问题: 大部分主流互联网企业线上Server JVM选用了CMS收集器(如Taobao、LinkedIn、Vdian), 虽然CMS可与用户线程并发GC以降低STW时间, 但它也并非十分完美, 尤其是当出现
Concurrent Mode Failure由并行GC转入串行时, 将导致非常长时间的Stop The World(详细可参考JVM初探- 内存分配、GC原理与垃圾收集器).解决: 由GCIH可以联想到: 将长期存活的对象(如Local Cache)移入堆外内存(off-heap, 又名直接内存/direct-memory), 从而减少CMS管理的对象数量, 以降低Full GC的次数和频率, 达到提高系统响应速度的目的.
引入
这个idea最初来源于TaobaoJVM对OpenJDK定制开发的GCIH部分(详见撒迦的分享-JVM定制改进@淘宝), 其中GCIH就是将CMS Old Heap区的一部分划分出来, 这部分内存虽然还在堆内, 但已不被GC所管理.将长生命周期Java对象放在Java堆外, GC不能管理GCIH内Java对象(GC Invisible Heap):
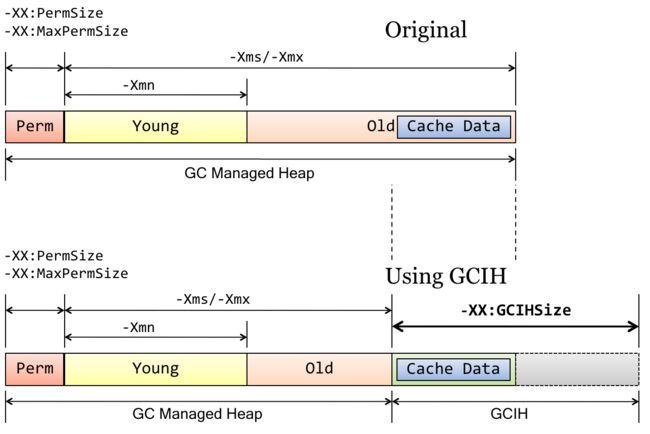
(图片来源: JVM@Taobao PPT)
- 这样做有两方面的好处:
- 减少GC管理内存:
由于GCIH会从Old区“切出”一块, 因此导致GC管理区域变小, 可以明显降低GC工作量, 提高GC效率, 降低Full GC STW时间(且由于这部分内存仍属于堆, 因此其访问方式/速度不变- 不必付出序列化/反序列化的开销). - GCIH内容进程间共享:
由于这部分区域不再是JVM运行时数据的一部分, 因此GCIH内的对象可供对个JVM实例所共享(如一台Server跑多个MR-Job可共享同一份Cache数据), 这样一台Server也就可以跑更多的VM实例.
- 减少GC管理内存:
(实际测试数据/图示可下载撒迦分享PPT).
但是大部分的互联公司不能像阿里这样可以有专门的工程师针对自己的业务特点定制JVM, 因此我们只能”眼馋”GCIH带来的性能提升却无法”享用”. 但通用的JVM开放了接口可直接向操作系统申请堆外内存(ByteBuffer or Unsafe), 而这部分内存也是GC所顾及不到的, 因此我们可用JVM堆外内存来模拟GCIH的功能(但相比GCIH不足的是需要付出serialize/deserialize的开销).
JVM堆外内存
在JVM初探 -JVM内存模型一文中介绍的Java运行时数据区域中是找不到堆外内存区域的:
因为它并不是JVM运行时数据区的一部分, 也不是Java虚拟机规范中定义的内存区域, 这部分内存区域直接被操作系统管理.
在JDK 1.4以前, 对这部分内存访问没有光明正大的做法: 只能通过反射拿到Unsafe类, 然后调用allocateMemory()/freeMemory()来申请/释放这块内存. 1.4开始新加入了NIO, 它引入了一种基于Channel与Buffer的I/O方式, 可以使用Native函数库直接分配堆外内存, 然后通过一个存储在Java堆里面的DirectByteBuffer对象作为这块内存的引用进行操作, ByteBuffer提供了如下常用方法来跟堆外内存打交道:
| API | 描述 |
|---|---|
static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) |
Allocates a new direct byte buffer. |
ByteBuffer put(byte b) |
Relative put method (optional operation). |
ByteBuffer put(byte[] src) |
Relative bulk put method (optional operation). |
ByteBuffer putXxx(Xxx value) |
Relative put method for writing a Char/Double/Float/Int/Long/Short value (optional operation). |
ByteBuffer get(byte[] dst) |
Relative bulk get method. |
Xxx getXxx() |
Relative get method for reading a Char/Double/Float/Int/Long/Short value. |
XxxBuffer asXxxBuffer() |
Creates a view of this byte buffer as a Char/Double/Float/Int/Long/Short buffer. |
ByteBuffer asReadOnlyBuffer() |
Creates a new, read-only byte buffer that shares this buffer’s content. |
boolean isDirect() |
Tells whether or not this byte buffer is direct. |
ByteBuffer duplicate() |
Creates a new byte buffer that shares this buffer’s content. |
下面我们就用通用的JDK API来使用堆外内存来实现一个local cache.
示例1.: 使用JDK API实现堆外Cache
注: 主要逻辑都集中在方法
invoke()内, 而AbstractAppInvoker是一个自定义的性能测试框架, 在后面会有详细的介绍.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
/**
* @author jifang
* @since 2016/12/31 下午6:05.
*/
public
class
DirectByteBufferApp
extends
AbstractAppInvoker {
@Test
@Override
public
void
invoke(Object... param) {
Map
// move in off-heap
byte
[] bytes = serializer.serialize(map);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(bytes.length);
buffer.put(bytes);
buffer.flip();
// for gc
map =
null
;
bytes =
null
;
System.out.println(
"write down"
);
// move out from off-heap
byte
[] offHeapBytes =
new
byte
[buffer.limit()];
buffer.get(offHeapBytes);
Map
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key =
"key-"
+ i;
FeedDO feedDO = deserMap.get(key);
checkValid(feedDO);
if
(i %
10000
==
0
) {
System.out.println(
"read "
+ i);
}
}
free(buffer);
}
private
Map
int
size) {
long
createTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Map
new
ConcurrentHashMap<>(size);
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < size; ++i) {
String key =
"key-"
+ i;
FeedDO value = createFeed(i, key, createTime);
map.put(key, value);
}
return
map;
}
}
|
由JDK提供的堆外内存访问API只能申请到一个类似一维数组的ByteBuffer, JDK并未提供基于堆外内存的实用数据结构实现(如堆外的Map、Set), 因此想要实现Cache的功能只能在write()时先将数据put()到一个堆内的HashMap, 然后再将整个Map序列化后MoveIn到DirectMemory, 取缓存则反之. 由于需要在堆内申请HashMap, 因此可能会导致多次Full GC. 这种方式虽然可以使用堆外内存, 但性能不高、无法发挥堆外内存的优势.
幸运的是开源界的前辈开发了诸如Ehcache、MapDB、Chronicle Map等一系列优秀的堆外内存框架, 使我们可以在使用简洁API访问堆外内存的同时又不损耗额外的性能.
其中又以Ehcache最为强大, 其提供了in-heap、off-heap、on-disk、cluster四级缓存, 且Ehcache企业级产品(BigMemory Max / BigMemoryGo)实现的BigMemory也是Java堆外内存领域的先驱.
示例2: MapDB API实现堆外Cache
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
public
class
MapDBApp
extends
AbstractAppInvoker {
private
static
HTreeMap
static
{
mapDBCache = DBMaker.hashMapSegmentedMemoryDirect()
.expireMaxSize(SIZE)
.make();
}
@Test
@Override
public
void
invoke(Object... param) {
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key =
"key-"
+ i;
FeedDO feed = createFeed(i, key, System.currentTimeMillis());
mapDBCache.put(key, feed);
}
System.out.println(
"write down"
);
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key =
"key-"
+ i;
FeedDO feedDO = mapDBCache.get(key);
checkValid(feedDO);
if
(i %
10000
==
0
) {
System.out.println(
"read "
+ i);
}
}
}
}
|
结果 & 分析
- DirectByteBufferApp
|
1
2
|
S0 S1 E O P YGC YGCT FGC FGCT GCT
0.00 0.00 5.22 78.57 59.85 19 2.902 13 7.251 10.153
|
- the last one jstat of MapDBApp
|
1
2
|
S0 S1 E O P YGC YGCT FGC FGCT GCT
0.00 0.03 8.02 0.38 44.46 171 0.238 0 0.000 0.238
|
运行
DirectByteBufferApp.invoke()会发现有看到很多Full GC的产生, 这是因为HashMap需要一个很大的连续数组, Old区很快就会被占满, 因此也就导致频繁Full GC的产生.
而运行MapDBApp.invoke()可以看到有一个DirectMemory持续增长的过程, 但FullGC却一次都没有了.
实验: 使用堆外内存减少Full GC
实验环境
- java -version
|
1
2
3
|
java version "1.7.0_79"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_79-b15)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.79-b02, mixed mode)
|
- VM Options
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
-Xmx512M
-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=512M
-XX:+PrintGC
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC
-XX:+CMSClassUnloadingEnabled
-XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction=80
-XX:+UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly
|
- 实验数据
170W条动态(FeedDO).
实验代码
第1组: in-heap、affect by GC、no serialize
- ConcurrentHashMapApp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public
class
ConcurrentHashMapApp
extends
AbstractAppInvoker {
private
static
final
Map
new
ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Test
@Override
public
void
invoke(Object... param) {
// write
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key = String.format(
"key_%s"
, i);
FeedDO feedDO = createFeed(i, key, System.currentTimeMillis());
cache.put(key, feedDO);
}
System.out.println(
"write down"
);
// read
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key = String.format(
"key_%s"
, i);
FeedDO feedDO = cache.get(key);
checkValid(feedDO);
if
(i %
10000
==
0
) {
System.out.println(
"read "
+ i);
}
}
}
}
|
GuavaCacheApp类似, 详细代码可参考完整项目.
第2组: off-heap、not affect by GC、need serialize
- EhcacheApp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
public
class
EhcacheApp
extends
AbstractAppInvoker {
private
static
Cache
static
{
ResourcePools resourcePools = ResourcePoolsBuilder.newResourcePoolsBuilder()
.heap(
1000
, EntryUnit.ENTRIES)
.offheap(
480
, MemoryUnit.MB)
.build();
CacheConfiguration
.newCacheConfigurationBuilder(String.
class
, FeedDO.
class
, resourcePools)
.build();
cache = CacheManagerBuilder.newCacheManagerBuilder()
.withCache(
"cacher"
, configuration)
.build(
true
)
.getCache(
"cacher"
, String.
class
, FeedDO.
class
);
}
@Test
@Override
public
void
invoke(Object... param) {
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key = String.format(
"key_%s"
, i);
FeedDO feedDO = createFeed(i, key, System.currentTimeMillis());
cache.put(key, feedDO);
}
System.out.println(
"write down"
);
// read
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key = String.format(
"key_%s"
, i);
Object o = cache.get(key);
checkValid(o);
if
(i %
10000
==
0
) {
System.out.println(
"read "
+ i);
}
}
}
}
|
MapDBApp与前同.
第3组: off-process、not affect by GC、serialize、affect by process communication
- LocalRedisApp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
public
class
LocalRedisApp
extends
AbstractAppInvoker {
private
static
final
Jedis cache =
new
Jedis(
"localhost"
,
6379
);
private
static
final
IObjectSerializer serializer =
new
Hessian2Serializer();
@Test
@Override
public
void
invoke(Object... param) {
// write
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key = String.format(
"key_%s"
, i);
FeedDO feedDO = createFeed(i, key, System.currentTimeMillis());
byte
[] value = serializer.serialize(feedDO);
cache.set(key.getBytes(), value);
if
(i %
10000
==
0
) {
System.out.println(
"write "
+ i);
}
}
System.out.println(
"write down"
);
// read
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < SIZE; ++i) {
String key = String.format(
"key_%s"
, i);
byte
[] value = cache.get(key.getBytes());
FeedDO feedDO = serializer.deserialize(value);
checkValid(feedDO);
if
(i %
10000
==
0
) {
System.out.println(
"read "
+ i);
}
}
}
}
|
RemoteRedisApp类似, 详细代码可参考下面完整项目.
实验结果
| * | ConcurrentMap | Guava |
|---|---|---|
| TTC | 32166ms/32s | 47520ms/47s |
| Minor C/T | 31/1.522 | 29/1.312 |
| Full C/T | 24/23.212 | 36/41.751 |
| MapDB | Ehcache | |
| TTC | 40272ms/40s | 30814ms/31s |
| Minor C/T | 511/0.557 | 297/0.430 |
| Full C/T | 0/0.000 | 0/0.000 |
| LocalRedis | NetworkRedis | |
| TTC | 176382ms/176s | 1h+ |
| Minor C/T | 421/0.415 | - |
| Full C/T | 0/0.000 | - |
备注:
- TTC: Total Time Cost 总共耗时
- C/T: Count/Time 次数/耗时(seconds)
结果分析
对比前面几组数据, 可以有如下总结:
- 将长生命周期的大对象(如cache)移出heap可大幅度降低Full GC次数与耗时;
- 使用off-heap存储对象需要付出serialize/deserialize成本;
- 将cache放入分布式缓存需要付出进程间通信/网络通信的成本(UNIX Domain/TCP IP)
附:
off-heap的Ehcache能够跑出比in-heap的HashMap/Guava更好的成绩确实是我始料未及的O(∩_∩)O~, 但确实这些数据和堆内存的搭配导致in-heap的Full GC太多了, 当heap堆开大之后就肯定不是这个结果了. 因此在使用堆外内存降低Full GC前, 可以先考虑是否可以将heap开的更大.
附: 性能测试框架
在main函数启动时, 扫描
com.vdian.se.apps包下的所有继承了AbstractAppInvoker的类, 然后使用Javassist为每个类生成一个代理对象: 当invoke()方法执行时首先检查他是否标注了@Test注解(在此, 我们借用junit定义好了的注解), 并在执行的前后记录方法执行耗时, 并最终对比每个实现类耗时统计.
- 依赖
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>org.apache.commons
<
artifactId
>commons-proxy
<
version
>${commons.proxy.version}
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>org.javassist
<
artifactId
>javassist
<
version
>${javassist.version}
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>com.caucho
<
artifactId
>hessian
<
version
>${hessian.version}
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>com.google.guava
<
artifactId
>guava
<
version
>${guava.version}
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>junit
<
artifactId
>junit
<
version
>${junit.version}
|
启动类: OffHeapStarter
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
/**
* @author jifang
* @since 2017/1/1 上午10:47.
*/
public
class
OffHeapStarter {
private
static
final
Map
new
HashMap<>();
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
IOException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Set
"com.vdian.se.apps"
);
for
(Class clazz : classes) {
AbstractAppInvoker invoker = createProxyInvoker(clazz.newInstance());
invoker.invoke();
//System.gc();
}
System.out.println(
"********************* statistics **********************"
);
for
(Map.Entry
System.out.println(
"method ["
+ entry.getKey() +
"] total cost ["
+ entry.getValue() +
"]ms"
);
}
}
private
static
AbstractAppInvoker createProxyInvoker(Object invoker) {
ProxyFactory factory =
new
JavassistProxyFactory();
Class superclass = invoker.getClass().getSuperclass();
Object proxy = factory
.createInterceptorProxy(invoker,
new
ProfileInterceptor(),
new
Class[]{superclass});
return
(AbstractAppInvoker) proxy;
}
private
static
class
ProfileInterceptor
implements
Interceptor {
@Override
public
Object intercept(Invocation invocation)
throws
Throwable {
Class clazz = invocation.getProxy().getClass();
Method method = clazz.getMethod(invocation.getMethod().getName(), Object[].
class
);
Object result =
null
;
if
(method.isAnnotationPresent(Test.
class
)
&& method.getName().equals(
"invoke"
)) {
String methodName = String.format(
"%s.%s"
, clazz.getSimpleName(), method.getName());
System.out.println(
"method ["
+ methodName +
"] start invoke"
);
long
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
result = invocation.proceed();
long
cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println(
"method ["
+ methodName +
"] total cost ["
+ cost +
"]ms"
);
STATISTICS_MAP.put(methodName, cost);
}
return
result;
}
}
}
|
- 包扫描工具: PackageScanUtil
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|