ROS进阶——通过MoveIt!控制实体机械臂PC层
环境:Ubuntu16.04+ROS Kinetic
硬件:
Arduino mega2560(需拥有两个串口)
总线舵机(可采用dynamixel舵机,其带有ROS的功能包dynamixel_controllersTutorials)
前期准备:
- 完成MoveIt!配置
- 完成机器人在ROS平台的搭建
一、修改功能包中文件
1.1、config文件夹
参考fake_controllers.yaml创建controllers.yaml
fake_controllers.yaml
controller_list:
- name: fake_hand_controller
joints:
- Joint_1
- Joint_2
- Joint_3
- Joint_4
- Joint_5
- Joint_6
- name: fake_tip_controller
joints:
[]controllers.yaml
controller_list:
- name: six_hand_controller
action_ns: follow_joint_trajectory
type: FollowJointTrajectory
default: true
joints:
- Joint_1
- Joint_2
- Joint_3
- Joint_4
- Joint_5
- Joint_6
- name: six_tip_controller
action_ns: gripper_action
type: GipperCommand
default: true
joints:
[]相关内容参考:
FollowJointTrajectory 控制器接口
参数:
- name: 控制器名称
- action_ns: 控制器的action命令空间
- type: 已使用的action类型
- default: 默认的控制器是MOVEit选择的主控制器!用于与一组特定的关节进行通信的
- joints: 被此接口寻址的所有关节的名称
GripperCommand 控制器接口
参数:
- name: 控制器名称
- action_ns: 控制器的action命令空间.
- type: 已使用的action类型
- default: 默认的控制器是MOVEit选择的主控制器!用于与一组特定的关节进行通信的
- joints: 被此接口寻址的所有关节的名称
1.2、launch文件夹
(1) 修改robothand_moveit_controller_manager.launch.xml
(2) 新建文件moveit_planning_execution.launch
# The planning and execution components of MoveIt! configured to
# publish the current configuration of the robot (simulated or real)
# and the current state of the world as seen by the planner
[/move_group/robothand_controller_joint_states]
二、修改MoveIt默认逆解算法
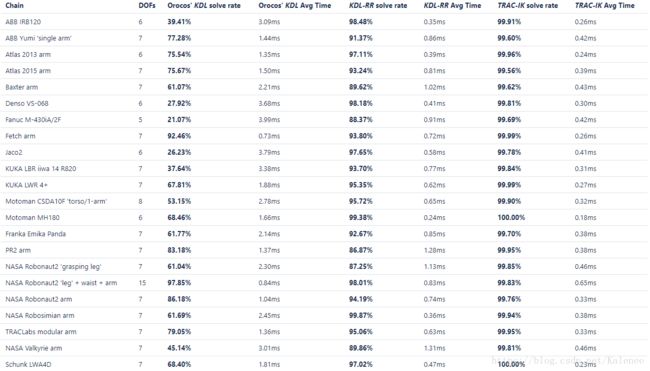
修改:数值解因其算法本身缺陷,容易导致同样目标位置出现多次规划不同解,可采用几何解代替解析解解决这一问高题并提高运算速度和成功率:https://blog.csdn.net/kalenee/article/details/80740258。
因Moveit自带的逆解包成功率较低及解算速度较慢,因此改用trac_ik。
链接:https://bitbucket.org/traclabs/trac_ik
逆解算法效率对比:
安装流程
(1)安装依赖
sudo apt-get install libnlopt-dev(2)下载trac_ik_kinematics_plugin和trac_ik_lib,将其放置在工作空间的src目录下,并添加到文件的依赖功能包中
(3)修改config目录下的kinematics.yaml
hand:
kinematics_solver: trac_ik_kinematics_plugin/TRAC_IKKinematicsPlugin
kinematics_solver_search_resolution: 0.005
kinematics_solver_timeout: 0.005
kinematics_solver_attempts: 3
三、配置ROS串口通讯
3.1、安装serial功能包
sudo apt-get install ros--serial 3.2、编写串口通讯节点
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "robothand_hard_driver");
FollowJointTrajectoryAction followJointTrajectoryAction("six_hand_controller/follow_joint_trajectory");
//serial
ros::NodeHandle n_("~");
std::string serial_port;
n_.getParam("port", serial_port);
ROS_INFO("port:%s",serial_port.c_str());
serial::Serial ser;
try
{
ser.setPort(serial_port);//串口端口
ser.setBaudrate(57600);//串口波特率
serial::Timeout To=serial::Timeout::simpleTimeout(10000);
ser.setTimeout(To);
ser.open();
}
catch(serial::IOException& e)
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("serial port open unsuccessfully");
return -1;
}
if(ser.isOpen())
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("serial port open successfully");
}
else
{
return -1;
}
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
四、实体机械臂控制通讯
4.1、actionlib包的简介(http://wiki.ros.org/actionlib)
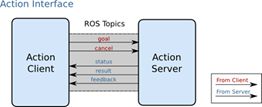
在ROS平台上构建机器人系统过程中,一般情况下会使用服务机制(services)来实现发送消息到某个节点来执行任务并接收该请求回复。但在某些情况下,服务需要很长时间才能完成任务的执行,因此若需要在这个过程中取消请求或者定期获得有关请求如何进展的反馈,就需要通过actionlib包实现。actionlib包可提供用于创建可被抢占的目标服务器的工具,即使该服务器处于长期执行任务中,同时其提供一个客户端接口,便于向该服务器发送请求。用actionlib包创建的客户端(ActionClient)和服务器(ActionServer)的信息交流类型和方式如下图所示。
为了实现客户端和服务器进行通信,ROS定义了一些标准的通信消息,用于规范两者的工作,包括目标(Goal),反馈(Feedback)和结果(Result)。
(1)目标(Goal):目标是由ActionClient发送到ActionServer的一种通讯消息,其包含的信息为控制对象需要完成的动作。在本课题中,控制对象为六轴机械臂,为了实现机械臂的运动控制,目标信息里将包含关节角度,速度,加速度和时间帧。
(2)反馈(Feedback):反馈的作用在于提供给ActionServer一种用于传递任务执行状况给ActionClient的方法。在本课题中,为保证ROS平台中建立的模型与实体模型处于相同状态,在进行运动规划输出时,需要获取姿态的反馈。
(3) 结果(Result):在完成任务的执行后,ActionServer会发送将结果信息到ActionClient,其与反馈不同的地方在于,在整个任务的执行过程中只发送一次。在本课题中,结果信息主要用于反馈任务执行是否成功及机械臂的最终姿态。
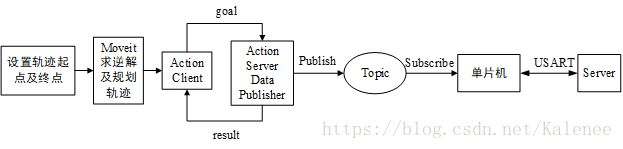
4.2、机械臂控制通讯流程
(1)首先,设置机械臂的初始姿态,其姿态需与实体机械臂的姿态一致,否则规划的运动会出现偏差,然后设置机械臂需要到达的终点坐标及其末端姿态。
(2)其次,使用预设置好的逆运动学算法插件计算机械臂运动学逆解并使用Moveit的运动规划完成设定起点到终点的轨迹规划。
(3)然后通过ActionClient接收规划结果并以目标信息的格式发送到ActionServer中,在ActionServer对数据进行二次处理,将规划的关节角度转换为关节舵机的控制信号,同时对整体数据进行缩减,重新规划中间姿态的密度。ActionServer完成数据的处理后,会发送结果信息到ActionClient,以接收下一批数据,同时将规划好的数据通过发布器发送到主题上。
(4)最后下位机通过监听该主题,实时检测运动规划的结果是否发布,当监测到主题上有数据发布,下位机会将所有数据接收下来,然后检测数据是否有效,若有效则对数据按照不同关节再次进行处理并发送到对应关节舵机,最终实现对实体机械臂的控制。
注意
(1)请注意避免对同一轨迹进行多次规划,容易造成奔溃,同时可根据情况选用不同的解算器,可以用较短的时间获得最优路径。
(2)接收Client发送的goal数据时,尽量采用指针,当赋值到数组前,需设定等量大小的数组。
(3)Arduino中应尽量避免使用延时函数,同时订阅器的回调函数内应减少数据操作,单纯以接收数据为主,同时在发送数据时,采用定时器避免使用for循环,若使arduino进入较长循环或延迟中,容易导致上下位机连接断开。
五、代码实现
5.1、配置控制接口
control_msgs/FollowJointTrajectoryAction Message内容
FollowJointTrajectoryActionGoal action_goal
Header header
uint32 seq
time stamp
string frame_id
actionlib_msgs/GoalID goal_id
time stamp
string id
control_msgs/FollowJointTrajectoryGoal goal
trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectory trajectory
Header header
uint32 seq
time stamp
string frame_id
string[] joint_names
trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectoryPoint[] points
float64[] positions
float64[] velocities
float64[] accelerations
duration time_from_start
control_msgs/JointTolerance[] path_tolerance
string name
float64 position
float64 velocity
float64 acceleration
control_msgs/JointTolerance[] goal_tolerance
string name
float64 position
float64 velocity
float64 acceleration
duration goal_time_tolerance
FollowJointTrajectoryActionResult action_result
Header header
uint32 seq
time stamp
string frame_id
actionlib_msgs/GoalStatus status
uint8 PENDING=0
uint8 ACTIVE=1
uint8 PREEMPTED=2
uint8 SUCCEEDED=3
uint8 ABORTED=4
uint8 REJECTED=5
uint8 PREEMPTING=6
uint8 RECALLING=7
uint8 RECALLED=8
uint8 LOST=9
actionlib_msgs/GoalID goal_id
time stamp
string id
uint8 status
string text
control_msgs/FollowJointTrajectoryResult result
int32 SUCCESSFUL=0
int32 INVALID_GOAL=-1
int32 INVALID_JOINTS=-2
int32 OLD_HEADER_TIMESTAMP=-3
int32 PATH_TOLERANCE_VIOLATED=-4
int32 GOAL_TOLERANCE_VIOLATED=-5
int32 error_code
FollowJointTrajectoryActionFeedback action_feedback
Header header
uint32 seq
time stamp
string frame_id
actionlib_msgs/GoalStatus status
uint8 PENDING=0
uint8 ACTIVE=1
uint8 PREEMPTED=2
uint8 SUCCEEDED=3
uint8 ABORTED=4
uint8 REJECTED=5
uint8 PREEMPTING=6
uint8 RECALLING=7
uint8 RECALLED=8
uint8 LOST=9
actionlib_msgs/GoalID goal_id
time stamp
string id
uint8 status
string text
control_msgs/FollowJointTrajectoryFeedback feedback
Header header
uint32 seq
time stamp
string frame_id
string[] joint_names
trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectoryPoint desired
float64[] positions
float64[] velocities
float64[] accelerations
duration time_from_start
trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectoryPoint actual
float64[] positions
float64[] velocities
float64[] accelerations
duration time_from_start
trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectoryPoint error
float64[] positions
float64[] velocities
float64[] accelerations
duration time_from_start基本代码实现,接收到goal后会调用回调函数处理,完成处理后通过as_.setSucceeded(result)返回处理成功与否。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class FollowJointTrajectoryAction
{
public:
FollowJointTrajectoryAction(std::string name) :
as_(nh_, name, false),
action_name_(name)
{
as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&FollowJointTrajectoryAction::goalCB, this));
as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&FollowJointTrajectoryAction::preemptCB, this));
as_.start();
ROS_INFO("action start");
}
~FollowJointTrajectoryAction(void)
{
}
void goalCB()
{
ROS_INFO("goal is receive");
if(as_.isNewGoalAvailable())
{
}
else
{
ROS_INFO("goal is not available");
}
control_msgs::FollowJointTrajectoryResult result;
result.error_code = 0;
as_.setSucceeded(result);
}
void preemptCB()
{
ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
// set the action state to preempted
as_.setPreempted();
}
protected:
ros::NodeHandle nh_;
actionlib::SimpleActionServer as_;
std::string action_name_;
}; 注意:当使用Arduino作为下位机时,在单次发送中,下位机能接收的数据大小存在一定限制,因此需进行了压缩,将其限制为36个,根据实际需要可进行扩展,但最好不要超过40个,根据网上资料为Arduino的串口缓存区对单次接收数据大小进行了限制,解决方法为修改ros_lib文件夹中的ros.h及ros文件夹中的node_handle.cpp。
5.2、配置机械臂实物姿态发布器joint_state_publish
在控制实体机械臂的时候需要将机械臂的姿态发布到/joint_states话题中,否则不会更新moveit中机械臂的初始姿态。在使用MoveItFakeControllerManager时,move_group会把机械臂在虚拟空间中的姿态发布到/joint_states话题,因此当使用虚拟控制接口进行算法验证时,不需要机械臂实物姿态发布器也可以更新moveit中机械臂的初始姿态。但用MoveItSimpleControllerManager后,move_group不会把机械臂在虚拟空间中的姿态发布到/joint_states话题,需要自行编写实物姿态发布器,否则会发生每一次规划的启动都是最开始的姿态而不是输出后的姿态的错误。
实物姿态发布的话题定义在moveit_planning_execution.launch中。
[/move_group/robothand_controller_joint_states]
因实物机械臂并没角度反馈,无法获得实际姿态,因此通过获取获取规划的最后一组数据作为机械臂运动输出后的实际状态,发送到/move_group/robothand_controller_joint_states,/joint_states会通过其获取机械臂状态。
参考:http://wiki.ros.org/urdf/Tutorials/Using%20urdf%20with%20robot_state_publisher
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class FollowJointTrajectoryAction
{
public:
FollowJointTrajectoryAction(std::string name) :
as_(nh_, name, false),
action_name_(name)
{
as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&FollowJointTrajectoryAction::goalCB, this));
as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&FollowJointTrajectoryAction::preemptCB, this));
as_.start();
Pub_jint = nh_.advertise("/move_group/robothand_controller_joint_states",10);
js.name.resize(6);
js.position.resize(6);
js.name[0] = "Joint_1";
js.name[1] = "Joint_2";
js.name[2] = "Joint_3";
js.name[3] = "Joint_4";
js.name[4] = "Joint_5";
js.name[5] = "Joint_6";
ROS_INFO("action start");
}
~FollowJointTrajectoryAction(void)
{
}
void goalCB()
{
ROS_INFO("goal is receive");
double points_end[6];
if(as_.isNewGoalAvailable())
{
js.position.clear();
points_=&(as_.acceptNewGoal()->trajectory.points);
Pos_length=points_->size();
for(int co =0; co<6;co++)
{
points_end[co] = points_->at(Pos_length-1).positions[co];// points_[Pos_length-6+co];
js.position.push_back(points_->at(Pos_length-1).positions[co]);
}
js.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
Pub_jint.publish(js);
}
else
{
ROS_INFO("goal is not available");
}
control_msgs::FollowJointTrajectoryResult result;
result.error_code = 0;
as_.setSucceeded(result);
}
void preemptCB()
{
ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
// set the action state to preempted
as_.setPreempted();
}
protected:
sensor_msgs::JointState js;
ros::NodeHandle nh_;
ros::Publisher Pub_jint;
actionlib::SimpleActionServer as_;
//to the client
control_msgs::FollowJointTrajectoryResult result_;
//receive
control_msgs::FollowJointTrajectoryGoal goal_;
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "robothand_hard_driver");
FollowJointTrajectoryAction followJointTrajectoryAction("six_hand_controller/follow_joint_trajectory");
ros::spin();
return 0;
} 注意:name要与关节定义名字一致。
参考
《ros by example vol 2 indigo》第11章 Arm Navigation using MoveIt!
《ros by example vol 1 indigo》
https://www.ncnynl.com/archives/201703/1425.html
https://www.ncnynl.com/archives/201610/1044.html