关于Multi-label Classification 多标签分类的问题
![]() 多分类:
多分类:
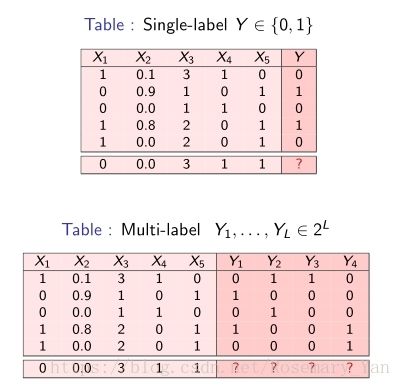
训练集中每个样本只有一个标签,该标签来自于一个不重合的标签集合L,|L| > 1。
当|L|=2 时,这是一个二分类问题。当|L| > 2 时,这是一个多分类问题。
单标签与多标签:
多标签:
令![]() 为训练样本集,
为训练样本集,![]() 为标签集合,给定一组形式为
为标签集合,给定一组形式为![]() 的训练样本,
的训练样本,![]() ,
,![]() ,目的是学习求出合适的误差低的函数
,目的是学习求出合适的误差低的函数![]() (
(![]() 中的unique values)。
中的unique values)。
大多数情况下,多标签的方法会涉及到一个给定样本可能有的标签的排序问题,因此这个学习算法可以看成函数![]() 。并按照
。并按照![]() 来对标签进行排序。
来对标签进行排序。
令![]() 为
为![]() 规则下样本
规则下样本![]() 所对应的标签
所对应的标签![]() 的排序。其中,
的排序。其中,![]() 是一个到
是一个到![]() 上的一对一的映射,且如果
上的一对一的映射,且如果![]() ,那么
,那么![]() 。
。
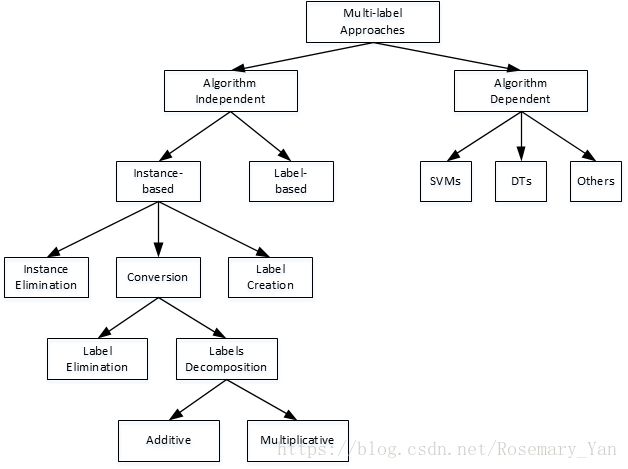
多标签分类的方法:
多标签分类的方法可以从 Algorithm Independent 和 Algorithm Dependent 的角度讲,也可以从 Problem Transformation Method 和 Algorithm Adaptation Method 的角度讲。Algorithm Dependent 和 Algorithm Adaptation Method 一样,也有很多方法是 Problem Transformation Method 和 Algorithm Adaptation Method 的结合。
Problem Transformation Method 问题转化
将多标签问题转化为单标签问题。改变data来适应算法。
At training time, with ![]() :
:
1 Transform the multi-label training data to single-label data
2 Learn from the single-label transformed data
At testing time, for ![]() :
:
1 Make single-label predictions
2 Translate these into multi-label predictions
e.g.
1 Binary Relevance (BR): ![]() binary problems (one vs. all)
binary problems (one vs. all)
缺点:不能model标签的dependency关系;分类不均衡
改进:Stacked BR (2BR) [Godbole and Sarawagi, 2004],Chain Classifier (CC) [Cheng et al., 2010, Read et al., 2011]
2 Label Powerset (LP): one multi-class problem of ![]() class-values 二进制
class-values 二进制
缺点:类标签多而复杂;不均衡(每个类别标签对应的实例不多);过拟合(预测新值)
改进:Ensembles of RAndom k-labEL subsets (RAkEL) [Tsoumakas and Vlahavas, 2007],Ensembles of Pruned Sets (EPS) [Read et al., 2008] 二者都通过投票机制进行预测
3 Pairwise (PW): ![]() binary problems (all vs. all)
binary problems (all vs. all)
Each model is trained based on examples annotated by at least one of the labels, but not both.
缺点:生成的是PW的Rankings,要得到标签集;找过拟合标签的decision boundary无意义;分类器数量大![]()
改进:Calibrated Label Ranking CLR ([Fürnkranz et al., 2008]),
4 Copy-Weight (CW): one multi-class problem of L class values
Make a single multi-class problem with L possible class values.Each example duplicated ![]() times, weighted as
times, weighted as![]() .
.
缺点:同一实例 / 不同标签的decision boundary;标签基数大导致数据集增长大;没有可以直观地对dependency进行model的方法
Algorithm Independent 独立于算法
分为基于标签和基于实例的两种转化方式。
Label-based Transformation 基于标签的转化
Instance-based Transformation 基于实例的转化
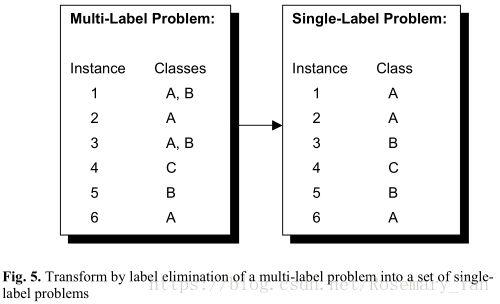
Instance Elimination
去除多标签实例
Label Creation
把多个标签变成一个新的标签
Conversion
把多标签的实例变成单标签的实例。简化或分解(加、乘)。
Label Elimination (Simplification)
保留一个最可能为true的或者随机选择一个标签。
Labels Decomposition
Additive
如下图,分类器数量1+1=2。
Multiplicative
如下图,分类器数量2×1×2×1×1×1=4
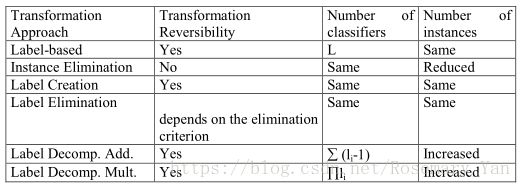
Algorithm Independent Method总结
Algorithm Adaptation / Dependent Method 算法适应
改变单标签算法生成多标签的输出。
e.g.,
k-Nearest Neighbours (KNN)
MLkNN [Zhang and Zhou, 2007]
Decision Trees (DT)
Multi-label C4.5 [Clare and King, 2001]
基于AdaBoost [Freund Y. & Schapire, R. E., 1995], ADTBoost [Freund Y. & Mason, L. , 1999]的de Comite, F., Gilleron, R. & and Tommasi, M. (2003) Learning Multi-label Alternating Decision Trees from Texts and Data. 和Adaboost.MH and Adaboost.MR (Schapire & Singer, 2000)
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
RankSVM, a Maximum Margin approach [Elisseeff and Weston, 2002]
Godbole and Sarawagi (2004) 结合PT4
Aiolli, F. & Sperduti, A. (2005) Multiclass Classification with Multi-Prototype Support Vector Machines.
Neural Networks (NN)
BPMLL [Zhang and Zhou, 2006]
其他方法可参见 A Tutorial on Multi-Label Classification Techniques 和 Multi-Label Classification: An Overview 等文献。
具体选哪种方法比较好取决于具体问题是什么,效率和速度:Decision Tree-based;灵活性:problem transformation methods, esp. BR-based;预测能力: ensembles (most modern methods)。
An extensive empirical study by [Madjarov et al., 2012] recommends:
RT-PCT: Random Forest of Predictive Clustering Trees (Algorithm Adaptation, Decision Tree based)
HOMER: Hierarchy Of Multilabel ClassifiERs (Problem Transformation, LP-based (original presentation))
CC: Classifier Chains (Problem Transformation, BR-based)
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27009517/article/details/80264919
Multi-label Classification-Part 01, Jesse Read
André C. P. L. F. de Carvalho, Freitas A A. A Tutorial on Multi-label Classification Techniques[M]// Foundations of Computational Intelligence Volume 5. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009:177-195.
Li T, Zhang C, Zhu S. Empirical Studies on Multi-label Classification.[C]// IEEE International Conference on TOOLS with Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Computer Society, 2006:86-92.
Multi-Label Classification: An Overview