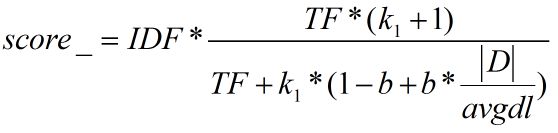记录一下,elasticsearch/lucene关于文档与query之间相关性的计算方式,目录如下,
- Lucene/es评分机制
- Lucene’s Practical Scoring Function
- Query-Time Boosting
- Ignoring TF/IDF
- Pluggable Similarity Algorithms
Lucene/es评分机制
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/guide/current/scoring-theory.html
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/By340-7g5rDxVKehY1izeQ
es使用Boolean model来匹配文档;使用practical scoring function(tfidf, BM25)来计算文档与query的相关性;使用vector space model来增加额外特征计算(如queryNorm,coord,norm,boost)。
注,一般query为指定在某个field中查询的。即score(field, query);而如果不指定field,且_all字段enable,那么就在该条doc中查询,即score(doc, query)。
Query & Term
query = quick brown fox
term1 = quick
term2 = brown
term3 = fox
Boolean Model
full AND text AND search AND (elasticsearch OR lucene).
Term Frequency/Inverse Document Frequency (TF/IDF)
词频/逆向文档频率,term的重要性随着它在文档doc中出现的次数成正比增加,但同时会随着它在语料库docs中出现的频率成反比下降。主要包含三部分,
- tf,该词在一篇文档中出现的次数,
tf(t in d) = √frequency - idf,该词出现在多少篇文档中(出现一次也算出现),
idf(t) = 1+ log((numDocs + 1)/(docFreq + 1)) - field-length norm,doc/field的文本长度,
norm(d) = 1 / √numTermsInDoc
//disable field-length norm可以减少index时候的计算量,加快index速度
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"text": {
"type": "string",
"norms": { "enabled": false }
}
}
}
}
}
Vector Space Model
使得query与doc之间的相关性可以比较。
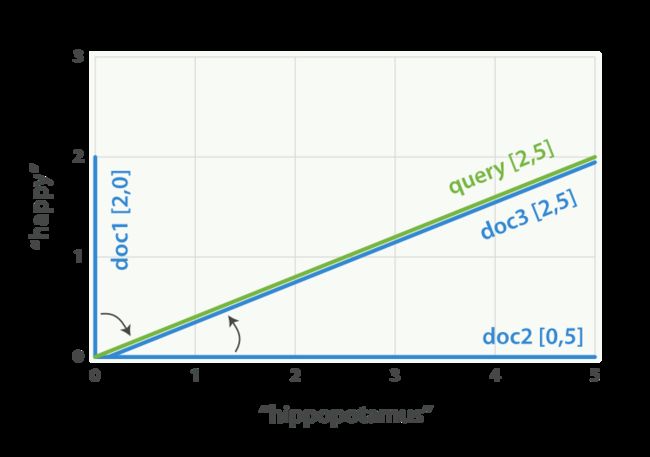
上图中,query = "happy hippopotamus",权重分别是2, 5,
doc1 = I am happy in summer.
doc2 = After Christmas I’m a hippopotamus.
doc3 = The happy hippopotamus helped Harry.
文档3与query最相关(夹角最小)。
Lucene’s Practical Scoring Function
lucene的计分函数,对于multiterm查询,lucene将布尔模型(Boolean)、词频/逆向文档频率(tfidf)、向量空间模型(vector space)合并到一个统一的jar包里面,用以收集匹配文档和分数计算。
//原生multiterm query语句
GET /my_index/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"text": "quick fox"
}
}
}
//布尔模型实现的改写
GET /my_index/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{"term": { "text": "quick" }},
{"term": { "text": "fox" }}
]
}
}
}
只要一个文档与查询匹配,lucene就会对该文档算分,然后合并每个term的得分,用到了practical scoring function,
score(q, d) = #1
queryNorm(q) #2
· coord(q, d) #3
· ∑ ( #4
tf(t in d) #5
· idf(t)² #6
· t.getBoost() #7
· norm(t, d) #8
) (t in q) #9
- score(q, d),文档d 与查询q 的相关度分数(relevance score)
- queryNorm(q),查询正则因子(query normalization factor)
- coord(q, d),协调因子(coordination factor)
- sum with #9
- tf(t in d),term t 在文档d 中的词频
- idf(t),term t 的逆向文档频率
- t.getBoost(),查询中使用的自定义boost
- norm(t, d),文档d的文本长度正则值
- sum with #4,查询 q 中每个term t 对于文档d 的权重和
queryNorm
queryNorm试图将查询正则化,以便可以比较两个不同query的结果。(不是很有效)
coord
协调因子,
query = "quick brown fox"
//without coord (the weight for each term is 1.5)
Document with fox → score: 1.5
Document with quick fox → score: 3.0
Document with quick brown fox → score: 4.5
//with coord
Document with fox → score: 1.5 * 1 / 3 = 0.5
Document with quick fox → score: 3.0 * 2 / 3 = 2.0
Document with quick brown fox → score: 4.5 * 3 / 3 = 4.5
{norm
文本长度。文本越短,文本的权重越高。norm(d) = 1 / √numTermsInDoc
boost}
自定义权重。
Query-Time Boosting
查询时权重提升,在搜索时令一个查询语句的自定义权重有别于其他查询语句,会更加符合个性化定制搜索的需求。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "quick brown fox",
"boost": 2
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"content": "quick brown fox"
}
}
]
}
}
}
query在title字段的自定义权重比在content字段的大(2>1),默认是1。
Ignoring TF/IDF
有时我们只关心一个term是否在某个doc中出现过,而不在乎它在doc中是否频繁出现,此时可以省去计算tfidf的耗时,加快检索速度。
constant_score
constant_score替代match,不计算tfidf,但是计算其余项的分数。
//match
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "wifi garden pool"
}
}
}
//constant_score
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score" : {
"filter" : {
"term" : { "user" : "kimchy"}
},
"boost" : 1.2
}
}
}
function_score query
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.0/query-dsl-function-score-query.html#function-decay
es检索时默认会以文档的相关性进行排序,而如果想要改变默认的排序规则,可以通过sort指定一个或多个排序字段。
GET /_search
{
"query" : {
"bool" : {
"filter" : { "term" : { "user_id" : 1 }}
}
},
"sort": { "date": { "order": "desc" }}
}
但是直接指定sort排序过于直接,可能效果不好(除非sort字段index前已经计算好)。此时就需要对多个字段进行综合评估,用到function_score,它允许我们为每个与query查询匹配的doc应用一个scoring函数,以达到改变默认规则的目的。es已有的function_score,如下,
- weight,为每个doc应用一个直接而不被正则化的权重提升值:当 weight=2 时,最终结果为 2 * _score(与constant_score的boost=2不同,constant_score的boost参与到_score的正则化计算中,只是constant_score没有计算tfidf,其余项quertNorm, coord, norm, boost都要参与到正则化计算中)
- random_score,根据seed随机种子,返回一个0到1的分数;seed相同,随机分相同。多用于个性化推荐
- field_value_factor,通过doc中指定filed从而计算出一个排序分
- field,指定的字段名
- factor,缩放系数,默认为1
- modifier,字段加工方式
- none,不处理
- log,对数
- log1p,字段值+1后取对数
- square,平方
- sqrt,开方
- reciprocal,倒数,etc.
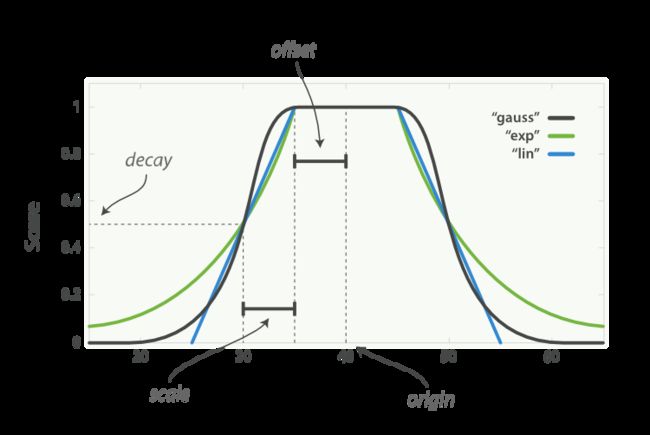
- decay_function,linear线性,exp指数,gauss高斯,入参如下,
- orgin,原点
- scale,衰减点
- offset,非零偏移量,默认0
- decay,从原点衰减到scale点的所得分,默认0.5,即scale点的文档得分是0.5
- script_score,通过脚本自定义不同字段的不同得分逻辑
//weight & random_score & score_mode & boost_mode
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"filter": {
"term": { "city": "Barcelona" }
},
"functions": [
{
"filter": { "term": { "features": "wifi" }},
"weight": 1
},
{
"filter": { "term": { "features": "garden" }},
"weight": 1
},
{
"filter": { "term": { "features": "pool" }},
"weight": 2
},
{
"random_score": {
"seed": "the_users_session_id"
}
}
],
"score_mode": "sum",
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}
//field_value_factor
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "likes",
"factor": 1.2,
"modifier": "sqrt",
"missing": 1
}
}
}
}
//delay function(d = day)
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"gauss": {
"date": {
"origin": "2013-09-17",
"scale": "10d",
"offset": "5d",
"decay" : 0.5
}
}
}
}
}
score combination
- score_mode,function_score与function_score之间的相处方式,
- multiply,默认
- sum
- avg
- max/min
- first
- boost_mode,function_score与_score之间的相处方式,
- multiply,默认
- sum
- avg
- max/min
- replace
Pluggable Similarity Algorithms
es配置了多种检索相关性算法可供选择,
- tfidf,默认
- BM25
- DFR, DFI, IB, etc.
其中,lucene自6.0起使用BM25代替了之前的tfidf。
//configure BM25 in mapping setting
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "string",
"similarity": "BM25"
},
"body": {
"type": "string",
"similarity": "default"
}
}
}
}
BM25
http://fjdu.github.io/coding/2017/03/16/bm25-elasticsearch-lucene.html
http://www.jianshu.com/p/0b372804ff45
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Okapi_BM25
Best Match 25,发布于1994年,是调整相关性计算的第25次迭代。
引入了Term frequency saturation(词频饱和度),计算如下,
其中,
- |D|:文档长度
- avgdl:所有文档的平均文档长度
- k1,b是自由参数,lucene默认k1=1.2,b=0.75
- IDF = log((#Docs - #DocsHit + 0.5)/(#DocsHit + 0.5))
- TF = query count in one doc
BM25F
http://www.cnblogs.com/bentuwuying/p/6730891.html
BM25F是BM25的改进版本,BM25在计算文档与query的相关性时将文档当做整体来考虑;但是随着advanced search的发展,文档的结构化(即每个文档都可以切分成多个独立的域field,比如title,abstract,keyword,body text等)需要被考虑,不同的域对相关性的贡献应该要更精细地处理,而BM25F就是query在文档的各个field中分值的加权求和。