Java中TreeSet的详细用法
第1部分 TreeSet介绍
TreeSet简介
TreeSet 是一个有序的集合,它的作用是提供有序的Set集合。它继承于AbstractSet抽象类,实现了NavigableSet, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable接口。
TreeSet 继承于AbstractSet,所以它是一个Set集合,具有Set的属性和方法。
TreeSet 实现了NavigableSet接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法。比如查找与指定目标最匹配项。
TreeSet 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆。
TreeSet 实现了java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化。
TreeSet是基于TreeMap实现的。TreeSet中的元素支持2种排序方式:自然排序 或者 根据创建TreeSet 时提供的 Comparator 进行排序。这取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeSet为基本操作(add、remove 和 contains)提供受保证的 log(n) 时间开销。
另外,TreeSet是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fast的。
TreeSet的构造函数
// 默认构造函数。使用该构造函数,TreeSet中的元素按照自然排序进行排列。
TreeSet()
// 创建的TreeSet包含collection
TreeSet(Collection collection)
// 指定TreeSet的比较器
TreeSet(Comparator comparator)
// 创建的TreeSet包含set
TreeSet(SortedSet set)
TreeSet的API
boolean add(E object)
boolean addAll(Collection collection)
void clear()
Object clone()
boolean contains(Object object)
E first()
boolean isEmpty()
E last()
E pollFirst()
E pollLast()
E lower(E e)
E floor(E e)
E ceiling(E e)
E higher(E e)
boolean remove(Object object)
int size()
Comparator comparator()
Iterator iterator()
Iterator descendingIterator()
SortedSet headSet(E end)
NavigableSet descendingSet()
NavigableSet headSet(E end, boolean endInclusive)
SortedSet subSet(E start, E end)
NavigableSet subSet(E start, boolean startInclusive, E end, boolean endInclusive)
NavigableSet tailSet(E start, boolean startInclusive)
SortedSet tailSet(E start)
说明:
(01) TreeSet是有序的Set集合,因此支持add、remove、get等方法。
(02) 和NavigableSet一样,TreeSet的导航方法大致可以区分为两类,一类时提供元素项的导航方法,返回某个元素;另一类时提供集合的导航方法,返回某个集合。
lower、floor、ceiling 和 higher 分别返回小于、小于等于、大于等于、大于给定元素的元素,如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。
第2部分 TreeSet数据结构
TreeSet的继承关系
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection
↳ java.util.AbstractSet
↳ java.util.TreeSet
public class TreeSet extends AbstractSet
implements NavigableSet, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{}
TreeSet与Collection关系如下图:
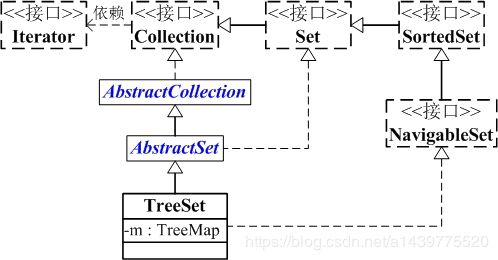
从图中可以看出:
(01) TreeSet继承于AbstractSet,并且实现了NavigableSet接口。
(02) TreeSet的本质是一个"有序的,并且没有重复元素"的集合,它是通过TreeMap实现的。TreeSet中含有一个"NavigableMap类型的成员变量"m,而m实际上是"TreeMap的实例"。
第3部分 TreeSet源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
为了更了解TreeSet的原理,下面对TreeSet源码代码作出分析。
1 package java.util;
2
3 public class TreeSet extends AbstractSet
4 implements NavigableSet, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
5 {
6 // NavigableMap对象
7 private transient NavigableMap m;
8
9 // TreeSet是通过TreeMap实现的,
10 // PRESENT是键-值对中的值。
11 private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
12
13 // 不带参数的构造函数。创建一个空的TreeMap
14 public TreeSet() {
15 this(new TreeMap());
16 }
17
18 // 将TreeMap赋值给 "NavigableMap对象m"
19 TreeSet(NavigableMap m) {
20 this.m = m;
21 }
22
23 // 带比较器的构造函数。
24 public TreeSet(Comparator comparator) {
25 this(new TreeMap(comparator));
26 }
27
28 // 创建TreeSet,并将集合c中的全部元素都添加到TreeSet中
29 public TreeSet(Collection c) {
30 this();
31 // 将集合c中的元素全部添加到TreeSet中
32 addAll(c);
33 }
34
35 // 创建TreeSet,并将s中的全部元素都添加到TreeSet中
36 public TreeSet(SortedSet s) {
37 this(s.comparator());
38 addAll(s);
39 }
40
41 // 返回TreeSet的顺序排列的迭代器。
42 // 因为TreeSet时TreeMap实现的,所以这里实际上时返回TreeMap的“键集”对应的迭代器
43 public Iterator iterator() {
44 return m.navigableKeySet().iterator();
45 }
46
47 // 返回TreeSet的逆序排列的迭代器。
48 // 因为TreeSet时TreeMap实现的,所以这里实际上时返回TreeMap的“键集”对应的迭代器
49 public Iterator descendingIterator() {
50 return m.descendingKeySet().iterator();
51 }
52
53 // 返回TreeSet的大小
54 public int size() {
55 return m.size();
56 }
57
58 // 返回TreeSet是否为空
59 public boolean isEmpty() {
60 return m.isEmpty();
61 }
62
63 // 返回TreeSet是否包含对象(o)
64 public boolean contains(Object o) {
65 return m.containsKey(o);
66 }
67
68 // 添加e到TreeSet中
69 public boolean add(E e) {
70 return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
71 }
72
73 // 删除TreeSet中的对象o
74 public boolean remove(Object o) {
75 return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
76 }
77
78 // 清空TreeSet
79 public void clear() {
80 m.clear();
81 }
82
83 // 将集合c中的全部元素添加到TreeSet中
84 public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
85 // Use linear-time version if applicable
86 if (m.size()==0 && c.size() > 0 &&
87 c instanceof SortedSet &&
88 m instanceof TreeMap) {
89 SortedSet set = (SortedSet) c;
90 TreeMap map = (TreeMap) m;
91 Comparator cc = (Comparator) set.comparator();
92 Comparator mc = map.comparator();
93 if (cc==mc || (cc != null && cc.equals(mc))) {
94 map.addAllForTreeSet(set, PRESENT);
95 return true;
96 }
97 }
98 return super.addAll(c);
99 }
100
101 // 返回子Set,实际上是通过TreeMap的subMap()实现的。
102 public NavigableSet subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,
103 E toElement, boolean toInclusive) {
104 return new TreeSet(m.subMap(fromElement, fromInclusive,
105 toElement, toInclusive));
106 }
107
108 // 返回Set的头部,范围是:从头部到toElement。
109 // inclusive是是否包含toElement的标志
110 public NavigableSet headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {
111 return new TreeSet(m.headMap(toElement, inclusive));
112 }
113
114 // 返回Set的尾部,范围是:从fromElement到结尾。
115 // inclusive是是否包含fromElement的标志
116 public NavigableSet tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) {
117 return new TreeSet(m.tailMap(fromElement, inclusive));
118 }
119
120 // 返回子Set。范围是:从fromElement(包括)到toElement(不包括)。
121 public SortedSet subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {
122 return subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false);
123 }
124
125 // 返回Set的头部,范围是:从头部到toElement(不包括)。
126 public SortedSet headSet(E toElement) {
127 return headSet(toElement, false);
128 }
129
130 // 返回Set的尾部,范围是:从fromElement到结尾(不包括)。
131 public SortedSet tailSet(E fromElement) {
132 return tailSet(fromElement, true);
133 }
134
135 // 返回Set的比较器
136 public Comparator comparator() {
137 return m.comparator();
138 }
139
140 // 返回Set的第一个元素
141 public E first() {
142 return m.firstKey();
143 }
144
145 // 返回Set的最后一个元素
146 public E first() {
147 public E last() {
148 return m.lastKey();
149 }
150
151 // 返回Set中小于e的最大元素
152 public E lower(E e) {
153 return m.lowerKey(e);
154 }
155
156 // 返回Set中小于/等于e的最大元素
157 public E floor(E e) {
158 return m.floorKey(e);
159 }
160
161 // 返回Set中大于/等于e的最小元素
162 public E ceiling(E e) {
163 return m.ceilingKey(e);
164 }
165
166 // 返回Set中大于e的最小元素
167 public E higher(E e) {
168 return m.higherKey(e);
169 }
170
171 // 获取第一个元素,并将该元素从TreeMap中删除。
172 public E pollFirst() {
173 Map.Entry e = m.pollFirstEntry();
174 return (e == null)? null : e.getKey();
175 }
176
177 // 获取最后一个元素,并将该元素从TreeMap中删除。
178 public E pollLast() {
179 Map.Entry e = m.pollLastEntry();
180 return (e == null)? null : e.getKey();
181 }
182
183 // 克隆一个TreeSet,并返回Object对象
184 public Object clone() {
185 TreeSet clone = null;
186 try {
187 clone = (TreeSet) super.clone();
188 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
189 throw new InternalError();
190 }
191
192 clone.m = new TreeMap(m);
193 return clone;
194 }
195
196 // java.io.Serializable的写入函数
197 // 将TreeSet的“比较器、容量,所有的元素值”都写入到输出流中
198 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
199 throws java.io.IOException {
200 s.defaultWriteObject();
201
202 // 写入比较器
203 s.writeObject(m.comparator());
204
205 // 写入容量
206 s.writeInt(m.size());
207
208 // 写入“TreeSet中的每一个元素”
209 for (Iterator i=m.keySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); )
210 s.writeObject(i.next());
211 }
212
213 // java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式读出
214 // 先将TreeSet的“比较器、容量、所有的元素值”依次读出
215 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
216 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
217 // Read in any hidden stuff
218 s.defaultReadObject();
219
220 // 从输入流中读取TreeSet的“比较器”
221 Comparator c = (Comparator) s.readObject();
222
223 TreeMap tm;
224 if (c==null)
225 tm = new TreeMap();
226 else
227 tm = new TreeMap(c);
228 m = tm;
229
230 // 从输入流中读取TreeSet的“容量”
231 int size = s.readInt();
232
233 // 从输入流中读取TreeSet的“全部元素”
234 tm.readTreeSet(size, s, PRESENT);
235 }
236
237 // TreeSet的序列版本号
238 private static final long serialVersionUID = -2479143000061671589L;
239 }
总结:
(01) TreeSet实际上是TreeMap实现的。当我们构造TreeSet时;若使用不带参数的构造函数,则TreeSet的使用自然比较器;若用户需要使用自定义的比较器,则需要使用带比较器的参数。
(02) TreeSet是非线程安全的。
(03) TreeSet实现java.io.Serializable的方式。当写入到输出流时,依次写入“比较器、容量、全部元素”;当读出输入流时,再依次读取。
第4部分 TreeSet遍历方式
4.1 Iterator顺序遍历
for(Iterator iter = set.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
iter.next();
}
4.2 Iterator顺序遍历
// 假设set是TreeSet对象
for(Iterator iter = set.descendingIterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
iter.next();
}
4.3 for-each遍历HashSet
// 假设set是TreeSet对象,并且set中元素是String类型
String[] arr = (String[])set.toArray(new String[0]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.printf("for each : %s\n", str);
TreeSet不支持快速随机遍历,只能通过迭代器进行遍历!
TreeSet遍历测试程序如下:
1 import java.util.*;
2
3 /**
4 * @desc TreeSet的遍历程序
5 *
6 * @author skywang
7 * @email [email protected]
8 */
9 public class TreeSetIteratorTest {
10
11 public static void main(String[] args) {
12 TreeSet set = new TreeSet();
13 set.add("aaa");
14 set.add("aaa");
15 set.add("bbb");
16 set.add("eee");
17 set.add("ddd");
18 set.add("ccc");
19
20 // 顺序遍历TreeSet
21 ascIteratorThroughIterator(set) ;
22 // 逆序遍历TreeSet
23 descIteratorThroughIterator(set);
24 // 通过for-each遍历TreeSet。不推荐!此方法需要先将Set转换为数组
25 foreachTreeSet(set);
26 }
27
28 // 顺序遍历TreeSet
29 public static void ascIteratorThroughIterator(TreeSet set) {
30 System.out.print("\n ---- Ascend Iterator ----\n");
31 for(Iterator iter = set.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
32 System.out.printf("asc : %s\n", iter.next());
33 }
34 }
35
36 // 逆序遍历TreeSet
37 public static void descIteratorThroughIterator(TreeSet set) {
38 System.out.printf("\n ---- Descend Iterator ----\n");
39 for(Iterator iter = set.descendingIterator(); iter.hasNext(); )
40 System.out.printf("desc : %s\n", (String)iter.next());
41 }
42
43 // 通过for-each遍历TreeSet。不推荐!此方法需要先将Set转换为数组
44 private static void foreachTreeSet(TreeSet set) {
45 System.out.printf("\n ---- For-each ----\n");
46 String[] arr = (String[])set.toArray(new String[0]);
47 for (String str:arr)
48 System.out.printf("for each : %s\n", str);
49 }
50 }
运行结果:
---- Ascend Iterator ----
asc : aaa
asc : bbb
asc : ccc
asc : ddd
asc : eee
---- Descend Iterator ----
desc : eee
desc : ddd
desc : ccc
desc : bbb
desc : aaa
---- For-each ----
for each : aaa
for each : bbb
for each : ccc
for each : ddd
for each : eee
第5部分 TreeSet示例
下面通过实例学习如何使用TreeSet
1 import java.util.*;
2
3 /**
4 * @desc TreeSet的API测试
5 *
6 * @author skywang
7 * @email [email protected]
8 */
9 public class TreeSetTest {
10
11 public static void main(String[] args) {
12 testTreeSetAPIs();
13 }
14
15 // 测试TreeSet的api
16 public static void testTreeSetAPIs() {
17 String val;
18
19 // 新建TreeSet
20 TreeSet tSet = new TreeSet();
21 // 将元素添加到TreeSet中
22 tSet.add("aaa");
23 // Set中不允许重复元素,所以只会保存一个“aaa”
24 tSet.add("aaa");
25 tSet.add("bbb");
26 tSet.add("eee");
27 tSet.add("ddd");
28 tSet.add("ccc");
29 System.out.println("TreeSet:"+tSet);
30
31 // 打印TreeSet的实际大小
32 System.out.printf("size : %d\n", tSet.size());
33
34 // 导航方法
35 // floor(小于、等于)
36 System.out.printf("floor bbb: %s\n", tSet.floor("bbb"));
37 // lower(小于)
38 System.out.printf("lower bbb: %s\n", tSet.lower("bbb"));
39 // ceiling(大于、等于)
40 System.out.printf("ceiling bbb: %s\n", tSet.ceiling("bbb"));
41 System.out.printf("ceiling eee: %s\n", tSet.ceiling("eee"));
42 // ceiling(大于)
43 System.out.printf("higher bbb: %s\n", tSet.higher("bbb"));
44 // subSet()
45 System.out.printf("subSet(aaa, true, ccc, true): %s\n", tSet.subSet("aaa", true, "ccc", true));
46 System.out.printf("subSet(aaa, true, ccc, false): %s\n", tSet.subSet("aaa", true, "ccc", false));
47 System.out.printf("subSet(aaa, false, ccc, true): %s\n", tSet.subSet("aaa", false, "ccc", true));
48 System.out.printf("subSet(aaa, false, ccc, false): %s\n", tSet.subSet("aaa", false, "ccc", false));
49 // headSet()
50 System.out.printf("headSet(ccc, true): %s\n", tSet.headSet("ccc", true));
51 System.out.printf("headSet(ccc, false): %s\n", tSet.headSet("ccc", false));
52 // tailSet()
53 System.out.printf("tailSet(ccc, true): %s\n", tSet.tailSet("ccc", true));
54 System.out.printf("tailSet(ccc, false): %s\n", tSet.tailSet("ccc", false));
55
56
57 // 删除“ccc”
58 tSet.remove("ccc");
59 // 将Set转换为数组
60 String[] arr = (String[])tSet.toArray(new String[0]);
61 for (String str:arr)
62 System.out.printf("for each : %s\n", str);
63
64 // 打印TreeSet
65 System.out.printf("TreeSet:%s\n", tSet);
66
67 // 遍历TreeSet
68 for(Iterator iter = tSet.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
69 System.out.printf("iter : %s\n", iter.next());
70 }
71
72 // 删除并返回第一个元素
73 val = (String)tSet.pollFirst();
74 System.out.printf("pollFirst=%s, set=%s\n", val, tSet);
75
76 // 删除并返回最后一个元素
77 val = (String)tSet.pollLast();
78 System.out.printf("pollLast=%s, set=%s\n", val, tSet);
79
80 // 清空HashSet
81 tSet.clear();
82
83 // 输出HashSet是否为空
84 System.out.printf("%s\n", tSet.isEmpty()?"set is empty":"set is not empty");
85 }
86 }
运行结果:
TreeSet:[aaa, bbb, ccc, ddd, eee]
size : 5
floor bbb: bbb
lower bbb: aaa
ceiling bbb: bbb
ceiling eee: eee
higher bbb: ccc
subSet(aaa, true, ccc, true): [aaa, bbb, ccc]
subSet(aaa, true, ccc, false): [aaa, bbb]
subSet(aaa, false, ccc, true): [bbb, ccc]
subSet(aaa, false, ccc, false): [bbb]
headSet(ccc, true): [aaa, bbb, ccc]
headSet(ccc, false): [aaa, bbb]
tailSet(ccc, true): [ccc, ddd, eee]
tailSet(ccc, false): [ddd, eee]
for each : aaa
for each : bbb
for each : ddd
for each : eee
TreeSet:[aaa, bbb, ddd, eee]
iter : aaa
iter : bbb
iter : ddd
iter : eee
pollFirst=aaa, set=[bbb, ddd, eee]
pollLast=eee, set=[bbb, ddd]
set is empty