Python数据可视化利器Matplotlib,如何绘制横向柱形图
Python绘图库Matplotlib中,横向柱形图主要通过barh函数绘制得到,该函数的使用方法与常见的纵向的柱形图绘制函数bar的用法相似。
Axes.barh(y, width, height, left, align=’center’, **kwargs)
或
matplotlib.pyplot.barh(y, width, height, left, align=’center’, **kwargs)
barh函数主要有四个参数:
参数y:柱体的纵坐标值
参数width:柱体的宽度值
参数height:柱体的高度值
参数left:柱体的左侧横坐标值
以上四个参数均可以是单个数字,也可以是一组数值。当参数为单个数字时,表示所有柱体的该项参数均相同,当为一组数值时,各柱体的该项参数与列表内数值一一对应。
这四个参数与柱体位置及形状关系示意图如下。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
#数据
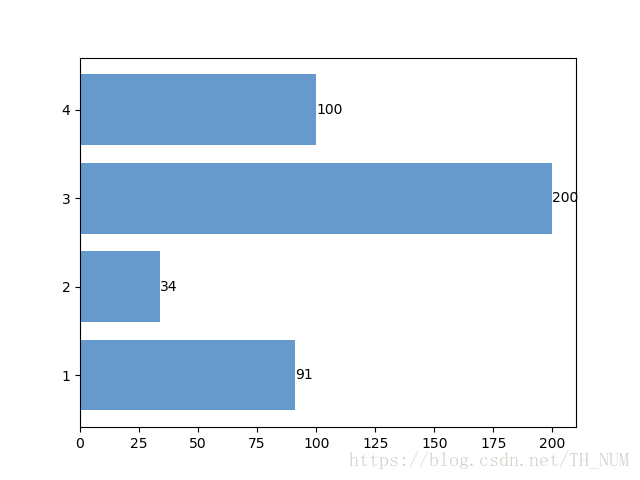
name=['1','2','3','4']
colleges=[91,34,200,100]
#图像绘制
fig,ax=plt.subplots()
b=ax.barh(range(len(name)),colleges,color='#6699CC')
#添加数据标签
for rect in b:
w=rect.get_width()
ax.text(w,rect.get_y()+rect.get_height()/2,'%d'%int(w),ha='left',va='center')
#设置Y轴刻度线标签
ax.set_yticks(range(len(name)))
#font=FontProperties(fname=r'/Library/Fonts/Songti.ttc')
ax.set_yticklabels(name)
plt.show()
绘制多个横向的图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
plt.rcdefaults()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# Example data
people = ('Tom', 'Dick', 'Harry', 'Slim', 'Jim')
y_pos = np.arange(len(people))
performance = 3 + 10 * np.random.rand(len(people))
performance2 = 3 + 10 * np.random.rand(len(people))
error = np.random.rand(len(people))
total_width, n = 0.8, 2
width = total_width / n
y_pos=y_pos - (total_width - width) / 2
b=ax.barh(y_pos, performance, align='center',
color='green', ecolor='black',height=0.2,label='a')
#添加数据标签
for rect in b:
w=rect.get_width()
ax.text(w,rect.get_y()+rect.get_height()/2,'%f'%w,ha='left',va='center')
b=ax.barh(y_pos+width, performance2, align='center',
color='red', ecolor='black',height=0.2,label='b')
#添加数据标签
for rect in b:
w=rect.get_width()
ax.text(w,rect.get_y()+rect.get_height()/2,'%f'%w,ha='left',va='center')
ax.set_yticks(y_pos+width/2.0)
ax.set_yticklabels(people)
ax.invert_yaxis() # labels read top-to-bottom
ax.set_xlabel('Performance')
ax.set_title('How fast do you want to go today?')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
print(y_pos+3)