- 8个Java TCP/UDP框架:优缺点及应用场景全解析!
技术男老张
#编程语言-JAVA编程语言javatcp/ipudpssl网络协议websockethttp
JavaTCP框架在现代网络编程中扮演着至关重要的角色,尤其是在需要高效、稳定且可扩展的网络通信解决方案时。本文将深入探讨一些主流的JavaTCP/UDP框架,分析它们的优缺点以及适用场景,旨在为开发者提供一份详尽的指南。一、NettyNetty是一个异步事件驱动的网络应用框架,用于快速开发高性能、高可靠性的网络IO程序。Netty的设计目标是简化网络编程的复杂性,同时提高网络应用的性能和可扩展性
- 【C语言网络编程】HTTP 客户端请求(域名解析过程)
在做C语言网络编程或模拟HTTP客户端时,第一步就离不开“把域名解析为IP地址”这一步。很多人可能直接复制粘贴一段gethostbyname的代码,但未必真正理解它的原理。本篇博客将围绕一个经典函数:char*host_to_ip(constchar*hostname)深入剖析DNS解析过程、IP地址转换机制,并进一步带你了解HTTP请求是如何基于TCP通信进行的。一、核心函数:host_to_i
- C#网络编程深度解析:TCP与UDP协议详解与实战示例
Leon@Lee
网络tcp/ipc#
作为现代网络通信的基石,TCP和UDP协议是开发者必须掌握的核心知识。本文将从协议原理、适用场景、C#实现三个维度全面解析两者差异,并通过10个代码示例展示如何用C#构建高效网络应用。一、TCP协议:可靠的字节流传输1.核心特性面向连接:通过三次握手建立通信信道(SYN→SYN-ACK→ACK)可靠性保障:通过序列号、确认应答(ACK)和重传机制确保数据完整流量控制:滑动窗口机制动态调节传输速率拥
- Python struct 模块:解析与打包二进制数据的利器
tekin
Python编程秘籍库python开发语言pythonstruct模块解析与打包二进制数据
Pythonstruct模块:解析与打包二进制数据的利器在Python编程中,处理二进制数据是一项常见且重要的任务,尤其是在网络编程、文件操作等场景中。Python的struct模块提供了强大的功能,能够将Python的数据类型与二进制数据进行相互转换,即把数据打包成二进制字节串,也能从二进制字节串中解析出数据。本文将详细介绍struct模块的使用方法、格式字符的含义以及实际应用场景,帮助你全面掌
- 新手向:Python网络编程,搭建简易HTTP服务器
本文将从零开始,通过一个简单的PythonHTTP服务器示例,带你走进网络编程的世界。一、准备工作:理解基本概念1.1什么是网络编程?网络编程简单来说就是让不同计算机上的程序能够相互通信。就像人与人之间通过语言交流一样,计算机之间也有自己的"语言"——网络协议。1.2HTTP协议简介HTTP(HyperTextTransferProtocol)是万维网的基础协议,我们每天浏览网页时都在使用它。它采
- C/C++ 知识总结
灿烂阳光g
后端
目录C/C++STL数据结构算法Problems操作系统计算机网络网络编程数据库设计模式链接装载库海量数据处理音视频其他书籍复习刷题网站招聘时间岗位面试题目经验C/C++const作用修饰变量,说明该变量不可以被改变;修饰指针,分为指向常量的指针和指针常量;常量引用,经常用于形参类型,即避免了拷贝,又避免了函数对值的修改;修饰成员函数,说明该成员函数内不能修改成员变量。使用const使用stati
- 腾讯QQ2009通信协议源码分析与应用
欧学东
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:本资源深入解析了腾讯QQ2009的私有通信协议,涉及登录、消息发送与接收的核心功能,为开发者提供了一套理解QQ通信机制的工具。通过分析源码,开发者可以掌握构造登录请求、消息格式设计、加密算法应用等网络编程技巧,并了解如何保持通信连接和处理消息错误。但需要注意,对QQ协议的研究应避免侵犯腾讯的知识产权。1.腾讯QQ2009协议源码概述1.1协议源码的重要性腾讯Q
- 突破性能瓶颈,几个高性能Python网络框架,高效实现网络应用
引言随着互联网和大数据时代的到来,高性能网络应用的需求日益增加。Python作为一种流行的编程语言,在高性能网络编程领域也具有广泛的应用。本文将深入探讨基于Python的几种高性能网络框架,分析它们各自的优势和适用场景,帮助开发者选择最适合自己需求的网络框架这里插播一条粉丝福利,如果你正在学习Python或者有计划学习Python,想要突破自我,对未来十分迷茫的,可以点击这里获取最新的Python
- Java网络编程:让你的程序学会“打电话“的神奇技能
当Java程序开始"社交"想象你的程序是一个宅男:没有网络→只能自言自语(单机程序)有了网络编程→可以给其他电脑"打电话"(通信)Java网络编程就是教你的程序如何通过网线"交朋友"的黑科技!今天我们就来揭开它的神秘面纱~一、网络编程基础:IP地址和端口号1.网络通信核心要素2.计算机世界的"电话号码"//IP地址就像手机号InetAddressaddress=InetAddress.getByN
- 【Linux | 网络】网络编程套接字
是阿建吖!
【Linux】【网络】linux网络
目录一、预备知识1.1理解IP地址1.2认识端口号1.3理解网络套接字1.4理解"端口号"和"进程ID"1.5认识TCP协议与UDP协议1.6网络字节序二、socket编程接口2.1socket常见API2.1.1socket函数2.1.2bind函数2.1.3listen函数2.1.4accept函数2.1.5connect函数2.2主机字节序和网络字节序的转换的函数2.2.1htonl函数2.
- 网络编程底层通信(socket)
En^_^Joy
python应用网络python
文章目录一、socket函数介绍二、TCP/IP服务端/客户端三、UDP/IP服务端/客户端四、多线程服务器(threading)五、网络编程常见问题(地址复用、粘包、数据长度)网络编程指通过计算机网络实现程序间通信的技术。Python提供了丰富的库支持各种网络协议和编程模式套接字是网络通信的基本操作单元,是应用层与TCP/IP协议族通信的中间软件抽象层。它提供了一组接口,允许不同主机或同一主机的
- C++多线程网络编程:助力高并发服务器性能提升
深度Linux
性能优化Linux开发多线程编程C/C++
在数字化时代,高并发是互联网服务的常态——电商购物节的海量订单、社交网络的热门话题讨论、在线游戏的万人同服,都需要强大的并发处理能力。高并发服务器作为核心支柱,其性能与稳定性直接影响用户体验和业务成败。C++凭借卓越性能、高效执行效率和对系统资源的精准掌控,在高并发服务器开发中地位关键。多线程网络编程更是其核心优势,能充分利用多核CPU算力,让服务器同时处理多个任务,大幅提升并发处理能力和响应速度
- Python编程电子书:从基础到实践
王奥雷
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:Python电子书汇集了基础语法、面向对象编程、标准及第三方库使用、文件操作、网络编程、并发编程、单元测试与调试、Python2与Python3的区别等核心知识点。通过实例和项目案例,帮助读者在Web开发、数据分析、人工智能等应用领域提升编程技能,跟上Python的技术进步。1.Python基础语法介绍Python作为一种高级编程语言,其易读性和简洁的语法使其
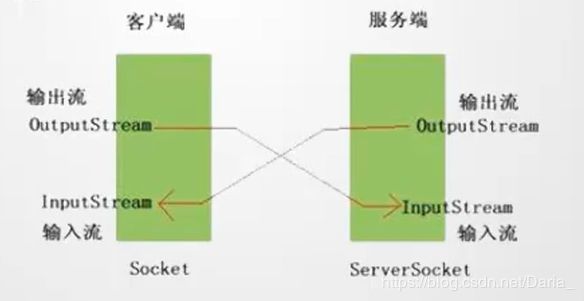
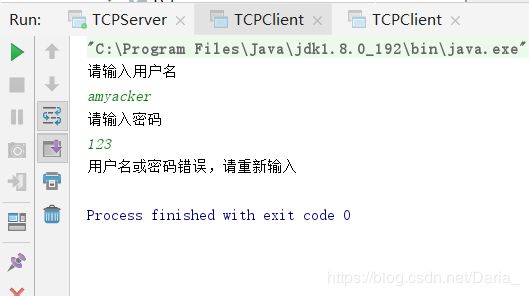
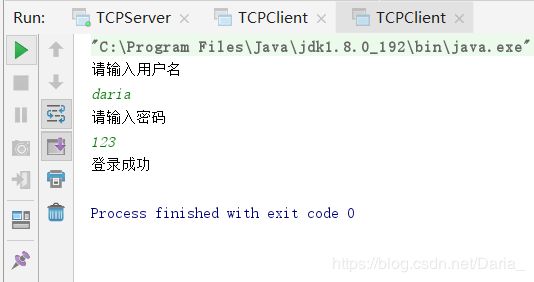
- 利用TCP协议,创建一个多人聊天室
在下Z.
tcp/ip网络协议网络
项目名称利用TCP协议,做一个带有登录,注册的无界面,控制版的多人聊天室。知识点循环,判断,集合,IO,多线程,网络编程准备内容在当前模块下新建txt文件,在文件中保存正确的用户名和密码zhangsan=123lisi=1234wangwu=12345页面搭建客户端连接服务器后,显示如下服务器已经连接成功==============欢迎来到小周聊天室================1登录2注册请输
- JavaEE 网络编程套接字详解与实战示例
我爱Jack
网络java后端开发语言
、套接字(Socket)是什么?套接字是网络通信的“端点”,就像打电话需要手机一样,网络通信需要套接字建立连接。两种类型:TCP套接字:可靠传输(类似打电话,需先拨通)UDP套接字:快速传输(类似发短信,无需确认对方收到)二、TCP套接字编程1.服务端开发步骤importjava.io.*;importjava.net.ServerSocket;importjava.net.Socket;publ
- C++ Socket多人聊天室完整源码详解
赵阿萌
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:本资源提供了一个使用C++实现的多人聊天室应用程序的源码,涵盖了网络编程的多个关键点。该聊天室利用Socket编程进行网络通信,通过C++的系统级功能实现多客户端处理。本文章将详细解析源码中所涉及的关键技术,包括Socket基础、TCP/IP协议、多线程编程、字节序转换、I/O复用技术、数据序列化与解析、错误处理和日志记录,以及安全性方面的考虑。1.Socke
- Java实现局域网TCP/Sockets多人聊天室项目
十二月极光
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:本项目是一个基于Java的局域网多用户聊天应用,使用TCP协议和Socket编程,以及多线程技术来保障聊天室的并发连接和高效稳定运行。该项目涉及Java网络编程基础、TCP协议细节、Socket编程实践以及多线程编程技能,包括关键类解析和实现。开发者可通过此项目深入理解Java网络通信和并发处理。1.Java网络编程基础知识1.1网络编程的意义和应用场景网络编
- Java爬虫技术详解:原理、实现与优势
cyc&阿灿
Java多线程java爬虫开发语言
一、什么是网络爬虫?网络爬虫(WebCrawler),又称网络蜘蛛或网络机器人,是一种自动化程序,能够按照一定的规则自动浏览和抓取互联网上的信息。爬虫技术是大数据时代获取网络数据的重要手段,广泛应用于搜索引擎、数据分析、价格监控等领域。Java作为一种稳定、高效的编程语言,凭借其强大的网络编程能力和丰富的生态库,成为开发网络爬虫的热门选择。二、Java爬虫核心组件一个完整的Java爬虫通常包含以下
- 网络编程学习路线图
weixin_47868976
Web云存储项目网络编程计算机网络八股文网络学习php
网络编程学习路线图第一阶段:理解整体架构(1-2周)1.核心概念理解你的项目采用了经典的Reactor模式,这是高并发网络编程的标准架构://整体架构层次应用层(HttpServer)↓传输层(TcpServer/TcpConnection)↓事件层(EventLoop/Channel)↓IO复用层(EPollPoller)↓系统调用层(epoll)2.重点学习顺序第一步:EventLoop(事件
- Linux之Socket 编程 UDP
孞㐑¥
linuxudp经验分享笔记c++服务器网络协议
一、UDP网络编程1.1、V1版本-echoserver功能:简单的回显服务器和客户端代码注意:云服务器不允许直接bind公有IP,我们也不推荐编写服务器的时候,bind明确的IP,推荐直接写成INADDR_ANY。C++/*Addresstoacceptanyincomingmessages.*/#defineINADDR_ANY((in_addr_t)0x00000000)在网络编程中,当一个
- 【网络编程】EPOLL 事件触发机制的服务器
啟明起鸣
网络服务器运维
文章目录业务拆解EPOLL机制介绍EPOLL的核心变量和函数EPOLL程序流程图C代码实现准备工作服务器代码代码运行效果总结推荐一个零声教育学习教程,个人觉得老师讲得不错,分享给大家:[Linux,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK等技术内容,点击立即学习:https:/
- C++网络编程Socket网络编程基础入门
weixin_47868976
网络c++开发语言
Socket网络编程基础入门-从理论到实践1.Socket基本概念1.1什么是Socket?Socket(套接字)是网络编程的基础,它是应用层与传输层之间的抽象接口。简单来说,Socket就是网络通信的端点,就像电话的听筒一样,用于发送和接收数据。在你的FileHub项目中,Socket被封装在多个层次中://从net/Socket.h可以看到Socket的封装classSocket:noncop
- muduo
2301_80355452
php前端开发语言
好的,我们来深入剖析陈硕老师开发的著名C++网络库——muduo。它以“简单、高效、易用”著称,是学习LinuxC++高性能网络编程的绝佳范本。我会尽量详细、通俗地讲解其核心思想、关键组件、源码结构和工作原理。核心思想:Reactor模式(Non-blocking+I/OMultiplexing)muduo的灵魂是Reactor模式。理解它就理解了muduo的一半。想象一下:传统阻塞模型的问题:想
- [Unity网络游戏实战]网络游戏的“Hello,World”——Echo(回响)(新手向)
码穿地球
unity游戏引擎
网络游戏的“Hello,World”——Echo(回响)文章目录网络游戏的“Hello,World”——Echo(回响)1,Socket1.1Socket1.2IP地址1.3端口1.4Socket通信流程1.5TCP和UDP协议2.3开始网络编程:Echo2.3.1什么是Echo程序2.3.2编写客户端程序2.4完成客户端2.5创建服务端2.5.1服务端知识点2.6测试Echo程序1,Socket
- lwIP协议栈深入应用与优化全攻略
lanjieying
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:lwIP是一套用于嵌入式系统的轻量级TCP/IP协议栈,适用于资源受限的微控制器环境。本文档集锦提供了从基础到高级应用的全面介绍,包括lwIP的架构、协议实现、用户指南、多线程实现、网络编程技巧、实战教程以及性能优化策略。这些文档旨在帮助开发者深入理解lwIP,并有效地应用到网络开发中。1.lwIP架构与基础在嵌入式系统和网络编程中,lwIP(lightwei
- 网络编程(17)——asio多线程模型IOThreadPool
爱吃土豆zzz
网络编程单例模式c++网络编程asio
十七、day17之前我们介绍了IOServicePool的方式,一个IOServicePool开启n个线程和n个iocontext,每个线程内独立运行iocontext,各个iocontext监听各自绑定的socket是否就绪,如果就绪就在各自线程里触发回调函数。为避免线程安全问题,我们将网络数据封装为逻辑包投递给逻辑系统,逻辑系统有一个单独线程处理,这样将网络IO和逻辑处理解耦合,极大的提高了服
- 46、C++中的网络编程
甲方克星947
C++网络编程套接字编程多线程
C++中的网络编程1.网络编程基础网络编程是现代软件开发中不可或缺的一部分,尤其是在分布式系统、互联网应用和服务端开发中。C++作为一种高效且灵活的编程语言,非常适合进行网络编程。本章将详细介绍如何使用C++进行网络编程,涵盖从基础概念到高级技术的各个方面。1.1网络编程的基本概念在开始编写网络程序之前,了解一些基本概念是非常重要的。以下是网络编程中的一些关键术语:TCP/IP协议栈:这是网络通信
- Netty学习路线图 - 第三阶段:Netty核心概念
by.G
学习java
Netty学习路线图-第三阶段:Netty核心概念Netty学习系列之三本文是Netty学习路线的第三篇,重点讲解Netty的核心概念和组件,帮助你理解Netty的设计思想和架构。引言在前两篇文章中,我们分别介绍了Java基础与网络编程基础,以及JavaNIO的核心概念。这些都为我们学习Netty打下了坚实基础。本篇文章将深入探讨Netty的核心概念,包括Netty的架构设计、启动引导、核心组件等
- Netty学习路线图 - 第二阶段:Java NIO基础
by.G
学习javanio
Netty学习路线图-第二阶段:JavaNIO基础Netty学习系列之二本文是Netty学习路线的第二篇,重点讲解JavaNIO的核心概念及编程模型,这是理解Netty设计理念的关键基础。引言在上一篇文章中,我们介绍了学习Netty的第一阶段:Java基础与网络编程基础。本篇文章我们将深入探讨JavaNIO(NewI/O或Non-blockingI/O)的核心概念和编程模型,这是理解Netty框架
- Linux下使用C/C++进行UDP网络编程
袁本美
Linux网络linuxudpc++
UDP是UserDatagramProtocol的简称,中文名是用户数据报协议,是一种无连接、不可靠的协议,同样它也是工作在传顺层。它只是简单地实现从一端主机到另一端主机的数据传输功能,这些数据通过IP层发送,在网络中传输,到达目标主机的顺序是无法预知的,因此需要应用程序对这些数据进行排序处理,这就带来了很大的不方便,此外,UDP协议更没有流量控制、拥塞控制等功能,在发送的一端,UDP只是把上层应
- 关于旗正规则引擎中的MD5加密问题
何必如此
jspMD5规则加密
一般情况下,为了防止个人隐私的泄露,我们都会对用户登录密码进行加密,使数据库相应字段保存的是加密后的字符串,而非原始密码。
在旗正规则引擎中,通过外部调用,可以实现MD5的加密,具体步骤如下:
1.在对象库中选择外部调用,选择“com.flagleader.util.MD5”,在子选项中选择“com.flagleader.util.MD5.getMD5ofStr({arg1})”;
2.在规
- 【Spark101】Scala Promise/Future在Spark中的应用
bit1129
Promise
Promise和Future是Scala用于异步调用并实现结果汇集的并发原语,Scala的Future同JUC里面的Future接口含义相同,Promise理解起来就有些绕。等有时间了再仔细的研究下Promise和Future的语义以及应用场景,具体参见Scala在线文档:http://docs.scala-lang.org/sips/completed/futures-promises.html
- spark sql 访问hive数据的配置详解
daizj
spark sqlhivethriftserver
spark sql 能够通过thriftserver 访问hive数据,默认spark编译的版本是不支持访问hive,因为hive依赖比较多,因此打的包中不包含hive和thriftserver,因此需要自己下载源码进行编译,将hive,thriftserver打包进去才能够访问,详细配置步骤如下:
1、下载源码
2、下载Maven,并配置
此配置简单,就略过
- HTTP 协议通信
周凡杨
javahttpclienthttp通信
一:简介
HTTPCLIENT,通过JAVA基于HTTP协议进行点与点间的通信!
二: 代码举例
测试类:
import java
- java unix时间戳转换
g21121
java
把java时间戳转换成unix时间戳:
Timestamp appointTime=Timestamp.valueOf(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()))
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:m
- web报表工具FineReport常用函数的用法总结(报表函数)
老A不折腾
web报表finereport总结
说明:本次总结中,凡是以tableName或viewName作为参数因子的。函数在调用的时候均按照先从私有数据源中查找,然后再从公有数据源中查找的顺序。
CLASS
CLASS(object):返回object对象的所属的类。
CNMONEY
CNMONEY(number,unit)返回人民币大写。
number:需要转换的数值型的数。
unit:单位,
- java jni调用c++ 代码 报错
墙头上一根草
javaC++jni
#
# A fatal error has been detected by the Java Runtime Environment:
#
# EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION (0xc0000005) at pc=0x00000000777c3290, pid=5632, tid=6656
#
# JRE version: Java(TM) SE Ru
- Spring中事件处理de小技巧
aijuans
springSpring 教程Spring 实例Spring 入门Spring3
Spring 中提供一些Aware相关de接口,BeanFactoryAware、 ApplicationContextAware、ResourceLoaderAware、ServletContextAware等等,其中最常用到de匙ApplicationContextAware.实现ApplicationContextAwaredeBean,在Bean被初始后,将会被注入 Applicati
- linux shell ls脚本样例
annan211
linuxlinux ls源码linux 源码
#! /bin/sh -
#查找输入文件的路径
#在查找路径下寻找一个或多个原始文件或文件模式
# 查找路径由特定的环境变量所定义
#标准输出所产生的结果 通常是查找路径下找到的每个文件的第一个实体的完整路径
# 或是filename :not found 的标准错误输出。
#如果文件没有找到 则退出码为0
#否则 即为找不到的文件个数
#语法 pathfind [--
- List,Set,Map遍历方式 (收集的资源,值得看一下)
百合不是茶
listsetMap遍历方式
List特点:元素有放入顺序,元素可重复
Map特点:元素按键值对存储,无放入顺序
Set特点:元素无放入顺序,元素不可重复(注意:元素虽然无放入顺序,但是元素在set中的位置是有该元素的HashCode决定的,其位置其实是固定的)
List接口有三个实现类:LinkedList,ArrayList,Vector
LinkedList:底层基于链表实现,链表内存是散乱的,每一个元素存储本身
- 解决SimpleDateFormat的线程不安全问题的方法
bijian1013
javathread线程安全
在Java项目中,我们通常会自己写一个DateUtil类,处理日期和字符串的转换,如下所示:
public class DateUtil01 {
private SimpleDateFormat dateformat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public void format(Date d
- http请求测试实例(采用fastjson解析)
bijian1013
http测试
在实际开发中,我们经常会去做http请求的开发,下面则是如何请求的单元测试小实例,仅供参考。
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient;
import
- 【RPC框架Hessian三】Hessian 异常处理
bit1129
hessian
RPC异常处理概述
RPC异常处理指是,当客户端调用远端的服务,如果服务执行过程中发生异常,这个异常能否序列到客户端?
如果服务在执行过程中可能发生异常,那么在服务接口的声明中,就该声明该接口可能抛出的异常。
在Hessian中,服务器端发生异常,可以将异常信息从服务器端序列化到客户端,因为Exception本身是实现了Serializable的
- 【日志分析】日志分析工具
bit1129
日志分析
1. 网站日志实时分析工具 GoAccess
http://www.vpsee.com/2014/02/a-real-time-web-log-analyzer-goaccess/
2. 通过日志监控并收集 Java 应用程序性能数据(Perf4J)
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-logforperf/
3.log.io
和
- nginx优化加强战斗力及遇到的坑解决
ronin47
nginx 优化
先说遇到个坑,第一个是负载问题,这个问题与架构有关,由于我设计架构多了两层,结果导致会话负载只转向一个。解决这样的问题思路有两个:一是改变负载策略,二是更改架构设计。
由于采用动静分离部署,而nginx又设计了静态,结果客户端去读nginx静态,访问量上来,页面加载很慢。解决:二者留其一。最好是保留apache服务器。
来以下优化:
- java-50-输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断树B是不是A的子结构
bylijinnan
java
思路来自:
http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/25411174201011445550396/
import ljn.help.*;
public class HasSubtree {
/**Q50.
* 输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断树B是不是A的子结构。
例如,下图中的两棵树A和B,由于A中有一部分子树的结构和B是一
- mongoDB 备份与恢复
开窍的石头
mongDB备份与恢复
Mongodb导出与导入
1: 导入/导出可以操作的是本地的mongodb服务器,也可以是远程的.
所以,都有如下通用选项:
-h host 主机
--port port 端口
-u username 用户名
-p passwd 密码
2: mongoexport 导出json格式的文件
- [网络与通讯]椭圆轨道计算的一些问题
comsci
网络
如果按照中国古代农历的历法,现在应该是某个季节的开始,但是由于农历历法是3000年前的天文观测数据,如果按照现在的天文学记录来进行修正的话,这个季节已经过去一段时间了。。。。。
也就是说,还要再等3000年。才有机会了,太阳系的行星的椭圆轨道受到外来天体的干扰,轨道次序发生了变
- 软件专利如何申请
cuiyadll
软件专利申请
软件技术可以申请软件著作权以保护软件源代码,也可以申请发明专利以保护软件流程中的步骤执行方式。专利保护的是软件解决问题的思想,而软件著作权保护的是软件代码(即软件思想的表达形式)。例如,离线传送文件,那发明专利保护是如何实现离线传送文件。基于相同的软件思想,但实现离线传送的程序代码有千千万万种,每种代码都可以享有各自的软件著作权。申请一个软件发明专利的代理费大概需要5000-8000申请发明专利可
- Android学习笔记
darrenzhu
android
1.启动一个AVD
2.命令行运行adb shell可连接到AVD,这也就是命令行客户端
3.如何启动一个程序
am start -n package name/.activityName
am start -n com.example.helloworld/.MainActivity
启动Android设置工具的命令如下所示:
# am start -
- apache虚拟机配置,本地多域名访问本地网站
dcj3sjt126com
apache
现在假定你有两个目录,一个存在于 /htdocs/a,另一个存在于 /htdocs/b 。
现在你想要在本地测试的时候访问 www.freeman.com 对应的目录是 /xampp/htdocs/freeman ,访问 www.duchengjiu.com 对应的目录是 /htdocs/duchengjiu。
1、首先修改C盘WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc目录下的
- yii2 restful web服务[速率限制]
dcj3sjt126com
PHPyii2
速率限制
为防止滥用,你应该考虑增加速率限制到您的API。 例如,您可以限制每个用户的API的使用是在10分钟内最多100次的API调用。 如果一个用户同一个时间段内太多的请求被接收, 将返回响应状态代码 429 (这意味着过多的请求)。
要启用速率限制, [[yii\web\User::identityClass|user identity class]] 应该实现 [[yii\filter
- Hadoop2.5.2安装——单机模式
eksliang
hadoophadoop单机部署
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2185414 一、概述
Hadoop有三种模式 单机模式、伪分布模式和完全分布模式,这里先简单介绍单机模式 ,默认情况下,Hadoop被配置成一个非分布式模式,独立运行JAVA进程,适合开始做调试工作。
二、下载地址
Hadoop 网址http:
- LoadMoreListView+SwipeRefreshLayout(分页下拉)基本结构
gundumw100
android
一切为了快速迭代
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.widget.SwipeRefreshLayo
- 三道简单的前端HTML/CSS题目
ini
htmlWeb前端css题目
使用CSS为多个网页进行相同风格的布局和外观设置时,为了方便对这些网页进行修改,最好使用( )。http://hovertree.com/shortanswer/bjae/7bd72acca3206862.htm
在HTML中加入<table style=”color:red; font-size:10pt”>,此为( )。http://hovertree.com/s
- overrided方法编译错误
kane_xie
override
问题描述:
在实现类中的某一或某几个Override方法发生编译错误如下:
Name clash: The method put(String) of type XXXServiceImpl has the same erasure as put(String) of type XXXService but does not override it
当去掉@Over
- Java中使用代理IP获取网址内容(防IP被封,做数据爬虫)
mcj8089
免费代理IP代理IP数据爬虫JAVA设置代理IP爬虫封IP
推荐两个代理IP网站:
1. 全网代理IP:http://proxy.goubanjia.com/
2. 敲代码免费IP:http://ip.qiaodm.com/
Java语言有两种方式使用代理IP访问网址并获取内容,
方式一,设置System系统属性
// 设置代理IP
System.getProper
- Nodejs Express 报错之 listen EADDRINUSE
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境nodejs纵观千象
当你启动 nodejs服务报错:
>node app
Express server listening on port 80
events.js:85
throw er; // Unhandled 'error' event
^
Error: listen EADDRINUSE
at exports._errnoException (
- C++中三种new的用法
_荆棘鸟_
C++new
转载自:http://news.ccidnet.com/art/32855/20100713/2114025_1.html
作者: mt
其一是new operator,也叫new表达式;其二是operator new,也叫new操作符。这两个英文名称起的也太绝了,很容易搞混,那就记中文名称吧。new表达式比较常见,也最常用,例如:
string* ps = new string("
- Ruby深入研究笔记1
wudixiaotie
Ruby
module是可以定义private方法的
module MTest
def aaa
puts "aaa"
private_method
end
private
def private_method
puts "this is private_method"
end
end