最短路径问题---SPEA算法详解
1、最短路径问题介绍
问题解释:
从图中的某个顶点出发到达另外一个顶点的所经过的边的权重和最小的一条路径,称为最短路径
解决问题的算法:
- 迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra算法)
- 弗洛伊德算法(Floyd算法)
- SPFA算法
之前已经对Dijkstra算法和Floyd算法做了介绍(不懂的可以看这篇博客:Dijkstra算法详解、Floyd算法详解),所以这篇博客打算对SPFA算法做详细的的介绍。
2、SPFA算法介绍
SPFA算法是求解单源最短路径问题的一种算法,由理查德·贝尔曼(Richard Bellman) 和 莱斯特·福特 创立的。有时候这种算法也被称为 Moore-Bellman-Ford 算法,因为 Edward F. Moore 也为这个算法的发展做出了贡献。它的原理是对图进行V-1次松弛操作,得到所有可能的最短路径。其优于迪科斯彻算法的方面是边的权值可以为负数、实现简单,缺点是时间复杂度过高,高达 O(VE)。但算法可以进行若干种优化,提高了效率。
算法的思路:
我们用数组dis记录每个结点的最短路径估计值,用邻接表或邻接矩阵来存储图G。我们采取的方法是动态逼近法:设立一个先进先出的队列用来保存待优化的结点,优化时每次取出队首结点u,并且用u点当前的最短路径估计值对离开u点所指向的结点v进行松弛操作,如果v点的最短路径估计值有所调整,且v点不在当前的队列中,就将v点放入队尾。这样不断从队列中取出结点来进行松弛操作,直至队列空为止
我们要知道带有负环的图是没有最短路径的,所以我们在执行算法的时候,要判断图是否带有负环,方法有两种:
- 开始算法前,调用拓扑排序进行判断(一般不采用,浪费时间)
- 如果某个点进入队列的次数超过N次则存在负环(N为图的顶点数)
3、SPFA算法手动操作过程
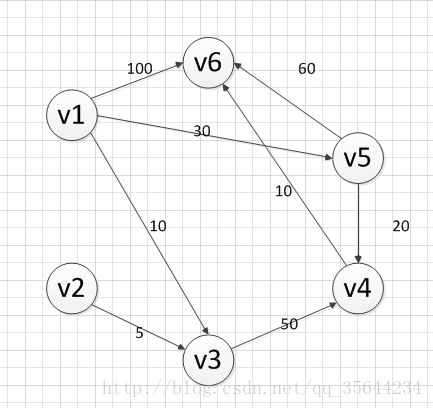
下面我们采用SPFA算法对下图求v1到各个顶点的最短路径,通过手动的方式来模拟SPFA每个步骤的过程
- 初始化:
首先我们先初始化数组dis如下图所示:(除了起点赋值为0外,其他顶点的对应的dis的值都赋予无穷大,这样有利于后续的松弛) 
此时,我们还要把v1如队列:{v1}
现在进入循环,直到队列为空才退出循环。
- 第一次循环:
首先,队首元素出队列,即是v1出队列,然后,对以v1为弧尾的边对应的弧头顶点进行松弛操作,可以发现v1到v3,v5,v6三个顶点的最短路径变短了,更新dis数组的值,得到如下结果: 
我们发现v3,v5,v6都被松弛了,而且不在队列中,所以要他们都加入到队列中:{v3,v5,v6}
- 第二次循环
此时,队首元素为v3,v3出队列,然后,对以v3为弧尾的边对应的弧头顶点进行松弛操作,可以发现v1到v4的边,经过v3松弛变短了,所以更新dis数组,得到如下结果: 
此时只有v4对应的值被更新了,而且v4不在队列中,则把它加入到队列中:{v5,v6,v4}
- 第三次循环
此时,队首元素为v5,v5出队列,然后,对以v5为弧尾的边对应的弧头顶点进行松弛操作,发现v1到v4和v6的最短路径,经过v5的松弛都变短了,更新dis的数组,得到如下结果: 
我们发现v4、v6对应的值都被更新了,但是他们都在队列中了,所以不用对队列做任何操作。队列值为:{v6,v4}
第四次循环
此时,队首元素为v6,v6出队列,然后,对以v6为弧尾的边对应的弧头顶点进行松弛操作,发现v6出度为0,所以我们不用对dis数组做任何操作,其结果和上图一样,队列同样不用做任何操作,它的值为:{v4}第五次循环
此时,队首元素为v4,v4出队列,然后,对以v4为弧尾的边对应的弧头顶点进行松弛操作,可以发现v1到v6的最短路径,经过v4松弛变短了,所以更新dis数组,得到如下结果:
因为我修改了v6对应的值,而且v6也不在队列中,所以我们把v6加入队列,{v6}
- 第六次循环
此时,队首元素为v6,v6出队列,然后,对以v6为弧尾的边对应的弧头顶点进行松弛操作,发现v6出度为0,所以我们不用对dis数组做任何操作,其结果和上图一样,队列同样不用做任何操作。所以此时队列为空。
OK,队列循环结果,此时我们也得到了v1到各个顶点的最短路径的值了,它就是dis数组各个顶点对应的值,如下图: 
4、SPFA算法的代码实现
核心代码:
bool Graph::SPFA(int begin) {
bool *visit;
//visit用于记录是否在队列中
visit = new bool[this->vexnum];
int *input_queue_time;
//input_queue_time用于记录某个顶点入队列的次数
//如果某个入队列的次数大于顶点数vexnum,那么说明这个图有环,
//没有最短路径,可以退出了
input_queue_time = new int[this->vexnum];
queue<int> s; //队列,用于记录最短路径被改变的点
/*
各种变量的初始化
*/
int i;
for (i = 0; i < this->vexnum; i++) {
visit[i] = false;
input_queue_time[i] = 0;
//路径开始都初始化为直接路径,长度都设置为无穷大
dis[i].path = this->node[begin-1].data + "-->" + this->node[i].data;
dis[i].weight = INT_MAX;
}
//首先是起点入队列,我们记住那个起点代表的是顶点编号,从1开始的
s.push(begin - 1);
visit[begin - 1] = true;
++input_queue_time[begin-1];
//
dis[begin - 1].path =this->node[begin - 1].data;
dis[begin - 1].weight = 0;
int temp;
int res;
ArcNode *temp_node;
//进入队列的循环
while (!s.empty()) {
//取出队首的元素,并且把队首元素出队列
temp = s.front(); s.pop();
//必须要保证第一个结点不为空
if (node[temp].firstarc)
{
temp_node = node[temp].firstarc;
while (temp_node) {
//如果边的权重加上temp这个点的最短路径
//小于之前temp_node的最短路径的长度,则更新
//temp_node的最短路径的信息
if (dis[temp_node->adjvex].weight > (temp_node->weight + dis[temp].weight)) {
//更新dis数组的信息
dis[temp_node->adjvex].weight = temp_node->weight + dis[temp].weight;
dis[temp_node->adjvex].path = dis[temp].path + "-->" + node[temp_node->adjvex].data;
//如果还没在队列中,加入队列,修改对应的信息
if (!visit[temp_node->adjvex]) {
visit[temp_node->adjvex] = true;
++input_queue_time[temp_node->adjvex];
s.push(temp_node->adjvex);
if (input_queue_time[temp_node->adjvex] > this->vexnum) {
cout << "图中有环" << endl;
return false;
}
}
}
temp_node = temp_node->next;
}
}
}
//打印最短路径
return true;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
上面我们给出了核心代码,下面我给出完整的代码:
- SPFA.h文件代码
/************************************************************/
/* 程序作者:Willam */
/* 程序完成时间:2017/3/12 */
/* 有任何问题请联系:[email protected] */
/************************************************************/
//@尽量写出完美的程序
//#pragma once是一个比较常用的C/C++杂注,
//只要在头文件的最开始加入这条杂注,
//就能够保证头文件只被编译一次。
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/*
本算法是使用SPFA来求解图的单源最短路径问题
采用了邻接表作为图的存储结构
可以应用于任何无环的图
*/
//表结构
struct ArcNode {
int adjvex; //边的另外一边的顶点下标
ArcNode * next; //下一条边的表结点
int weight;
};
struct Vnode {
string data; //顶点信息
ArcNode * firstarc; //第一条依附在该顶点的边
};
struct Dis {
string path; //从顶点到该该顶点最短路径
int weight; //最短路径的权重
};
class Graph {
private:
int vexnum; //边的个数
int edge; //边的条数
Vnode * node; //邻接表
Dis * dis; //记录最短路径信息的数组
public:
Graph(int vexnum, int edge);
~Graph();
void createGraph(int); //创建图
bool check_edge_value(int , int ,int); //判断边的信息是否合法
void print(); //打印图的邻接表
bool SPFA(int begin); //求解最短路径
void print_path(int begin); //打印最短路径
}; - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- SPFA.cpp文件代码
#include"SFPA.h"
Graph::Graph(int vexnum, int edge) {
//对顶点个数和边的条数进行赋值
this->vexnum = vexnum;
this->edge = edge;
//为邻接矩阵开辟空间
node = new Vnode[this->vexnum];
dis = new Dis[this->vexnum];
int i;
//对邻接表进行初始化
for (i = 0; i < this->vexnum; ++i) {
node[i].data = "v" + to_string(i + 1);
node[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
}
Graph::~Graph() {
int i;
//释放空间,但是记住图中每个结点的链表也要一一释放
ArcNode * p, *q;
for (i = 0; i < this->vexnum; ++i) {
//一定要注意这里,要判断该顶点的出度到底是否为空,不然会出错
if (this->node[i].firstarc) {
p = node[i].firstarc;
while (p) {
q = p->next;
delete p;
p = q;
}
}
}
delete [] node;
delete [] dis;
}
// 判断我们每次输入的的边的信息是否合法
//顶点从1开始编号
bool Graph::check_edge_value(int start, int end, int weight) {
if (start<1 || end<1 || start>vexnum || end>vexnum || weight < 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
void Graph::print() {
cout << "图的邻接表的打印:" << endl;
int i;
ArcNode *temp;
//遍历真个邻接表
for (i = 0; i < this->vexnum; ++i) {
cout << node[i].data << " ";
temp = node[i].firstarc;
while (temp) {
cout << "<"
<< node[i].data
<< ","
<< node[temp->adjvex].data
<< ">="
<< temp->weight
<< " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << "^" << endl;
}
}
void Graph::createGraph(int kind) {
//kind代表图的种类,2为无向图
cout << "输入边的起点和终点以及各边的权重(顶点编号从1开始):" << endl;
int i;
int start;
int end;
int weight;
for (i = 0; i < this->edge; ++i) {
cin >> start >> end >> weight;
//判断输入的边是否合法
while (!this->check_edge_value(start, end, weight)) {
cout << "输入边的信息不合法,请重新输入:" << endl;
cin >> start >> end >> weight;
}
ArcNode *temp = new ArcNode;
temp->adjvex = end - 1;
temp->weight = weight;
temp->next = NULL;
//如果该顶点依附的边为空,则从以第一个开始
if (node[start - 1].firstarc == NULL) {
node[start - 1].firstarc = temp;
}
else {//否则,则插入到该链表的最后一个位置
ArcNode * now = node[start - 1].firstarc;
//找到链表的最后一个结点
while (now->next) {
now = now->next;
}
now->next = temp;
}
//如果是无向图,则反向也要添加新的结点
if (kind == 2) {
//新建一个新的表结点
ArcNode *temp_end = new ArcNode;
temp_end->adjvex = start - 1;
temp_end->weight = weight;
temp_end->next = NULL;
//如果该顶点依附的边为空,则从以第一个开始
if (node[end - 1].firstarc == NULL) {
node[end - 1].firstarc = temp_end;
}
else {//否则,则插入到该链表的最后一个位置
ArcNode * now = node[end - 1].firstarc;
//找到链表的最后一个结点
while (now->next) {
now = now->next;
}
now->next = temp_end;
}
}
}
}
bool Graph::SPFA(int begin) {
bool *visit;
//visit用于记录是否在队列中
visit = new bool[this->vexnum];
int *input_queue_time;
//input_queue_time用于记录某个顶点入队列的次数
//如果某个入队列的次数大于顶点数vexnum,那么说明这个图有环,
//没有最短路径,可以退出了
input_queue_time = new int[this->vexnum];
queue<int> s; //队列,用于记录最短路径被改变的点
/*
各种变量的初始化
*/
int i;
for (i = 0; i < this->vexnum; i++) {
visit[i] = false;
input_queue_time[i] = 0;
//路径开始都初始化为直接路径,长度都设置为无穷大
dis[i].path = this->node[begin-1].data + "-->" + this->node[i].data;
dis[i].weight = INT_MAX;
}
//首先是起点入队列,我们记住那个起点代表的是顶点编号,从1开始的
s.push(begin - 1);
visit[begin - 1] = true;
++input_queue_time[begin-1];
//
dis[begin - 1].path =this->node[begin - 1].data;
dis[begin - 1].weight = 0;
int temp;
int res;
ArcNode *temp_node;
//进入队列的循环
while (!s.empty()) {
//取出队首的元素,并且把队首元素出队列
temp = s.front(); s.pop();
//必须要保证第一个结点不为空
if (node[temp].firstarc)
{
temp_node = node[temp].firstarc;
while (temp_node) {
//如果边的权重加上temp这个点的最短路径
//小于之前temp_node的最短路径的长度,则更新
//temp_node的最短路径的信息
if (dis[temp_node->adjvex].weight > (temp_node->weight + dis[temp].weight)) {
//更新dis数组的信息
dis[temp_node->adjvex].weight = temp_node->weight + dis[temp].weight;
dis[temp_node->adjvex].path = dis[temp].path + "-->" + node[temp_node->adjvex].data;
//如果还没在队列中,加入队列,修改对应的信息
if (!visit[temp_node->adjvex]) {
visit[temp_node->adjvex] = true;
++input_queue_time[temp_node->adjvex];
s.push(temp_node->adjvex);
if (input_queue_time[temp_node->adjvex] > this->vexnum) {
cout << "图中有环" << endl;
return false;
}
}
}
temp_node = temp_node->next;
}
}
}
//打印最短路径
return true;
}
void Graph::print_path(int begin) {
cout << "以顶点" << this->node[begin - 1].data
<< "为起点,到各个顶点的最短路径的信息:" << endl;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < this->vexnum; ++i) {
if (dis[i].weight == INT_MAX) {
cout << this->node[begin - 1].data << "---"
<< this->node[i].data
<< " 无最短路径,这两个顶点不连通" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << this->node[begin - 1].data << "---"
<< this->node[i].data
<< " weight: "
<< dis[i].weight
<< " path: "
<< dis[i].path
<< endl;
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- main.cpp文件代码
#include"SFPA.h"
//检验输入边数和顶点数的值是否有效,可以自己推算为啥:
//顶点数和边数的关系是:((Vexnum*(Vexnum - 1)) / 2) < edge
bool check(int Vexnum, int edge) {
if (Vexnum <= 0 || edge <= 0 || ((Vexnum*(Vexnum - 1)) / 2) < edge)
return false;
return true;
}
int main() {
int vexnum; int edge;
cout << "输入图的种类:1代表有向图,2代表无向图" << endl;
int kind;
cin >> kind;
//判读输入的kind是否合法
while (1) {
if (kind == 1 || kind == 2) {
break;
}
else {
cout << "输入的图的种类编号不合法,请重新输入:1代表有向图,2代表无向图" << endl;
cin >> kind;
}
}
cout << "输入图的顶点个数和边的条数:" << endl;
cin >> vexnum >> edge;
while (!check(vexnum, edge)) {
cout << "输入的数值不合法,请重新输入" << endl;
cin >> vexnum >> edge;
}
Graph graph(vexnum, edge);
graph.createGraph(kind);
graph.print();
//记得SPFA一个参数,代表起点,这个起点从1开始
graph.SPFA(1);
graph.print_path(1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
输入:
2
7 12
1 2 12
1 6 16
1 7 14
2 3 10
2 6 7
3 4 3
3 5 5
3 6 6
4 5 4
5 6 2
5 7 8
6 7 9 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
输入:
1
6 8
1 3 10
1 5 30
1 6 100
2 3 5
3 4 50
4 6 10
5 6 60
5 4 20- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
输出:
文章转自:
http://blog.csdn.net/qq_35644234/article/details/61614581