操作系统实验四之实现shell
一、题目
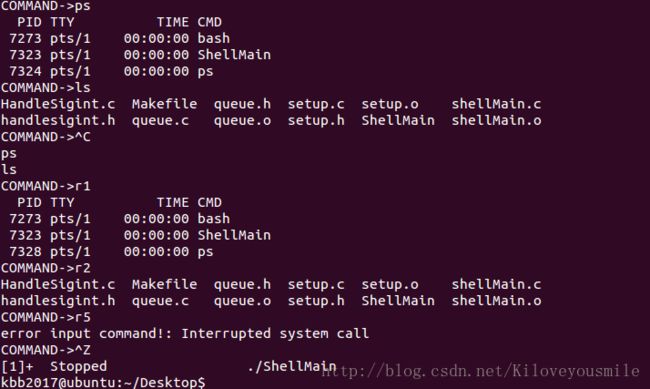
实现简单的shell, 程序可以在后台运行,按下ctrl+c系统不会终止shell。实现历史记录功能,按下ctrl+c展示最近10条命令,使用“rx”执行其中的命令,x 代表第x条命令。
二、基础知识
1. read函数
include
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
/**
返回值:
(1)成功读取,则返回读取的字节数,
(2)出错返回-1并设置errno
(3)若在调read之前已到达文件末尾,则返回0
count
是请求读取的字节数,读上来的数据保存在缓冲区buf中,
同时文件的当前读写位置向后移。
有些情况下,实际读到的字节数(返回值)会小于请求读的字节数count,
例如:读常规文件时,在读到count个字节之前已到达文件末尾。
例如:距文件末尾还有30个字节而请求读100个字节,则read返回30,下次read将返回0。
*/ 2. perror
#include这个头文件,perror是包含在这个文件里的
perror( )用来将上一个函数发生错误的原因输出到标准设备(stderr)。
参数 s所代表的字符串会先打印出,后面再加上错误原因字符串。
此错误原因依照全局变量errno 的值来决定要输出的字符串。
*/
//eg:
#include三、实验代码
setup.h
#include setup.c
#include "setup.h"
void setup(char *inputBuffer, char *args[], int *background){
int length;//命令的字符数目
int i;//循环变量
int start;//命令的第一个字符位置
int ct;//下一个参数存入args[]的位置
ct = 0;
/**
*读入命令行字符,存入inputBuffer
*/
length = read(STDIN_FILENO, inputBuffer, MAX_LINE);
start = -1;
if(length == 0) exit(0);
if(length < 0){//ctrl+c will read error, and return null
args[0] = NULL;
//perror("error reading the command.");
return;//输入ctrl+c时,会进入错误读取。从而退出setup函数,避免异常
}
//int len = strlen(inputBuffer);
/*
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
printf("%c\n",inputBuffer[i]);
}
*/
//printf("%d\n", len);
if(inputBuffer[0] == 'r' && isdigit(inputBuffer[1]) && (inputBuffer[2] == '\n' || inputBuffer[2] == '\t')){
//按下rx,重载第x条命令
char *str;
if((str = gethistory(inputBuffer[1] - '0')) == NULL){
perror("error input command!");//x 大于现有历史记录条数
return;
}
else
strcpy(inputBuffer, str);
//printf("%s\n", str);
inputBuffer[strlen(str)] = '\n';//便于下面代码统一读取inputBuffer
inputBuffer[strlen(str)+1] = '\0';//添加结束符
length = strlen(str)+1;
}
//检查inputBuffer中每一个char
for(int i = 0; iswitch(inputBuffer[i]){
case ' ':
case '\t'://字符为参数的空格或者Tab
if(start != -1){
args[ct] = &inputBuffer[start];
ct++;
}
inputBuffer[i] = '\0'; //设置c string 的结束符
start= -1;
break;
case '\n': //命令行结束符
if(start != -1){
args[ct] = &inputBuffer[start];
ct++;
}
inputBuffer[i] = '\0';
args[ct] = NULL;
break;
default: //其他字符
if(start == -1) start = i;
if(inputBuffer[i] == '&'){
*background = 1;
inputBuffer[i] = '\0';
}
}
}
add(inputBuffer);//添加历史记录
args[ct] = NULL;//命令字符数 > 80
} queue.h
#include queue.c
#include "queue.h"
void add( char *str){
if( queue.front == -1)//history是否为空
{
strcpy(queue.history[queue.rear], str);
queue.front = queue.rear;
return;
}
queue.rear = (queue.rear + 1) % HISTORYNUM;
strcpy(queue.history[queue.rear], str);
if(queue.front == queue.rear) queue.front++;
}
void print(){
if(queue.front == -1){
printf("No comand!");
return;
}
int index = queue.front;
printf("\n");
fflush(stdout);
while((index % HISTORYNUM) != (queue.rear + 1)){
printf("%s\n", queue.history[index]);
fflush(stdout);
index++;
}
}
char *gethistory(int index){
if(index > getNum() || index <= 0)
return NULL;
int count = 1;
int temp = queue.front;
while(count < index){
count++;
temp = (temp + 1) % HISTORYNUM;
}
return queue.history[temp];
}
int getNum(){
return (queue.rear + HISTORYNUM - queue.front + 1) % HISTORYNUM;
}shellMain.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "setup.h"
//#include "queue.h"
void handle_SIGINT();
int main(void){
char inputBuffer[MAX_LINE];//这个缓存用来存放输入的命令
int background;// == 1时,表示在后台运行命令,即在命令后加上“*”
char *args[MAX_LINE/2+1];//命令最多40个参数
pid_t pid;
struct sigaction hander;
queue.front = -1;
queue.rear = 0;
while(1){//程序在setup中正常结束
background = 0;
printf("COMMAND->");
fflush(stdout);//输出
setup(inputBuffer, args, &background);
//这一步要做
if((pid = fork()) == -1) { printf("Fork Error.\n"); }
if(pid == 0) { execvp(args[0], args); exit(0); }
if(background == 0) { wait(0); }
/**
*生成输出消息
*/
//strcpy(buffer, "Caught Control C\n");
/**
*创建信号处理器
*/
hander.sa_handler = (void (*)(int))handle_SIGINT;
sigaction(SIGINT, &hander, NULL);
/**
*循环运行,直到收到ctrl+c
*/
//while(1);
}
return 0;
}
void handle_SIGINT(){
print();
signal(SIGINT, SIG_IGN);
//exit(0);
} 如果喜欢命令行,编译,可以使用以下Makefile.
ShellMain: shellMain.o setup.o queue.o
gcc -std=c99 shellMain.o setup.o queue.o -o ShellMain
shellMain.o: shellMain.c
gcc -c -std=c99 -D_XOPEN_SOURCE=600 shellMain.c
setup.o: setup.c setup.h
gcc -c -std=c99 setup.c
queue.o: queue.c queue.h
gcc -c queue.c
clean:
rm ShellMain shellMain.o setup.o queue.o四、实验结果
这次实验到这里就结束了,希望对大家有帮助。