文章原创,转载请注明出处:http://abc08010051.iteye.com/blog/2409693
后面会再修改一下,让文章读起来更好读,现在的版本还比较粗糙
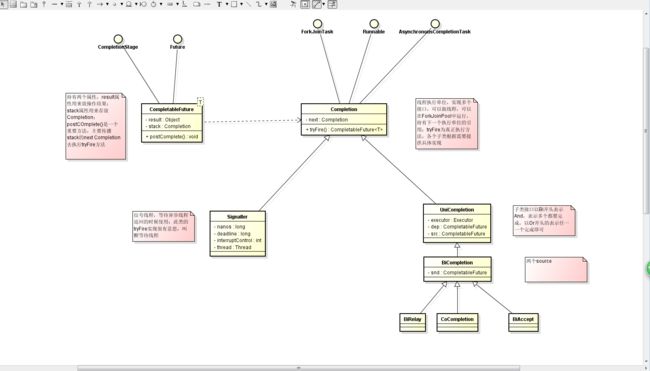
CompletableFuture是java 1.8提供的一个新类,是对Future的增强,吸收了guava异步线程的特点,可以实现一系列的异步线程操作,很多常规的用法网上有很多博客,这里说说部分代码的实现:
这是CompletableFuture的基本结构
CompletableFuture基本属性方法
volatile Object result; // Either the result or boxed AltResult
volatile Completion stack; // Top of Treiber stack of dependent actionsresult用来存放线程返回的结果
stack 行为上就是一个栈的功能,先进后出,用来存放要执行的动作,这个在单个异步线程返回时是没用的,多个线程等待的时候才排上用场
Completion基本属性方法
volatile Completion next; // Treiber stack link
abstract CompletableFuture tryFire(int mode);next链式结构,存放下一个
tryFire 方法,主要返回一个依赖的Completion
名词解释:
dependent:依赖,多个线程操作时,如何等待每个线程都完成才返回,主要是依靠这个依赖,没处理完就会调用依赖的postComplete()方法向上传递
source:源,用户自定义的线程的CompletableFuture
1 单一使用
/**
* Returns a new CompletableFuture that is asynchronously completed
* by a task running in the {@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} with
* the value obtained by calling the given Supplier.
*
* @param supplier a function returning the value to be used
* to complete the returned CompletableFuture
* @param the function's return type
* @return the new CompletableFuture
*/
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
static CompletableFuture asyncSupplyStage(Executor e,
Supplier f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture d = new CompletableFuture();
e.execute(new AsyncSupply(d, f));
return d;
}
static final class AsyncSupply extends ForkJoinTask
implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask {
CompletableFuture dep; Supplier fn;
AsyncSupply(CompletableFuture dep, Supplier fn) {
this.dep = dep; this.fn = fn;
}
public final Void getRawResult() { return null; }
public final void setRawResult(Void v) {}
public final boolean exec() { run(); return true; }
public void run() {
//CompletableFuture句柄,把Supplier的返回值放到CompletableFuture的result属性中,当前线程的执行是在默认的线程池中执行,在外部可以获取
CompletableFuture d; Supplier f;
if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) {
dep = null; fn = null;
if (d.result == null) {
try {
d.completeValue(f.get());
} catch (Throwable ex) {
d.completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
d.postComplete();
}
}
}
/**
* Pops and tries to trigger all reachable dependents. Call only
* when known to be done.
*/
final void postComplete() {
/*
* On each step, variable f holds current dependents to pop
* and run. It is extended along only one path at a time,
* pushing others to avoid unbounded recursion.
*/
CompletableFuture f = this; Completion h;
//循环遍历CompletableFuture的stack属性,Completion是一个链式的操作,如果有下一个,触发下一个Completion的tryFire方法
while ((h = f.stack) != null ||
(f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) {
CompletableFuture d; Completion t;
if (f.casStack(h, t = h.next)) {
if (t != null) {
if (f != this) {
pushStack(h);
continue;
}
h.next = null; // detach
}
f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d;
}
}
}
等待获取结果:
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Object r;
return reportGet((r = result) == null ? waitingGet(true) : r);
}
private Object waitingGet(boolean interruptible) {
Signaller q = null;
boolean queued = false;
int spins = -1;
Object r;
//循环获取result属性,判断是否为空,不为空获取到结果,跳出while循环
while ((r = result) == null) {
if (spins < 0)
//多个线程在允许,就给spins赋值256,然后循环递减,如果此时还没有返回值,则走下面的else分支
spins = (Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1) ?
1 << 8 : 0; // Use brief spin-wait on multiprocessors
else if (spins > 0) {
if (ThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed() >= 0)
--spins;
}
else if (q == null)
//创建等待信号线程
q = new Signaller(interruptible, 0L, 0L);
else if (!queued)
//替换stack属性,把替换是否成功的结果赋值给queued
queued = tryPushStack(q);
else if (interruptible && q.interruptControl < 0) {//允许中断,并且q.interruptControl = 1,不会走此分支, 下面的循环出现出现线程中断会走此分支
q.thread = null;
cleanStack();
return null;
}
else if (q.thread != null && result == null) {//如果结果没有返回,会进入当前分支
try {
//循环判断q是否释放,等待一直到满足Signaller释放条件(主要判断是否超时),上面Signaller的构造方法中,deadline为0, 不会因为超时释放,只有线程中断的时候才会释放
ForkJoinPool.managedBlock(q);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {//如果发生线程中断,把Signaller的interruptControl置为-1,等到下一个循环使用
q.interruptControl = -1;
}
}
}
if (q != null) {//信号线程不为null, 如果Signaller的中断控制标记位小于0,则返回null或者线程中断
q.thread = null;
if (q.interruptControl < 0) {
if (interruptible)
r = null; // report interruption
else
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
//传递给下一个Completion,没有则不执行
postComplete();
return r;
}
private static T reportGet(Object r)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//根据不同的情况做返回值的包装
if (r == null) // by convention below, null means interrupted
throw new InterruptedException();
if (r instanceof AltResult) {
Throwable x, cause;
if ((x = ((AltResult)r).ex) == null)
return null;
if (x instanceof CancellationException)
throw (CancellationException)x;
if ((x instanceof CompletionException) &&
(cause = x.getCause()) != null)
x = cause;
throw new ExecutionException(x);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T t = (T) r;
return t;
}
2 等待多个线程执行完成再做返回
//demo , stageRunnable是一个实现Runnable类型的变量
CompletableFuture future = CompletableFuture.allOf(CompletableFuture.runAsync(stageRunnable),
CompletableFuture.runAsync(stageRunnable), CompletableFuture.runAsync(stageRunnable));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(future));
future.get();
public static CompletableFuture allOf(CompletableFuture... cfs) {
return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}
//此方法是一个递归方法, 二分法把两个任务执行一个等待,每次二分都会创建一个CompletableFuture的depency
static CompletableFuture andTree(CompletableFuture[] cfs,
int lo, int hi) {
CompletableFuture d = new CompletableFuture();
if (lo > hi) // empty
d.result = NIL;
else {
CompletableFuture a, b;
int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
if ((a = (lo == mid ? cfs[lo] :
andTree(cfs, lo, mid))) == null ||
(b = (lo == hi ? a : (hi == mid+1) ? cfs[hi] :
andTree(cfs, mid+1, hi))) == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!d.biRelay(a, b)) {//a,b两个子任务没有全部完成,走此分支
BiRelay c = new BiRelay<>(d, a, b);//创建一个Completion,一个依赖,两个source
a.bipush(b, c);//把c推送到a,b的stack属性当中去
c.tryFire(SYNC);//BiRelay触发实际操作
}
}
return d;
}
//根据方法名直译的意思:是否两个传播都已经完成;两个任务有任何一个未完成,则返回false, 只有全部完成的时候才会返回true
boolean biRelay(CompletableFuture a, CompletableFuture b) {
Object r, s; Throwable x;
if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null ||
b == null || (s = b.result) == null)
return false;
if (result == null) {
if (r instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult)r).ex) != null)
completeThrowable(x, r);
else if (s instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult)s).ex) != null)
completeThrowable(x, s);
else
completeNull();
}
return true;
}