PyTorch(二)——搭建和自定义网络
目录连接
(1) 数据处理
(2) 搭建和自定义网络
(3) 使用训练好的模型测试自己图片
(4) 视频数据的处理
(5) PyTorch源码修改之增加ConvLSTM层
(6) 梯度反向传递(BackPropogate)的理解
(7) 模型的训练和测试、保存和加载
(8) pyTorch-To-Caffe
(总) PyTorch遇到令人迷人的BUG
PyTorch的学习和使用(二)
最近刚好在看一篇与Siamese network有关的论文,在PyTorch中没有example,caffe中有,刚好使用PyTorch实现。(PS:图片单独打开更清晰)
主要步骤为:
- 数据预处理
- 模型搭建
- 模型训练
数据预处理
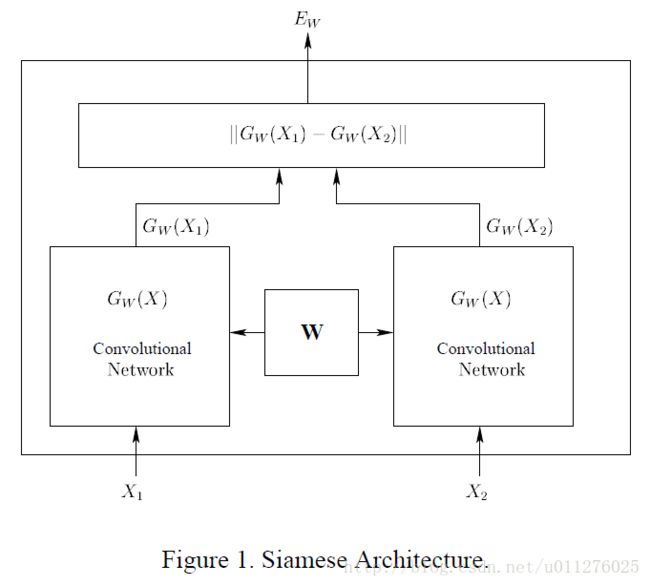
Siamese的网络结构如下:
通过输入两张图片X1和X2,经过权重共享的CNN,各自得到一个输出特征向量 G w ( X 1 ) G_w(X_1) Gw(X1)和 G w ( X 2 ) G_w(X_2) Gw(X2),然后使用特征向量的距离度量两张图片的相似度。
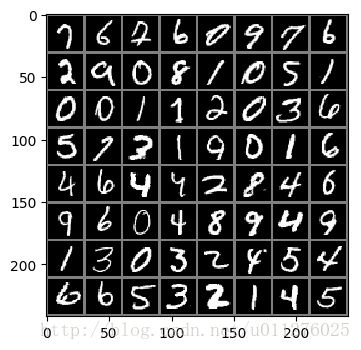
我们还是使用手写数据集MINIST作为测试(主要有mnist的列子可以参考),网络输入的图片为成对的,因此在构造训练的batch时需要定义2张图片,其标签为两张图片是否为同一个数字。根据上篇文章讲的,重新定义transforms.Compose()和torchvision.datasets.SIAMESE()。
由于对数据的读取和处理都没有改变,因此不用修改Compose()。torchvision.datasets.SIAMESE()则把相邻的图片捆绑在一起,作为一对输入图片,如果相同的数字,则标签为1,不同则为0。
如下所示:
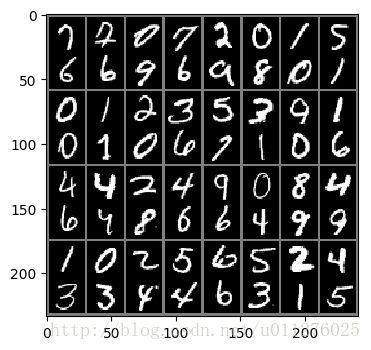
如图所示每个batch中有2个图片,但是在训练中我们希望每个相邻的batch为一对图片,因此做如下处理:images.view(batch*2, 1, 28, 28)得到如下结果:
网络的搭建
Siamese的网络定义与LeNet模型基本一致,唯一不同的是把生成10个数字类别概率的顶层替换为生成二维向量的特征层,最后损失函数换为对比损失函数(Contrastive_loss)(很忧伤,该损失函数在PyTorch中暂时没有实现)。因此需要自己实现Contrastive_loss层。
Contrastive_loss函数定义
**首先,**理解caffe中Siamese网络如和实现的。contrastive_loss_layer定义如下:
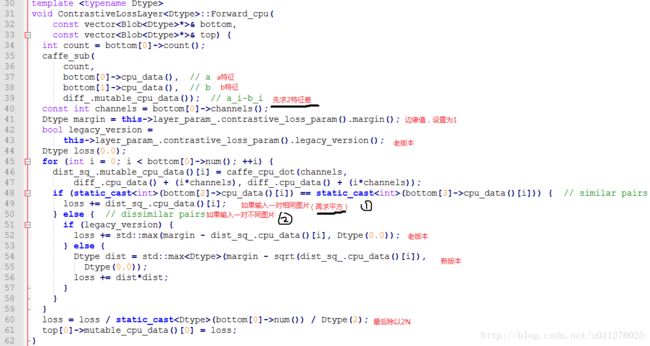
其**forward()**实现如下:
上述代码中,bottom[0],bottom[1]存的2张图片的特征,bottom[2],bottom[3]存的2张图片的标签,然后根据其是否相同进行如下计算:
l o s s = { ∣ ∣ a i − b i ∣ ∣ 2 2 , if a == b m a x { 0 , m − ∣ ∣ a i − b i ∣ ∣ 2 2 } 2 , if a != b loss = \begin{cases} ||a_i - b_i||_2^2, & \text{if a == b} \\[2ex] max \{ 0, m - ||a_i - b_i||_2^2\}^2, & \text{if a != b} \end{cases} loss=⎩⎨⎧∣∣ai−bi∣∣22,max{0,m−∣∣ai−bi∣∣22}2,if a == bif a != b
L o s s = 1 2 N ⋅ l o s s Loss = \frac{1}{2N} \cdot loss Loss=2N1⋅loss
在论文Learning a Similarity Metric Discriminatively, with Application to Face Verification中,其定义的损失函数为:
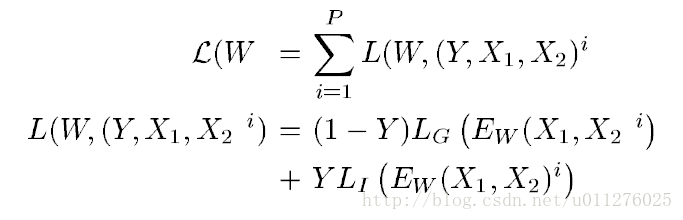
要求满足:

则当 E W ( X 1 , X 2 ′ ) − > 0 E_W(X_1,X_2^{'})->0 EW(X1,X2′)−>0时, E W ( X 1 , X 2 ) − > m E_W(X_1,X_2)->m EW(X1,X2)−>m
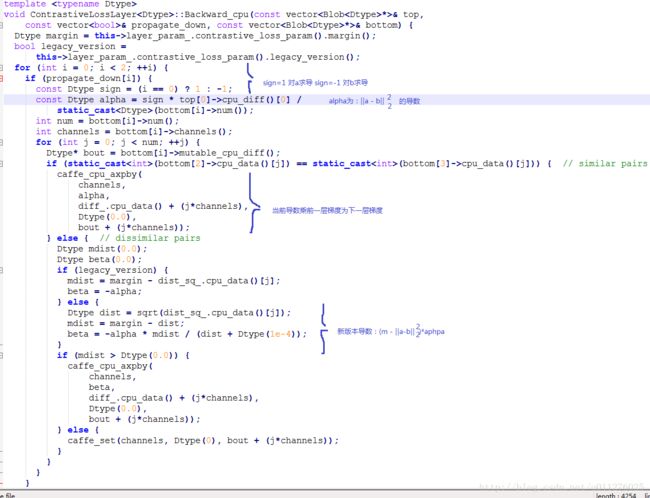
1 2 l o s s \frac{1}{2}loss 21loss的导数为
∂ l o s s ∂ a = { ∑ ( a − b ) , if a == b ( m − ∣ ∣ a i − b i ∣ ∣ 2 2 ) ⋅ ∑ ( a − b ) , if a != b \frac{\partial loss}{\partial a}= \begin{cases} \sum(a-b), & \text{if a == b} \\[2ex] (m - ||a_i - b_i||_2^2)\cdot \sum(a-b), & \text{if a != b} \end{cases} ∂a∂loss=⎩⎨⎧∑(a−b),(m−∣∣ai−bi∣∣22)⋅∑(a−b),if a == bif a != b
根据导数计算,实现bankward()。当前导数乘后一层梯度为当前梯度。
CosineEmbeddingLoss实现
然后,在PyTorch中实现。在PyTorch中有实现CosineEmbeddingLoss损失函数,其定义为:
l o s s ( x , y ) = { 1 − c o s ( x 1 , x 2 ) , if y == 1 m a x { 0 , c o s ( x 1 , x 2 ) } , if y == -1 loss(x, y) = \begin{cases} 1 - cos(x1, x2), & \text{if y == 1} \\[2ex] max \{ 0, cos(x1, x2) \}, & \text{if y == -1} \end{cases} loss(x,y)=⎩⎨⎧1−cos(x1,x2),max{0,cos(x1,x2)},if y == 1if y == -1
该函数和我们需要实现的Contrastive_loss损失函数类似,我们先分析CosineEmbeddingLoss函数的实现,任何构造自己的Contrastive_loss损失函数。
就如同PyTorch文档中所讲的,如果实现扩展 torch.autograd,需要实现3个方法:
- init (optional), 用于传递一些参数,比如margin, 和size_average.。
- forward(), 前向传播,就是进行计算。
- backward(), 反向传播,就是求导计算梯度。
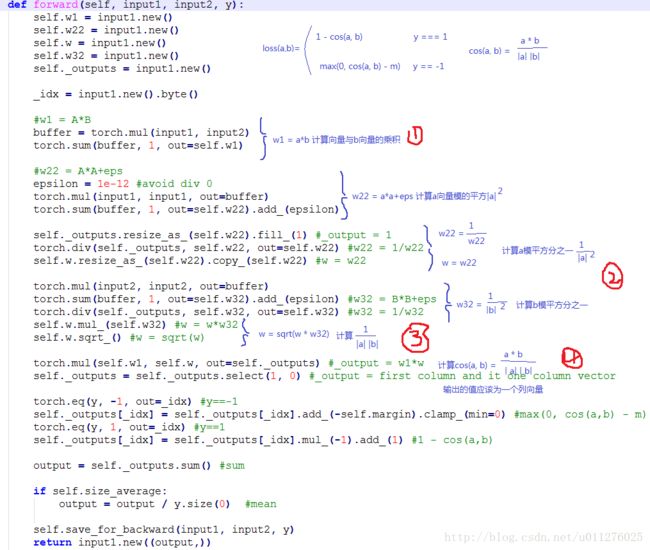
其**forward()**实现如下:
实现CosineEmbeddingLoss函数主要就是完成cos(a, b)的计算。 c o s ( a , b ) = a ∗ b ∣ a ∣ ∣ b ∣ cos(a, b) = \frac{a*b}{|a| |b|} cos(a,b)=∣a∣∣b∣a∗b.
代码主要可以分为4部分,如下图所示:
- 第一部分计算 a a a向量和 b b b向量的乘积 a ∗ b a*b a∗b
- 第二部分计算 a a a向量和 b b b向量模平方分之1, 1 ∣ a ∣ 2 \frac{1}{|a|^2} ∣a∣21和 1 ∣ b ∣ 2 \frac{1}{|b|^2} ∣b∣21
- 第三部分计算 a a a向量乘 b b b向量模分之1, 1 ∣ a ∣ ∣ b ∣ \frac{1}{|a| |b|} ∣a∣∣b∣1
- 第四部分计算 c o s ( a , b ) = a ∗ b ∣ a ∣ ∣ b ∣ cos(a, b) = \frac{a*b}{|a| |b|} cos(a,b)=∣a∣∣b∣a∗b
**backward()**就是实现CosineEmbeddingLoss的导数,主要计算 c o s ( a , b ) = a ∗ b ∣ a ∣ ∣ b ∣ cos(a, b) = \frac{a*b}{|a| |b|} cos(a,b)=∣a∣∣b∣a∗b的导数。根据 ( u v ) ′ = u ′ v − u v ′ v 2 (\frac{u}{v})'=\frac{u'v - uv'}{v^2} (vu)′=v2u′v−uv′得:
KaTeX parse error: No such environment: align at position 8: \begin{̲a̲l̲i̲g̲n̲}̲ cos(a, b)' & =…
由于:
( a ∗ b ) ′ = [ ( a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n ) ∗ b ] ′ = b (a*b)'=[(a_1, a_2, ..., a_n)*b]'=b (a∗b)′=[(a1,a2,...,an)∗b]′=b
∣ a ∣ ′ = [ ( a 1 2 , a 2 2 , . . . , a n 2 ) 1 / 2 ] ′ = 1 2 2 ( a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n ) ( a 1 2 , a 2 2 , . . . , a n 2 ) 1 / 2 = a ∣ a ∣ |a|'=[(a_1^2, a_2^2, ..., a_n^2)^{1/2}]'=\frac{1}{2} \frac{2(a_1, a_2, ..., a_n)}{(a_1^2, a_2^2, ..., a_n^2)^{1/2}} = \frac{a}{|a|} ∣a∣′=[(a12,a22,...,an2)1/2]′=21(a12,a22,...,an2)1/22(a1,a2,...,an)=∣a∣a
因此,可得:
KaTeX parse error: No such environment: align at position 8: \begin{̲a̲l̲i̲g̲n̲}̲ \frac{1}{|b|} …
在上图代码的说明中:
- 1表示: a ∗ b ∣ a ∣ 2 \frac{a*b}{|a|^2} ∣a∣2a∗b
- 2表示: a ∗ b ∣ a ∣ 2 ⋅ a − b \frac{a*b}{|a|^2} \cdot a - b ∣a∣2a∗b⋅a−b
- 3表示: a ∗ b ∣ a ∣ 2 ⋅ a − b ∣ a ∣ ∣ b ∣ \frac{\frac{a*b}{|a|^2} \cdot a - b}{|a| |b|} ∣a∣∣b∣∣a∣2a∗b⋅a−b
最后,当前导数乘后一层梯度为当前梯度。
###Contrastive_loss损失函数实现
ps:虽然看了CosineEmbeddingLoss的实现,但是对PyTorch的矩阵计算函数还是不太熟悉,前前后后花了不少时间。
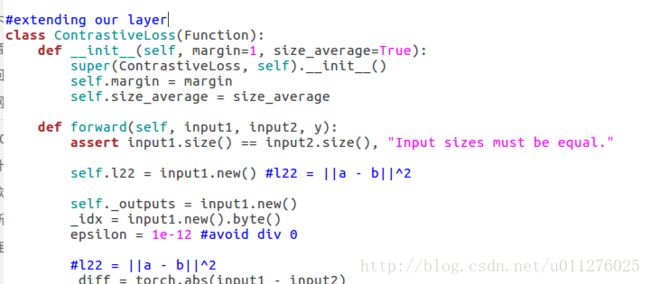
根据上面的公式,Contrastive_loss的代码实现如下:(输入为一对图片input1, input2和标签y,y1表示同一物体,y0表示不同物体)
class ContrastiveLoss(Function):
def __init__(self, margin=1, size_average=True):
super(ContrastiveLoss, self).__init__()
self.margin = margin
self.size_average = size_average
def forward(self, input1, input2, y):
assert input1.size() == input2.size(), "Input sizes must be equal."
self.l22 = input1.new() #l22 = ||a - b||^2
self._outputs = input1.new()
_idx = input1.new().byte()
epsilon = 1e-12 #avoid div 0
#l22 = ||a - b||^2
_diff = torch.abs(input1 - input2)
self.l22 = torch.pow(_diff + epsilon, 2).sum(dim=1)
#_output = l22
self._outputs.resize_as_(self.l22).copy_(self.l22)
self._outputs = self._outputs.select(1, 0) #_output = first column and it one column vector
torch.eq(y, 0, out=_idx) #y==0
self._outputs[_idx] = self._outputs[_idx].mul_(-1).add_(self.margin).clamp_(min=0) #max{0, m-||a-b||}^2
self._outputs[_idx] = self._outputs[_idx].pow_(2)
#_output = 1/2 * _output
self._outputs.mul_(1.0 / 2.0)
output = self._outputs.sum() #sum
if self.size_average:
output = output / y.size(0) #mean
self.save_for_backward(input1, input2, y)
return input1.new((output,))
def backward(self, grad_output):
v1, v2, y = self.saved_tensors
buffer = v1.new()
_idx = v1.new().byte()
gw1 = grad_output.new()
gw2 = grad_output.new()
gw1.resize_as_(v1).copy_(v2) #gw1 = b
gw2.resize_as_(v2).copy_(v1) #gw2 = a
gw1.mul_(-1).add_(v1) #a' = sum(a - b)
gw2.mul_(-1).add_(v2) #b' = sum(b- a)
torch.le(self._outputs, 0, out=_idx) #find _output < 0 because loss>0
_idx = _idx.view(-1, 1).expand(gw1.size())
gw1[_idx] = 0
gw2[_idx] = 0
#y==0
torch.eq(y, 0, out=_idx)
_idx = _idx.view(-1, 1).expand(gw2.size())
torch.add(self.l22, -self.margin, out=buffer)
buffer = buffer.expand(gw1.size())
gw1[_idx] = gw1[_idx].mul(buffer[_idx])
gw2[_idx] = gw2[_idx].mul(buffer[_idx]).mul_(-1)
if self.size_average:
gw1.div_(y.size(0))
gw2.div_(y.size(0))
grad_output_val = grad_output[0] #current = lastgrad*dervative
if grad_output_val != 1:
gw1.mul_(grad_output_val)
gw2.mul_(grad_output_val)
return gw1, gw2, None
使用梯度检验:
input = (Variable(torch.randn(20, 2).double(), requires_grad = True),
Variable(torch.randn(20, 2).double(), requires_grad = True),)
test = gradcheck(ContrastiveLoss(), input, eps=1e-6, atol=1e-4)
print test
返回的值为True,说明求导的backward没有问题。(需要注意的是:我们的loss函数需要3个输入,input1, input2, target. 但是在增加target时会报Kernel died, restarting错误,以为是loss代码写错了,使用自带的CosineEmbeddingLoss进行测试也是同样的结果,最后去除target得以解决。)(PS:2017.2.15, 官方以修复此bug)
通过以上代码,可以发现PyTorch的实现要比caffe使用C++实现要方便的多(至少不用指针指来指去),值得注意的有以下几点:
-
in-palce 和out-place. 比如有Tensor变量a和b,torch.add() 和torch.add_(), 分别为in-palce 和out-place版本。a.add(b) 输出 a+b,a和b的值不改变,a.add_(b) 输出a+b 并且把结果给b。这样做在进行连续计算时有好处,比如计算a*b+c, 只需要a.mul_(b).add_©即可。

-
使用索引时不能进行in-place。 比如有个索引idx,Tensor变量a,当使用a[idx].add_()时不会改变a的值。
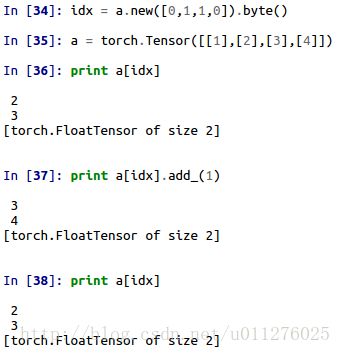
-
少使用=进行赋值,多使用in-place和out=。 因为=进行赋值为浅拷贝,赋值的是地址指针,当其中一个改变时,会影响另一个值。如下所示:

Contrastive_loss损失层的增加
Contrastive_loss的算法已经实现,需要增加到PyTorch中。PyTorch为动态的实现,因此在改变源码后不需要重新编译。
增加一个自定义的层需要完成以下几步:
- 找到PyTorch的包路径。一般在自己python环境路径下的torch下。
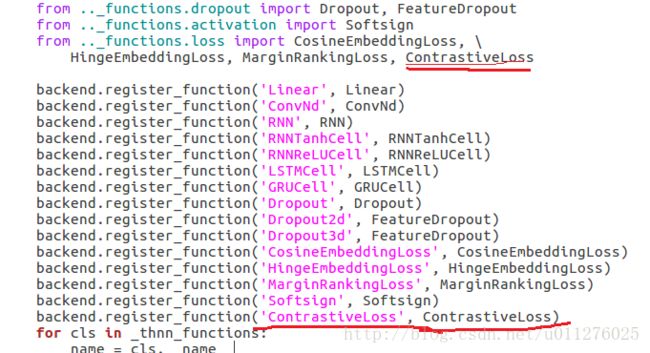
- 在nn._functions.loss.py中增加上面的Contrastive_loss实现代码。
- 在nn.functional.py 中增加Contrastive_loss的包装。(可选)
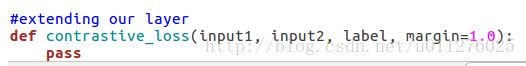
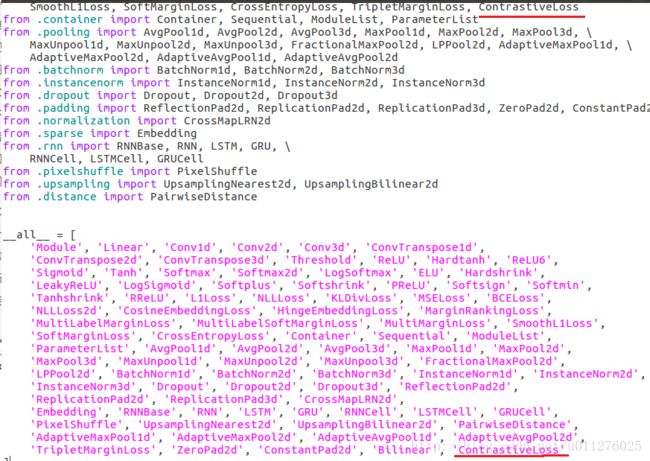
- 在nn.modules.loss.py中增加Contrastive_loss扩展。

然后在nn.modules.init.py中进行定义,以便可以进行调用。
最后在nn.backends.thnn.py中进行backend访问定义。
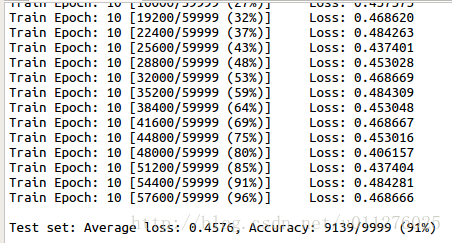
Siamese网络训练结果
至此,数据的处理和网络的搭建都已近完成了。其训练结果如下: