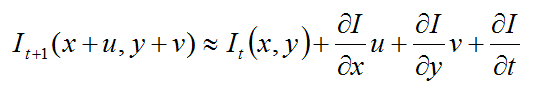【OpenCV学习笔记 013】处理视频序列
视频信号是由按序列排放的图像(帧)组成,它们是通过有规律的间隔进行拍摄以展示动态的场景。
一、读取视频序列
1.原理及概念
(1)通过重复调用read方法获取视频序列,这里需要注意为了打开视频计算机中必须安装有对应的解码器,否则cv::VideoCapture将无法理解视频格式,关于视频的编解码可以查看ffmpeg.org站点提供了完整的开源及跨平台解决方案,可用于音视频录制、转换以及流媒体,Opencv中操作视频文件的类就是基于ffmpeg。xvid.org站点提供了基于MPEG-4视频压缩标准的开源编解码库。Xvid也有名为DivX的竞争者,后者提供私有但免费的编解码工具。
2.实验
源码示例
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(){
//打开视频文件
VideoCapture capture("屌丝男士.mov"); //ID为0将打开默认的摄像头
//检查视频是否成功打开
if (!capture.isOpened())
return -1;
//获取帧率
double rate = capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FPS);
bool stop(false);
Mat frame; //当前视频帧
namedWindow("Extracted Frame");
//每一帧之间的延迟
//与视频的帧率相对应
int delay = 1000 / rate;
//遍历每一帧
while (!stop)
{
//尝试读取下一帧
if (!capture.read(frame))break;
imshow("Extracted Frame", frame);
//引入延迟
//也可通过按键停止
if (waitKey(delay) >= 0) stop = true;
}
//关闭视频文件
//将由析构函数调用,因此非必须
capture.release();
} 播放视频
二、处理视频帧
源码示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
class VideoProcessor{
private:
//Opencv视频捕捉对象
VideoCapture capture;
//每帧调用的回调函数
void(*process)(Mat&, Mat&);
//确定是否调用回调函数的bool变量
bool callIt;
//输入窗口的名称
string windowNameInput;
string windowNameOutput;
//延迟
int delay;
//已处理的帧数
long fnumber;
//在该帧数停止
long frameToStop;
//是否停止处理
bool stop;
public:
VideoProcessor() :callIt(true), delay(0), fnumber(0), stop(false), frameToStop(-1){};
//设置回调函数
void setFrameProcessor(
void(*frameProcessingCallback)(Mat&, Mat&)){
process = frameProcessingCallback;
}
//设置视频文件的名称
bool setInput(string filename){
fnumber = 0;
//释放之前打开过的资源
capture.release();
//打开视频文件
return capture.open(filename);
}
//创建输入窗口
void displayInput(string wn){
windowNameInput = wn;
namedWindow(windowNameInput);
}
//创建输出窗口
void displayOutput(string wn){
windowNameOutput = wn;
namedWindow(windowNameOutput);
}
//不再显示处理后的帧
void dontDisplay(){
destroyWindow(windowNameInput);
destroyWindow(windowNameOutput);
windowNameInput.clear();
windowNameOutput.clear();
}
//获取并处理序列帧
void run(){
//当前帧
Mat frame;
//输出帧
Mat output;
//打开失败时
if (!isOpened())return;
stop = false;
while (!isStopped())
{
//读取下一帧
if (!readNextFrame(frame))break;
//显示输出帧
if (windowNameInput.length() != 0)
imshow(windowNameInput, frame);
//调用处理函数
if (callIt){
//处理当前帧
process(frame, output);
//增加帧数
fnumber++;
}
else
{
output = frame;
}
//显示输出帧
if (windowNameOutput.length() != 0)
imshow(windowNameOutput, output);
//引入延迟
if (delay >= 0 && waitKey(delay) >= 0)
stopIt();
//检查是否需要停止运行
if (frameToStop >= 0 && getFrameNumber() == frameToStop)
stopIt();
}
}
//停止运行
void stopIt(){
stop = true;
}
//是否已停止
bool isStopped(){
return stop;
}
//是否开始了捕获设备
bool isOpened(){
return capture.isOpened();
}
//设置帧间的延迟 0意味着在每帧都等待用户按键 负数意味着没有延迟
void setDelay(int d){
delay = d;
}
//得到下一帧 可能是视频文件或摄像头
bool readNextFrame(Mat &frame){
return capture.read(frame);
}
//需要调用回调函数
void callProcess(){
callIt = true;
}
//不需要调用回调函数
void dontCallProcess(){
callIt = false;
}
void stopAtFrameNo(long frame){
frameToStop = frame;
}
//返回下一帧的帧数
long getFrameNumber(){
//得到捕获设备的信息
long fnumber = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES));
return fnumber;
}
int getFrameRate(){
return capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FPS);
}
};
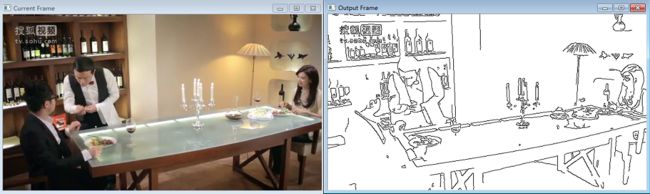
void canny(Mat &img, Mat &out){
//灰度转换
if (img.channels()==3)
{
cvtColor(img, out, CV_BGR2GRAY);
}
//计算Canny边缘
Canny(out, out, 100, 200);
//反转图像
threshold(out, out, 128, 255, THRESH_BINARY_INV);
}
int main(){
//创建实例
VideoProcessor processor;
//打开视频文件
processor.setInput("屌丝男士.mov");
//声明显示窗口
processor.displayInput("Current Frame");
processor.displayOutput("Output Frame");
//以原始帧率播放视频
processor.setDelay(1000. / processor.getFrameRate());
//设置处理回调函数
processor.setFrameProcessor(canny);
//开始处理过程
processor.run();
waitKey();
return 0;
} 程序运行效果
三、写入视频序列
比较简单直接上代码
源码示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
class FrameProcessor;
class FrameProcessor{
public:
virtual void process(Mat &input, Mat &ouput);
};
class VideoProcessor{
private:
//Opencv视频捕捉对象
VideoCapture capture;
//每帧调用的回调函数
void(*process)(Mat&, Mat&);
//确定是否调用回调函数的bool变量
bool callIt;
//输入窗口的名称
string windowNameInput;
string windowNameOutput;
//延迟
int delay;
//已处理的帧数
long fnumber;
//在该帧数停止
long frameToStop;
//是否停止处理
bool stop;
//opencv的写视频对象
VideoWriter writer;
//输出文件名称
string outputFile;
//输出图像的当前索引
int currentIndex;
//输出图像名称中的数字位数
int digits;
//输出图像的扩展名
string extension;
FrameProcessor *frameprocessor;
//图像序列作为输入视频流
vector images;
public:
VideoProcessor() :callIt(true), delay(0), fnumber(0), stop(false), frameToStop(-1){};
//设置回调函数
void setFrameProcessor(
void(*frameProcessingCallback)(Mat&, Mat&)){
process = frameProcessingCallback;
}
//设置视频文件的名称
bool setInput(string filename){
fnumber = 0;
//释放之前打开过的资源
capture.release();
//打开视频文件
return capture.open(filename);
}
//创建输入窗口
void displayInput(string wn){
windowNameInput = wn;
namedWindow(windowNameInput);
}
//创建输出窗口
void displayOutput(string wn){
windowNameOutput = wn;
namedWindow(windowNameOutput);
}
//不再显示处理后的帧
void dontDisplay(){
destroyWindow(windowNameInput);
destroyWindow(windowNameOutput);
windowNameInput.clear();
windowNameOutput.clear();
}
//获取并处理序列帧
void run(){
//当前帧
Mat frame;
//输出帧
Mat output;
//打开失败时
if (!isOpened())return;
stop = false;
while (!isStopped())
{
//读取下一帧
if (!readNextFrame(frame))break;
//显示输出帧
if (windowNameInput.length() != 0)
imshow(windowNameInput, frame);
//调用处理函数
if (callIt){
//处理当前帧
if (process)
process(frame, output);
else if (frameprocessor)
frameprocessor->process(frame, output);
//增加帧数
fnumber++;
}
else
{
output = frame;
}
//输出图像序列
if (outputFile.length() != 0)
writeNextFrame(output);
//显示输出帧
if (windowNameOutput.length() != 0)
imshow(windowNameOutput, output);
//引入延迟
if (delay >= 0 && waitKey(delay) >= 0)
stopIt();
//检查是否需要停止运行
if (frameToStop >= 0 && getFrameNumber() == frameToStop)
stopIt();
}
}
//停止运行
void stopIt(){
stop = true;
}
//是否已停止
bool isStopped(){
return stop;
}
//是否开始了捕获设备
bool isOpened(){
return capture.isOpened();
}
//设置帧间的延迟 0意味着在每帧都等待用户按键 负数意味着没有延迟
void setDelay(int d){
delay = d;
}
//得到下一帧 可能是视频文件或摄像头
bool readNextFrame(Mat &frame){
return capture.read(frame);
}
//需要调用回调函数
void callProcess(){
callIt = true;
}
//不需要调用回调函数
void dontCallProcess(){
callIt = false;
}
void stopAtFrameNo(long frame){
frameToStop = frame;
}
//返回下一帧的帧数
long getFrameNumber(){
//得到捕获设备的信息
long fnumber = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES));
return fnumber;
}
int getFrameRate(){
return capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FPS);
}
//获得编码类型
int getCodec(char codec[4]) {
if (images.size() != 0)
return -1;
union { // 数据结构4-char
int value;
char code[4];
} returned;
//获得编码值
returned.value = static_cast(
capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FOURCC));
// get the 4 characters
codec[0] = returned.code[0];
codec[1] = returned.code[1];
codec[2] = returned.code[2];
codec[3] = returned.code[3];
return returned.value;
}
//获得帧大小
Size getFrameSize() {
if (images.size() == 0) {
// 从视频流获得帧大小
int w = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH));
int h = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT));
return Size(w, h);
}
else {
//从图像获得帧大小
cv::Mat tmp = cv::imread(images[0]);
return (tmp.data) ? (tmp.size()) : (Size(0, 0));
}
}
//设置输出视频文件
//默认使用于输入视频相同的参数
bool setOutput(const string &filename, int codec = 0, double framerate = 0.0, bool isColor = true){
outputFile = filename;
extension.clear();
if (framerate == 0.0)
framerate = getFrameRate();//与输入相同
char c[4];
//使用相同的编码格式
if (codec==0)
{
codec = getCodec(c);
}
//打开输出视频
return writer.open(outputFile, //文件名
codec, //将使用的编码格式
framerate, //帧率
getFrameSize(), //尺寸
isColor); //是否是彩色视频?
}
//输出帧 可能是视频文件或图像文件
void writeNextFrame(Mat &frame){
if (extension.length())//我们输出到图像文件
{
stringstream ss;
//组成输出文件名称
ss << outputFile << setfill('0')
<< setw(digits)
<< currentIndex++ << extension;
imwrite(ss.str(), frame);
}
else
{//我们输出到视频文件
writer.write(frame);
}
}
//设置输出为独立的图像文件 扩展名必须是".jpg" ".bmp"
bool setOutput(const string &filename,//前缀
const string&ext,//后缀
int numberofDigits = 3,//数字位数
int startIndex = 0){ //开始索引
//数字位数必须是正的
if (numberofDigits < 0)return false;
//文件名及其后缀
outputFile = filename;
extension = ext;
//文件名中的数字位数
digits = numberofDigits;
//开始索引
currentIndex = startIndex;
return true;
}
};
void canny(Mat &img, Mat &out){
//灰度转换
if (img.channels() == 3)
{
cvtColor(img, out, CV_BGR2GRAY);
}
//计算Canny边缘
Canny(out, out, 100, 200);
//反转图像
threshold(out, out, 128, 255, THRESH_BINARY_INV);
}
int main(){
//创建实例
VideoProcessor processor;
//打开视频文件
processor.setInput("屌丝男士.mov");
processor.setFrameProcessor(canny);
processor.setOutput("out.mov");
//开始处理过程
processor.run();
waitKey();
return 0;
} 四、用光流法实现视频中的特征跟踪
1.概念及原理
(1)在开始跟踪前,首先要在初始帧中检测特征点,之后在下一帧中尝试跟踪这些点。你必须找到新的图像帧中这些点的位置。很明显的,由于我们处理的是视频序列,很有可能特征点所在的物体已经移动过(运动也有可能是相机引起的)。因此,你必须在特征点的先前位置附近进行搜索,以找到下一帧中它的新位置。这正是cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK函数所实现的工作。你输入两个连续的图像帧以及第一幅图像中检测到的特征点数组,该函数将返回一组新的特征点为位置。为了跟踪完整的序列,你需要在帧与帧之间重复这个过程,不可避免地你也会丢失其中一些点,于是被跟踪的特征点数目会减少。为了解决这个问题,我们可以不时地检测新的特征值。
(2)我们假设特征点的强度在相邻帧之间不发生变化,那么我们要找到一个偏移量(u,v):
其中,分别是当前帧以及下一时刻的值,这个强度不变的假设对于拍摄时间相近的图像中的微小偏移量而言都是成立的。我们可以使用泰勒展开式来近似这个方程即
如果强度不变假设成立,可以推出另一个方程式
这个著名的约束便是基础光流约束方程式,引入另一个假设,它被使用于Lukas-Kanade特征跟踪算法。
2.实验
源码示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//帧处理基类
class FrameProcessor{
public:
virtual void process(Mat &input, Mat &ouput)=0;
};
class VideoProcessor{
private:
//Opencv视频捕捉对象
VideoCapture capture;
//每帧调用的回调函数
void(*process)(Mat&, Mat&);
//确定是否调用回调函数的bool变量
bool callIt;
//输入窗口的名称
string windowNameInput;
string windowNameOutput;
//延迟
int delay;
//已处理的帧数
long fnumber;
//在该帧数停止
long frameToStop;
//是否停止处理
bool stop;
//opencv的写视频对象
VideoWriter writer;
//输出文件名称
string outputFile;
//输出图像的当前索引
int currentIndex;
//输出图像名称中的数字位数
int digits;
//输出图像的扩展名
string extension;
FrameProcessor *frameprocessor;
//图像序列作为输入视频流
vector images;
public:
VideoProcessor() :callIt(true), delay(0), fnumber(0), stop(false), frameToStop(-1){}
//设置回调函数
void setFrameProcessor(
void(*frameProcessingCallback)(Mat&, Mat&)){
process = frameProcessingCallback;
}
//设置视频文件的名称
bool setInput(string filename){
fnumber = 0;
//释放之前打开过的资源
capture.release();
//打开视频文件
return capture.open(filename);
}
//创建输入窗口
void displayInput(string wn){
windowNameInput = wn;
namedWindow(windowNameInput);
}
//创建输出窗口
void displayOutput(string wn){
windowNameOutput = wn;
namedWindow(windowNameOutput);
}
//不再显示处理后的帧
void dontDisplay(){
destroyWindow(windowNameInput);
destroyWindow(windowNameOutput);
windowNameInput.clear();
windowNameOutput.clear();
}
//获取并处理序列帧
void run(){
//当前帧
Mat frame;
//输出帧
Mat output;
//打开失败时
if (!isOpened())return;
stop = false;
while (!isStopped())
{
//读取下一帧
if (!readNextFrame(frame))break;
//显示输出帧
if (windowNameInput.length() != 0)
imshow(windowNameInput, frame);
//调用处理函数
if (callIt){
//处理当前帧
if (process)
process(frame, output);
else if (frameprocessor)
frameprocessor->process(frame, output);
//增加帧数
fnumber++;
}
else
{
output = frame;
}
//输出图像序列
if (outputFile.length() != 0)
writeNextFrame(output);
//显示输出帧
if (windowNameOutput.length() != 0)
imshow(windowNameOutput, output);
//引入延迟
if (delay >= 0 && waitKey(delay) >= 0)
stopIt();
//检查是否需要停止运行
if (frameToStop >= 0 && getFrameNumber() == frameToStop)
stopIt();
}
}
//停止运行
void stopIt(){
stop = true;
}
//是否已停止
bool isStopped(){
return stop;
}
//是否开始了捕获设备
bool isOpened(){
return capture.isOpened();
}
//设置帧间的延迟 0意味着在每帧都等待用户按键 负数意味着没有延迟
void setDelay(int d){
delay = d;
}
//得到下一帧 可能是视频文件或摄像头
bool readNextFrame(Mat &frame){
return capture.read(frame);
}
//需要调用回调函数
void callProcess(){
callIt = true;
}
//不需要调用回调函数
void dontCallProcess(){
callIt = false;
}
void stopAtFrameNo(long frame){
frameToStop = frame;
}
//返回下一帧的帧数
long getFrameNumber(){
//得到捕获设备的信息
long fnumber = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES));
return fnumber;
}
int getFrameRate(){
return capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FPS);
}
//获得编码类型
int getCodec(char codec[4]) {
if (images.size() != 0)
return -1;
union { // 数据结构4-char
int value;
char code[4];
} returned;
//获得编码值
returned.value = static_cast(
capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FOURCC));
// get the 4 characters
codec[0] = returned.code[0];
codec[1] = returned.code[1];
codec[2] = returned.code[2];
codec[3] = returned.code[3];
return returned.value;
}
//获得帧大小
Size getFrameSize() {
if (images.size() == 0) {
// 从视频流获得帧大小
int w = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH));
int h = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT));
return Size(w, h);
}
else {
//从图像获得帧大小
cv::Mat tmp = cv::imread(images[0]);
return (tmp.data) ? (tmp.size()) : (Size(0, 0));
}
}
//设置输出视频文件
//默认使用于输入视频相同的参数
bool setOutput(const string &filename, int codec = 0, double framerate = 0.0, bool isColor = true){
outputFile = filename;
extension.clear();
if (framerate == 0.0)
framerate = getFrameRate();//与输入相同
char c[4];
//使用相同的编码格式
if (codec == 0)
{
codec = getCodec(c);
}
//打开输出视频
return writer.open(outputFile, //文件名
codec, //将使用的编码格式
framerate, //帧率
getFrameSize(), //尺寸
isColor); //是否是彩色视频?
}
//输出帧 可能是视频文件或图像文件
void writeNextFrame(Mat &frame){
if (extension.length())//我们输出到图像文件
{
stringstream ss;
//组成输出文件名称
ss << outputFile << setfill('0')
<< setw(digits)
<< currentIndex++ << extension;
imwrite(ss.str(), frame);
}
else
{//我们输出到视频文件
writer.write(frame);
}
}
//设置输出为独立的图像文件 扩展名必须是".jpg" ".bmp"
bool setOutput(const string &filename,//前缀
const string&ext,//后缀
int numberofDigits = 3,//数字位数
int startIndex = 0){ //开始索引
//数字位数必须是正的
if (numberofDigits < 0)return false;
//文件名及其后缀
outputFile = filename;
extension = ext;
//文件名中的数字位数
digits = numberofDigits;
//开始索引
currentIndex = startIndex;
return true;
}
void setFrameProcessor(FrameProcessor *frameprocessor){
process = 0;
this->frameprocessor = frameprocessor;
callProcess();
}
};
class FeatureTracker :public FrameProcessor{
Mat gray; //当前灰度图像
Mat gray_prev; //之前灰度图像
//两幅图像间跟踪的特征点 0->1
vectorpoints[2];
//跟踪的点初始位置
vector initial;
vectorfeatures; //检测到的特征
int max_count; //需要跟踪的最大特征数目
double qlevel; //特征检测中的质量等级
double minDist; //两点之间的最小距离
vector status; //检测到的特征的状态
vectorerr; //跟踪过程中的错误
public:
FeatureTracker() :max_count(500), qlevel(0.01), minDist(10.){};
void process(Mat&frame, Mat&output){
//转换为灰度图像
cvtColor(frame, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
frame.copyTo(output);
//1.如果需要添加新的特征点
if (addNewPoints()){
//进行检测
detectFeaturePoints();
//添加检测到的特征到当前跟踪的特征中
points[0].insert(points[0].end(), features.begin(), features.end());
initial.insert(initial.end(), features.begin(), features.end());
}
//对于序列中的第一幅图像
if (gray_prev.empty()){
gray.copyTo(gray_prev);
}
//2.跟踪特征点
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(
gray_prev, gray, //两幅连续图
points[0], //图1中的输入点坐标
points[1], //图2中的输出点坐标
status, //跟踪成功
err //跟踪错误
);
//3.遍历所有跟踪的点进行筛选
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points[1].size(); i++)
{
//是否需要保留该点
if (acceptTrackedPoint(i)){
//进行保留
initial[k] = initial[i];
points[1][k++] = points[1][i];
}
}
//去除不成功的点
points[1].resize(k);
initial.resize(k);
//4.处理接受的跟踪点
handleTrackedPoints(frame, output);
//5.当前帧的点和图像变为前一帧的点和图像
swap(points[1], points[0]);
swap(gray_prev, gray);
}
//检测特征点
void detectFeaturePoints(){
//检测特征
goodFeaturesToTrack(gray, //图像
features, //检测到的特征
max_count, //特征的最大数目
qlevel, //质量等级
minDist); //两个特征之间的最小距离
}
//是否需要检测新的特征点
bool addNewPoints(){
//如果点的数量太少
return points[0].size() <= 10;
}
//决定哪些点应该跟踪
bool acceptTrackedPoint(int i){
return status[i] && (abs(points[0][i].x - points[1][i].x) + abs(points[0][i].y - points[1][i].y) > 2);
}
//处理当前跟踪的点
void handleTrackedPoints(Mat &frame, Mat &output){
//遍历所有跟踪点
for (int i = 0; i < points[1].size(); i++)
{
//绘制直线与圆
line(output,
initial[i],
points[1][i],
Scalar(255, 255, 255));
circle(output, points[1][i], 3, Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1);
}
}
};
int main(){
//创建视频处理器实例
VideoProcessor processor;
//创建特征跟踪器实例
FeatureTracker tracker;
//打开视频文件
processor.setInput("walkMan.mov");
//设置帧处理器对象
processor.setFrameProcessor(&tracker);
//声明显示窗口
processor.displayOutput("Tracked Features");
//以原始帧率播放视频
processor.setDelay(1000. / processor.getFrameRate());
//开始处理过程
processor.run();
return 0;
} 五、提取视频中的前景物
1.概念及原理
(1)有时相机固定背景几乎不变,我们感兴趣的元素只有场景中运动的物体,我们可以通过对背景建模然后将当前帧的模型与背景模型进行比较检测前景物体,前景提取是只能监控中的基础步骤。
(2)如果我们能够获取当前场景背景的图像,那么通过简单的图像差分便可以提取出前景:
cv::absdiff(backgroundImage,currentImage,foreground);2.实验
源码示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//帧处理基类
class FrameProcessor{
public:
virtual void process(Mat &input, Mat &ouput) = 0;
};
class VideoProcessor{
private:
//Opencv视频捕捉对象
VideoCapture capture;
//每帧调用的回调函数
void(*process)(Mat&, Mat&);
//确定是否调用回调函数的bool变量
bool callIt;
//输入窗口的名称
string windowNameInput;
string windowNameOutput;
//延迟
int delay;
//已处理的帧数
long fnumber;
//在该帧数停止
long frameToStop;
//是否停止处理
bool stop;
//opencv的写视频对象
VideoWriter writer;
//输出文件名称
string outputFile;
//输出图像的当前索引
int currentIndex;
//输出图像名称中的数字位数
int digits;
//输出图像的扩展名
string extension;
FrameProcessor *frameprocessor;
//图像序列作为输入视频流
vector images;
public:
VideoProcessor() :callIt(true), delay(0), fnumber(0), stop(false), frameToStop(-1){}
//设置回调函数
void setFrameProcessor(
void(*frameProcessingCallback)(Mat&, Mat&)){
process = frameProcessingCallback;
}
//设置视频文件的名称
bool setInput(string filename){
fnumber = 0;
//释放之前打开过的资源
capture.release();
//打开视频文件
return capture.open(filename);
}
//创建输入窗口
void displayInput(string wn){
windowNameInput = wn;
namedWindow(windowNameInput);
}
//创建输出窗口
void displayOutput(string wn){
windowNameOutput = wn;
namedWindow(windowNameOutput);
}
//不再显示处理后的帧
void dontDisplay(){
destroyWindow(windowNameInput);
destroyWindow(windowNameOutput);
windowNameInput.clear();
windowNameOutput.clear();
}
//获取并处理序列帧
void run(){
//当前帧
Mat frame;
//输出帧
Mat output;
//打开失败时
if (!isOpened())return;
stop = false;
while (!isStopped())
{
//读取下一帧
if (!readNextFrame(frame))break;
//显示输出帧
if (windowNameInput.length() != 0)
imshow(windowNameInput, frame);
//调用处理函数
if (callIt){
//处理当前帧
if (process)
process(frame, output);
else if (frameprocessor)
frameprocessor->process(frame, output);
//增加帧数
fnumber++;
}
else
{
output = frame;
}
//输出图像序列
if (outputFile.length() != 0)
writeNextFrame(output);
//显示输出帧
if (windowNameOutput.length() != 0)
imshow(windowNameOutput, output);
//引入延迟
if (delay >= 0 && waitKey(delay) >= 0)
stopIt();
//检查是否需要停止运行
if (frameToStop >= 0 && getFrameNumber() == frameToStop)
stopIt();
}
}
//停止运行
void stopIt(){
stop = true;
}
//是否已停止
bool isStopped(){
return stop;
}
//是否开始了捕获设备
bool isOpened(){
return capture.isOpened();
}
//设置帧间的延迟 0意味着在每帧都等待用户按键 负数意味着没有延迟
void setDelay(int d){
delay = d;
}
//得到下一帧 可能是视频文件或摄像头
bool readNextFrame(Mat &frame){
return capture.read(frame);
}
//需要调用回调函数
void callProcess(){
callIt = true;
}
//不需要调用回调函数
void dontCallProcess(){
callIt = false;
}
void stopAtFrameNo(long frame){
frameToStop = frame;
}
//返回下一帧的帧数
long getFrameNumber(){
//得到捕获设备的信息
long fnumber = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES));
return fnumber;
}
int getFrameRate(){
return capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FPS);
}
//获得编码类型
int getCodec(char codec[4]) {
if (images.size() != 0)
return -1;
union { // 数据结构4-char
int value;
char code[4];
} returned;
//获得编码值
returned.value = static_cast(
capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FOURCC));
// get the 4 characters
codec[0] = returned.code[0];
codec[1] = returned.code[1];
codec[2] = returned.code[2];
codec[3] = returned.code[3];
return returned.value;
}
//获得帧大小
Size getFrameSize() {
if (images.size() == 0) {
// 从视频流获得帧大小
int w = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH));
int h = static_cast(capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT));
return Size(w, h);
}
else {
//从图像获得帧大小
cv::Mat tmp = cv::imread(images[0]);
return (tmp.data) ? (tmp.size()) : (Size(0, 0));
}
}
//设置输出视频文件
//默认使用于输入视频相同的参数
bool setOutput(const string &filename, int codec = 0, double framerate = 0.0, bool isColor = true){
outputFile = filename;
extension.clear();
if (framerate == 0.0)
framerate = getFrameRate();//与输入相同
char c[4];
//使用相同的编码格式
if (codec == 0)
{
codec = getCodec(c);
}
//打开输出视频
return writer.open(outputFile, //文件名
codec, //将使用的编码格式
framerate, //帧率
getFrameSize(), //尺寸
isColor); //是否是彩色视频?
}
//输出帧 可能是视频文件或图像文件
void writeNextFrame(Mat &frame){
if (extension.length())//我们输出到图像文件
{
stringstream ss;
//组成输出文件名称
ss << outputFile << setfill('0')
<< setw(digits)
<< currentIndex++ << extension;
imwrite(ss.str(), frame);
}
else
{//我们输出到视频文件
writer.write(frame);
}
}
//设置输出为独立的图像文件 扩展名必须是".jpg" ".bmp"
bool setOutput(const string &filename,//前缀
const string&ext,//后缀
int numberofDigits = 3,//数字位数
int startIndex = 0){ //开始索引
//数字位数必须是正的
if (numberofDigits < 0)return false;
//文件名及其后缀
outputFile = filename;
extension = ext;
//文件名中的数字位数
digits = numberofDigits;
//开始索引
currentIndex = startIndex;
return true;
}
void setFrameProcessor(FrameProcessor *frameprocessor){
process = 0;
this->frameprocessor = frameprocessor;
callProcess();
}
};
class BGFGSegmentor :public FrameProcessor{
Mat gray;
Mat background;
Mat backImage;
Mat foreground;
//背景累加中的学习率
double learningRate;
int ithreshold;
public:
BGFGSegmentor() :ithreshold(10), learningRate(0.01){}
//处理方法
void process(Mat &frame, Mat &output){
//转换为灰度图
cvtColor(frame, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
//初始化背景为第一帧
if (background.empty()) gray.convertTo(background, CV_32F);
//转换背景图像为8U格式
background.convertTo(backImage, CV_8U);
//计算差值
absdiff(backImage, gray, foreground);
//应用阈值化到前景图像
threshold(foreground, output, ithreshold, 255, THRESH_BINARY_INV);
//对图像累加
accumulateWeighted(gray, background, learningRate, output);
}
void setThreshold(int ithreshold){
this->ithreshold = ithreshold;
}
};
int main(){
//创建视频处理器实例
VideoProcessor processor;
//创建背景 / 前景分段器
BGFGSegmentor segmentor;
segmentor.setThreshold(25);
//打开视频文件
processor.setInput("walkMan.mov");
//设置帧处理器对象
processor.setFrameProcessor(&segmentor);
//声明显示窗口
processor.displayOutput("Extracted Foreground");
//以原始帧率播放视频
processor.setDelay(1000. / processor.getFrameRate());
//开始处理过程
processor.run();
return 0;
} 实验结果
Reference:
http://blog.csdn.net/lengwuqin/article/details/26606785
【OpenCV学习笔记 013】处理视频序列 配套的源码下载