使用Spring-retry 1.1.4完成重试功能
前言
在实际项目中,经常需要在某种情况下对调用的方法进行重试,例如超时重试。通过Spring-retry能简化重试功能的实现,并实现更多样的重试操作。
Spring-retry结构
Spring-retry提供的RetryOperations接口,该接口提供了若干方法来执行重试操作。在Spring-retry 1.1.4 中该接口的定义如下。
public interface RetryOperations {
<T, E extends Throwable> T execute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback) throws E;
<T, E extends Throwable> T execute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback, RecoveryCallback<T> recoveryCallback) throws E;
<T, E extends Throwable> T execute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback, RecoveryCallback<T> recoveryCallback, RetryState retryState)
throws E;
}调用者通过传入RetryCallback来完成调用者的重试操作。如果callback执行失败(抛出某些异常),那么会按照调用者设定的策略进行重试。重试操作直到成功,或根据使用者设定的条件而退出。
RetryCallback的接口定义如下:
public interface RetryCallback<T, E extends Throwable> {
T doWithRetry(RetryContext context) throws E;
}
Spring-retry提供了RetryOperations接口的实现类RetryTemplate。通过RetryTemplate来完成重试,下面是使用RetryTemplate重试的一个简单例子。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate();
TimeoutRetryPolicy policy = new TimeoutRetryPolicy();
template.setRetryPolicy(policy);
String result = template.execute(
new RetryCallback() {
public String doWithRetry(RetryContext arg0) throws Exception {
return "Retry";
}
}
);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
代码定义了TimeoutRetryPolicy策略,TimeoutRetryPolicy超时时间默认是1秒。TimeoutRetryPolicy超时是指在execute方法内部,从open操作开始到调用TimeoutRetryPolicy的canRetry方法这之间所经过的时间。这段时间未超过TimeoutRetryPolicy定义的超时时间,那么执行操作,否则抛出异常。
protected T doExecute(RetryCallback retryCallback,RecoveryCallback recoveryCallback, RetryState state) throws E,ExhaustedRetryException {
……略
RetryContext context = open(retryPolicy, state);
……略
while (canRetry(retryPolicy, context) && !context.isExhaustedOnly())
// 调用canRetry检查是否可以重试
……略
}
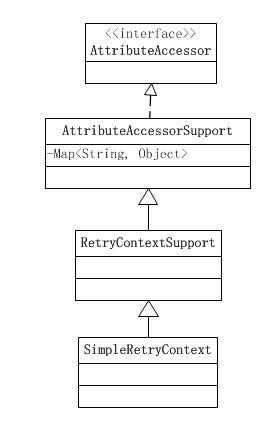
RetryCallback中的方法doWithRetry有一个RetryContext类型的参数。大多数的doWithRetry操作都会会略该参数。但也可以在重试的过程中通过RetryContext来存储数据,RetryContext结构如下。
不同的RetryContext维护了不同类型的重试信息,例如TimeoutRetryContext会维护超时时间与任务开始时间。
private static class TimeoutRetryContext extends RetryContextSupport {
private long timeout;
private long start;
public TimeoutRetryContext(RetryContext parent, long timeout) {
super(parent);
this.start = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.timeout = timeout;
}
public boolean isAlive() {
return (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) <= timeout;
}
}执行重试时,具体的RetryContext类型,会根据使用者创建的重试策略来创建具体的RetryContext。例如,创建SimpleRetryPolicy,那么最终创建的Context为SimpleRetryContext。
org.springframework.core.AttributeAccessorSupport实现了org.springframework.core.AttributeAccessor,并定了一个Map,通过AttributeAccessor中定义的方法来访问map,以便在重试过程中进行数据存储与获取数据。
在RetryOperations接口中还会看到RecoveryCallback这个参数。RecoveryCallback的定义如下。
public interface RecoveryCallback {
/**
* @param context the current retry context
* @return an Object that can be used to replace the callback result that failed
* @throws Exception when something goes wrong
*/
T recover(RetryContext context) throws Exception;
}
当重试执行完闭,操作还未成为,那么可以通过RecoveryCallback完成一些失败事后处理。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate();
SimpleRetryPolicy policy = new SimpleRetryPolicy();
policy.setMaxAttempts(2);
template.setRetryPolicy(policy);
String result = template.execute(
new RetryCallback() {
public String doWithRetry(RetryContext arg0) throws Exception {
throw new NullPointerException("nullPointerException");
}
}
,
new RecoveryCallback() {
public String recover(RetryContext context) throws Exception {
return "recovery callback";
}
}
);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
上面的代码重试两次后,仍然失败,RecoveryCallback被调用,返回”recovery callback”。如果没有定义RecoveryCallback,那么重试2次后,将会抛出异常。
重试策略
重试策略定义了当操作失败时如何进行重试操作,框架提供的重试策略包括。
SimpleRetryPolicy 策略
该策略定义了对指定的异常进行若干次重试。默认情况下,对Exception异常及其子类重试3次。如果创建SimpleRetryPolicy并指定重试异常map,可以选择性重试或不进行重试。下面的代码定义了对TimeOutException进行重试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate();
Map<Class extends Throwable>, Boolean> maps = new HashMap<Classextends Throwable>, Boolean>();
maps.put(TimeoutException.class, true);
SimpleRetryPolicy policy2 = new SimpleRetryPolicy(2, maps);
template.setRetryPolicy(policy2);
new RetryCallback<String, Exception>() {
public String doWithRetry(RetryContext arg0) throws Exception {
throw new TimeoutException("TimeoutException");
}
}
,
new RecoveryCallback() {
public String recover(RetryContext context) throws Exception {
return "recovery callback";
}
}
);
System.out.println(result);
}
当Map中的的value为false,那么执行方法,随后抛出异常不进行重试。
NeverRetryPolicy 策略
执行一次待执行操作,若出现异常后不进行重试。
AlwaysRetryPolicy 策略
异常后一直重试直到成功。
TimeoutRetryPolicy 策略
在执行execute方法时从open操作开始到调用TimeoutRetryPolicy的canRetry方法这之间所经过的时间。这段时间未超过TimeoutRetryPolicy定义的超时时间,那么执行操作,否则抛出异常。
ExceptionClassifierRetryPolicy 策略
根据产生的异常选择重试策略。
Map<Classextends Throwable>, RetryPolicy> policyMap = new HashMap<Classextends Throwable>, RetryPolicy>();
policyMap.put(TimeoutException.class, new AlwaysRetryPolicy());
policyMap.put(NullPointerException.class, new NeverRetryPolicy());
policy.setPolicyMap(policyMap);
通过PolicyMap定义异常及其重试策略。下面的代码在抛出NullPointerException采用NeverRetryPolicy策略,而TimeoutException采用AlwaysRetryPolicy。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate();
ExceptionClassifierRetryPolicy policy = new ExceptionClassifierRetryPolicy();
Map<Classextends Throwable>, RetryPolicy> policyMap = new HashMap<Classextends Throwable>, RetryPolicy>();
policyMap.put(TimeoutException.class, new AlwaysRetryPolicy());
policyMap.put(NullPointerException.class, new NeverRetryPolicy());
policy.setPolicyMap(policyMap);
template.setRetryPolicy(policy);
String result = template.execute(
new RetryCallback<String, Exception>() {
public String doWithRetry(RetryContext arg0) throws Exception {
if(arg0.getRetryCount() >= 2) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
throw new NullPointerException();
}
throw new TimeoutException("TimeoutException");
}
}
,
new RecoveryCallback() {
public String recover(RetryContext context) throws Exception {
return "recovery callback";
}
}
);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
此外可以通过setExceptionClassifier来为异常指定重试策略。
Classifier exceptionClassifier = new Classifier(){
public RetryPolicy classify(Throwable classifiable) {
if(classifiable instanceof TimeoutException)
return new SimpleRetryPolicy();
return new NeverRetryPolicy();
}
};
policy.setExceptionClassifier(exceptionClassifier);
setPolicyMap与setExceptionClassifier使用一个即可。
CompositeRetryPolicy 策略
用户指定一组策略,随后根据optimistic选项来确认如何重试。
下面的代码中创建CompositeRetryPolicy策略,并创建了RetryPolicy数组,数组有两个具体策略SimpleRetryPolicy与AlwaysRetryPolicy。当CompositeRetryPolicy设置optimistic为true时,Spring-retry会顺序遍历RetryPolicy[]数组,如果有一个重试策略可重试,例如SimpleRetryPolicy没有达到重试次数,那么就会进行重试。 如果optimistic选项设置为false。那么有一个重试策略无法重试,那么就不进行重试。例如SimpleRetryPolicy达到重试次数不能再重试,而AlwaysRetryPolicy可以重试,那么最终是无法重试的。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate();
CompositeRetryPolicy policy = new CompositeRetryPolicy();
RetryPolicy[] polices = {new SimpleRetryPolicy(), new AlwaysRetryPolicy()};
policy.setPolicies(polices);
policy.setOptimistic(true);
template.setRetryPolicy(policy);
String result = template.execute(
new RetryCallback() {
public String doWithRetry(RetryContext arg0) throws Exception {
if(arg0.getRetryCount() >= 2) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
throw new NullPointerException();
}
throw new TimeoutException("TimeoutException");
}
}
,
new RecoveryCallback() {
public String recover(RetryContext context) throws Exception {
return "recovery callback";
}
}
);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
上述代码,设置setOptimistic(true),而AlwaysRetryPolicy一直可重试,那么最终可以不断进行重试。
退避(BackOff)策略
当操作执行失败时,根据设置的重试策略进行重试。通过BackoffPolicy可以设定再次重试的时间间隔。
public interface BackOffPolicy {
BackOffContext start(RetryContext context);
void backOff(BackOffContext backOffContext) throws BackOffInterruptedException;
}
StatelessBackoffPolicy下的3个实现类
org.springframework.retry.backoff.FixedBackOffPolicy
在等待一段固定的时间后,再进行重试。默认为1秒。
org.springframework.retry.backoff.NoBackOffPolicy
实现了空方法,因此采用次策略,重试不会等待。这也是RetryTemplate采用的默认退避(backOff)策略。
private volatile BackOffPolicy backOffPolicy = new NoBackOffPolicy();org.springframework.retry.backoff.UniformRandomBackOffPolicy
均匀随机退避策略,等待时间为 最小退避时间 + [0,最大退避时间 - 最小退避时间)间的一个随机数,如果最大退避时间等于最小退避时间那么等待时间为0。
SleepingbackOffPolicy的下的4个实现类
org.springframework.retry.backoff.ExponentialBackOffPolicy
指数退避策略 ,每次等待时间为 等待时间 = 等待时间 * N ,即每次等待时间为上一次的N倍。如果等待时间超过最大等待时间,那么以后的等待时间为最大等待时间。
ExponentialBackOffPolicy exponentialBackOffPolicy = new ExponentialBackOffPolicy();
exponentialBackOffPolicy.setInitialInterval(1500);
exponentialBackOffPolicy.setMultiplier(2);
exponentialBackOffPolicy.setMaxInterval(6000);上面的代码创建了一个ExponentialBackOffPolicy,初始时间间隔为1500毫秒,N = 2,¸最大间隔为6000毫秒,那么从第4次重试开始,以后每次等待时间都为6000毫秒。
org.springframework.retry.backoff.ExponentialRandomBackOffPolicy
指数随机策略,该类是ExponentialBackOffPolicy的子类,计算等待时间的算法为
@Override
public synchronized long getSleepAndIncrement() {
long next = super.getSleepAndIncrement();
next = (long)(next*(1 + r.nextFloat()*(getMultiplier()-1)));
return next;
}该方法调用ExponentialBackOffPolicy方法,返回等待时间,随后next*(Multiplier – 1)最为等待时间。 即 [next,next* Multiplier) 之间的一个随机数。
org.springframework.retry.backoff.FixedBackOffPolicy
org.springframework.retry.backoff.UniformRandomBackOffPolicy
这两个类与StatelessBackoffPolicy的同名实现类返回等待时间的方法是一致的。而两者的主要区别是,SleepingbackOffPolicy可以设置用户定义的Sleeper。
public interface Sleeper {
void sleep(long backOffPeriod) throws InterruptedException;
}监听器
通过监听器,可以在重试操作的某些位置嵌入调用者定义的一些操作,以便在某些场景触发。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate();
ExponentialRandomBackOffPolicy exponentialBackOffPolicy = new ExponentialRandomBackOffPolicy();
exponentialBackOffPolicy.setInitialInterval(1500);
exponentialBackOffPolicy.setMultiplier(2);
exponentialBackOffPolicy.setMaxInterval(6000);
CompositeRetryPolicy policy = new CompositeRetryPolicy();
RetryPolicy[] polices = {new SimpleRetryPolicy(), new AlwaysRetryPolicy()};
policy.setPolicies(polices);
policy.setOptimistic(true);
template.setRetryPolicy(policy);
template.setBackOffPolicy(exponentialBackOffPolicy);
template.registerListener(new RetryListener() {
public boolean open(RetryContext context, RetryCallback callback) {
System.out.println("open");
return true;
}
public void onError(RetryContext context, RetryCallback callback,
Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("onError");
}
public void close(RetryContext context, RetryCallback callback,
Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("close");
}
});
template.registerListener(new RetryListener() {
public boolean open(RetryContext context, RetryCallback callback) {
System.out.println("open2");
return true;
}
public void onError(RetryContext context, RetryCallback callback,
Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("onError2");
}
public void close(RetryContext context, RetryCallback callback,
Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("close2");
}
});
String result = template.execute(
new RetryCallback() {
public String doWithRetry(RetryContext arg0) throws Exception {
arg0.getAttribute("");
if(arg0.getRetryCount() >= 2) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
throw new TimeoutException("TimeoutException");
}
}
);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
上述代码注册了两个Listener,Listener中的三个实现方法,onError,open,close会在执行重试操作时被调用,在RetryTemplate中doOpenInterceptors,doCloseInterceptors,doOnErrorInterceptors会调用监听器对应的open,close,onError 方法。
doOpenInterceptors方法在第一次重试之前会被调用,如果该方法返回true,则会继续向下直接,如果返回false,则抛出异常,停止重试。
doCloseInterceptors 会在重试操作执行完毕后调用。
doOnErrorInterceptors 在抛出异常后执行,
当注册多个Listener时,open方法按会按Listener的注册顺序调用,而onError和close则按Listener注册的顺序逆序调用。
参考
- Spring-retry官方文档 http://docs.spring.io/spring-batch/reference/html/retry.html
- Spring-retry源码1.1.4