimg:
f.write(row + '\n')
# cleanup
f.close()
print("ASCII art written to %s" % outFile)
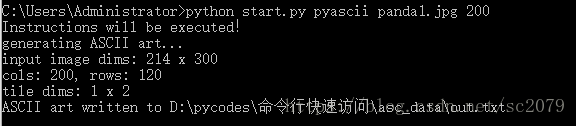
命令行上输入python start.py pyascii panda1.jpg 200,回车,便得到由字符拼接的萌萌的大熊猫宝宝啦。由于截图大小有限,这里仅放上它炯炯有神的大眼睛。
萌死我啦!注意:图片名后的数字代表像素,数字越大,图片细节越清晰,但txt文档打开一个界面看不完(必须滑动)
-
主程序
你可能会奇怪,为什么命令行执行的都是start.py文件,难道不可以直接运行各个子程序吗?本来是可以的,但是为了追求简洁统一,避免C:\Users\Administrator\目录下放到py文件过多,便写了个主程序start.py(必须放于C:\Users\Administrator\目录下!)。
Created on Mon Aug 6 21:05:09 2018
@author: Administrator
命令行快速查询、启动、运行
"""
import sys
sys.path.append('D:\\pycodes\\命令行快速访问')
import weather
import pyascii
import webopen
import setup
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
sys.exit()
code= ' '.join(sys.argv[1:2])
word= ' '.join(sys.argv[2:3])
if len(sys.argv)>3:
t=' '.join(sys.argv[3:4])
word=[word,t]
codes=['weather','pyascii','webopen','setup']
if code not in codes:
print('Wrong instructions!')
else:
for i in range(len(codes)):
if code==codes[i]:
print('Instructions will be executed!')
break
if i==0:
weather.data_of_tianqi(word)
elif i==1:
pyascii.ascii_write(word)
elif i==2:
webopen.webopen(word)
elif i==3:
setup.setup(word)Github传送门:https://github.com/SCHaoZhang/python/tree/master/python_cmd
如果你还有其他的好点子,请分享给我哈!如果文中有不足之处,请私聊哈!