Linux内核实验(一):proc文件系统
一、引言
Proc文件系统,以文件系统的形式向用户提供系统当前状态,动态地从同内核中读出所需的信息,只存在内存中,不占用外存空间。
二、实验内容
问题A:
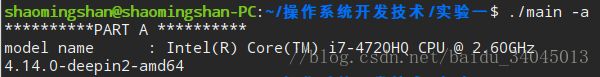
1、cpu类型
2、内核版本
问题B:
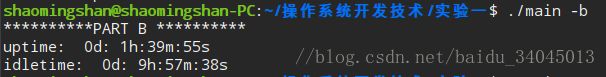
1、系统启动以来的时间,以dd:hh:mm:ss报告
问题C:
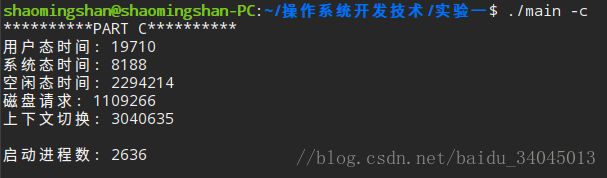
1、cpu执行用户态、系统态、空闲态所用时间
2、多少次磁盘请求
3、多少次上下文切换
4、启动了多少次进程
问题D:
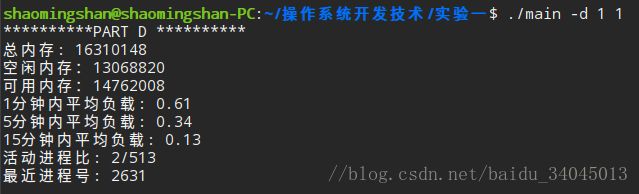
1、内存总量
2、可用内存
3、系统平均负荷
三、实验代码
/*****************************************
*
* Proc 文件系统
*
* Copyright: (C) 2018.3.31 by shaomingshan
*
* Compile: gcc -o main main.c
*
* Execute: ./main -a
*
*****************************************/
#include 四、运行结果
如有错误请指正