ansible入门,ansible安装与管理机群环境搭建,ansible基本命令,ansible模块的介绍(一)
一、概述
1.什么是ansible
ansible是2013年推出的一款IT自动化和DevOps(部署)软件,2015年被RedHat收购,基于Python研发,糅合很多老运维工具的优点,实现了批量化操作系统配置,批量程序部署,批量运行命令等功能
2.ansible可以做到的事
-自动化部署APP
-自动化管理配置项
-自动化持续交付
-自动化云(AWS)服务管理
3.为什么选择ansible
-活跃度高(开源社区)
-使用成本低(开源免费)
-编码语言,python支持,更新快
-性能比老一代的自动化工具高出一大截
-使用非常广泛
4.ansible软件特点
-只需要SSH和Python即可使用
-无客户端,部署简单
-功能强大,模块丰富,支持自定义模块
-上手容易,门槛低
-基于Python开发,二次开发容易
-模块化设计,调用特定的模块完成特定任务
-基于Python语言实现,支持Python支持的文本格式,paramiko,PyYAML,Jinja2,JSON,可以采用任何编程语言重写
-主从模式工作
-支持playbook,类脚本运维
-支持多层部署,异构IT环境
5.工作流程
读取配置->抓取机器分组表->使用过滤器过滤列表>根据参数确定执行模块和配置->返回执行结果->输出执行结果,结束
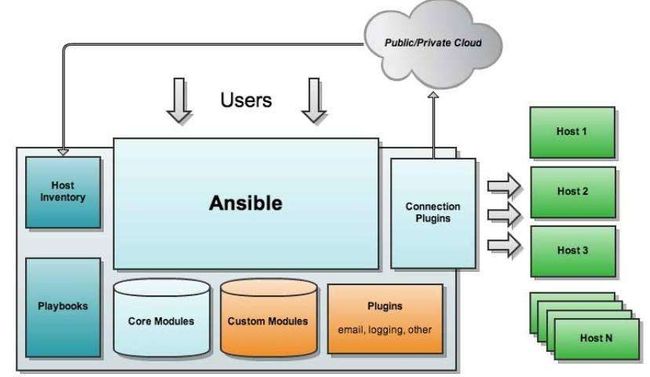
6.整体架构
本章主要讲Ansible,Core Modules(核心模块),Host Inventory(托管机清单),Host机群(主机需要准备什么才可以与ansible主机交流,环境准备),Connection Plugins(连接插件,ansible主机与被管理集群联系方式)
二、安装ansible
为你准备的rpm包(贴心吧)
[ansible依赖包,使用git clone下载]https://github.com/ck784101777/ansibleRPM
流程:yun仓库准备->yum源配置->安装ansible
1.环境准备
-python2.6以上
-安装paramiko
-PyYAML
-httplib2
-six
2.准备rmp包,配置yum仓库
我们使用ftp作为yum仓库,使用createrepo制作yum仓库
- [student@room9pc01 ~]$ cd /var/ftp
- [student@room9pc01 ~]$ mkdir ansible
- [student@room9pc01 ~]$cp /rmps/* /var/ftp/ansible //将rpm包拷贝到anisble下,以自己的文件目录为准
- ansible-2.4.2.0-2.el7.noarch.rpm python-paramiko-2.1.1-4.el7.noarch.rpm
- python2-jmespath-0.9.0-3.el7.noarch.rpm python-passlib-1.6.5-2.el7.noarch.rpm
- python-httplib2-0.9.2-1.el7.noarch.rpm sshpass-1.06-2.el7.x86_64.rpm
- [student@room9pc01 ansible]$ createrepo /var/ftp/ansible/ //制作yum仓库
3.配置yum源
- [student@room9pc01 ~]$vim /etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo
- [local]
- name=local
- baseurl="ftp://192.168.1.254/ansible"
- enabled=1
- gpgcheck=0
4.安装ansible
- [root@ansible ~]# yum -y install ansible
- [root@ansible ~]# ansible --version
- ansible 2.4.2.0 //显示版本说明安装成功
三、ansible托管主机配置(与管理机建立联系),ansible基本使用方式
流程: 检查托管主机的ssh协议,python版本-->管理机发布证书文件->了解ansible配置文件->了解ansible命令->主机定义与分组->测试托管机与管理机连通性
ip拓扑图:
准备5台托管机,ip如下,使用虚拟机创建.如果觉得太多仅创建web1,web2,ansible即可
1.对于被托管主句的要求
-需要打开SSH协议
-需要python2.5或以上
-如果托管节点开启了SElinux,需要安装libselinux-python
[root@ansible web1]# python //查看python版本,每台主机都要查看
Python 2.7.5 (default, Apr 11 2018, 07:36:10)[root@ansible web1]# setenforce 0 //实验关闭selinux或者安装libselinux-python
2.管理机分发证书文件
ansible是通过SSH在远程执行命令的,ssh远程执行命令必须要通过认证,可以通过-k声明交互式密码(ansible参数),所以需要通过key方式认证,给所以托管机部署公钥,如果没有配置公钥又没有写-k选项,就会报错,连接不上
用于免密访问ssh端口
[root@ansible ~]#ssh-keygen -t tsa -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa
[root@ansible ~]#vim /etc/hosts //配置域名解析
192.168.1.41 web1
192.168.1.42 web2
192.168.1.43 db1
192.168.1.44 db2
192.168.1.45 cache
[root@ansible ~]#for i in web1 web2 db1 db2 cache //发送秘钥
do
ssh-copy-id $i
done
[root@ansible ~]#ssh web1 //web2 db1 db2 cache都要尝试
....successeful
3.修改ansible配置文件
本实验需要修改两个地方,一个是设置host_key_checking,还有inventory
host_key_checking=Flase:
ssh主机key验证配置参数,为False,不需要手动输入yes,为true需要输入yes,一般设置为False
inventory:
定义托管主机地址配置文件路径名,指定配置文件,写入远程主机的地址.主要用于定义用户组
ansible配置文件查找顺序:
-首先检测当前目录下的./ansible.cfg
-再检车当前家目录下的 ~/ansible.cfg文件
-最后检查/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg文件
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg文件是ansible默认配置文件路径
本次实验修改/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg文件
[root@ansible .ssh]# vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts //默认注释,打开注释即可
host_key_checking = False //默认注释,打开注释即可
4.ansible命令
命令格式和基本参数:
ansible 主机集合 -m 模块名称 -a 模块参数
-主机集合 主机名或分组名.多个使用逗号分割
--m 模块名称,默认为command(不填写名称时使用)
- -a or --args 模块参数 常用''包起,是具体执行的命令,根据每个模块的使用方式有不同的参数
其他参数:
--i 指定inventory文件路径,或可执行脚本
--k交互式登录密码
--e定义变量
--v显示详细信息
常用命令:
-ansible all -list 列出要执行的主机
-ansible all -m ping 批量检测主机连通性
5.主机定义与分组
[组名称:变量/子组]
托管主机ip或主机名
如果有多台可以携程主机名[n:m]代表n-m台
vars变量:用于组名后面
可用于定义ssh秘钥变量,如:
[all:vars]
ansible_ssh_private_key_file="/root/.ssh/id_rsa" #定义ssh秘钥变量
ansible_ssh_port=端口号 #如果修改了端口就需要写修改后的端口号默认不写
children子组定义:用于引用其他组名称
如:
[app:children]
web
db
修改/etc/ansible/hosts文件,将文件之前的信息都删除,就改成如下所示
- [root@ansible .ssh]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
- [web]
- web1
- web2
- [db]
- db[1:2]
- [other]
- cache
- [all:vars]
- ansible_ssh_private_key_file="/root/.ssh/id_rsa"
- [root@ansible .ssh]# ansible all -m ping
- [root@ansible myansible]# ansible app -m ping //测试连通性,pong代表与托管机连接成功
- web1 | SUCCESS => {
- "changed": false,
- "ping": "pong"
- }
- db1 | SUCCESS => {
- "changed": false,
- "ping": "pong"
- }
- db2 | SUCCESS => {
- "changed": false,
- "ping": "pong"
- }
- web2 | SUCCESS => {
- "changed": false,
- "ping": "pong"
- }
- cache | SUCCESS => {
- "changed": false,
- "ping": "pong"
- }
6.自定义分组(补充)
上面的案例是使用ansible自带的文件进行修改,我们也可以自定义分组,但是执行ansible命令时需要进到这个目录下,且一个文件下不可以存在一个以上配置文件
- [root@ansible ~]# mkdir myansible //创建一个文件夹夹
- [root@ansible ~]# cd myansible/
- [root@ansible myansible]# vim myhost //可以将不同的类型的主机放到一个组中,或将不同类型的组添加到一个大组,使这些组成为大组的子组
- [app1]
- web1
- db1
- [app2]
- web2
- db2
- [app:children]
- app1
- app2
- [other]
- cache
- [all:vars]
- ansible_ssh_private_key_file="/root/.ssh/key"
- [root@ansible myansible]# touch ansible.cfg
- [root@ansible myansible]# vim ansible.cfg //指定组的引用文件
- [defaults]
- inventory = myhost
- host_key_checking = False
- [root@ansible myansible]# ansible app --list-host //查看app组,将显示app1和app2全部主机
- hosts (4):
- web1
- db1
- web2
- db2
7.动态发现(补充)
ansible Inventory(组定义)包含静态和动态的Inventory,静态Inventory指在文件/etc/ansible/hosts中指定的主机和组,动态Inventory指通过外部脚本(shell或python)获取主机列表,按照其要求格式(通常是json)返回给ansible
三、ansible模块以及使用模块管理托管机
1.ansible模块
查看模块命令:ansible-doc
-模块手册相当于man命令,可以查看模块的使用方式
查看所有模块:ansible-doc -l
查看某个模块(列出详细信息):ansible-doc 模块名
例:查看shell模块的信息
仅列出部分,首先是shell的基本介绍,然后是可选选项(OPTIONS),接着是注意实现(NOTES),作者(AUTHOR),举例(EXAMPLES这个部分很重要,记录了如何使用该模块),返回值(RETURN VALUES)
[root@ansible ~]#ansible-doc shell
SHELL (/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible/modules/commands/shell.py)
The `shell' module takes the command name followed by a list
of space-delimited arguments. It is almost exactly like the
[command] module but runs the command through a shell
(`/bin/sh') on the remote node. For Windows targets, use the
[win_shell] module instead.OPTIONS (= is mandatory):
- chdir
cd into this directory before running the command
[Default: None]
version_added: 0.6
NOTES:
* If you want to execute a command securely and
predictably, it may be better to use the [command]
module instead. Best practices when writing playbooks
will follow the trend of using [command] unless the
`shell' module is explicitly required. When running ad-
hoc commands, use your best judgement.
AUTHOR: Ansible Core Team, Michael DeHaan
METADATA:
status:
- stableinterface
supported_by: core
EXAMPLES:
- name: Execute the command in remote shell; stdout goes to the specified file on the remote.
shell: somescript.sh >> somelog.txt- name: Change the working directory to somedir/ before executing the command.
shell: somescript.sh >> somelog.txt
args:
chdir: somedir/# You can also use the 'args' form to provide the options.
- name: This command will change the working directory to somedir/ and will only run when somedir/somelog.txt doesn't exist.
shell: somescript.sh >> somelog.txt
args:
chdir: somedir/
creates: somelog.txt
RETURN VALUES:
msg:
description: changed
returned: always
type: boolean
sample: True
start:
description: The command execution start time
returned: always
type: string
sample: '2016-02-25 09:18:26.429568'
下面介绍几个常用的模块
2.command模块
-默认模块,远程执行命令
这个模块是默认执行的模块,如果不输入模块名如ansible 组名 -m -a '执行参数',将使用command模块
注意事项:
-该模块通过-a跟上要执行的命令可以直接执行,若命令中有类似"<>|&"的字符则不会被解析
如ansible all -m command -a "ps aux | grep ssh"会执行失败
报错信息:错误的语法
web1 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
error: unsupported option (BSD syntax)
3.shell模块
shell模块用法类似command,基本上你所有可以用command执行的命令都可以用shell执行,并且shell还能执行command所不能执行的
shell的短板:无法执行交互式命令,如vim top
注意事项:
使用shell创建文件必须使用绝对路径
ansible all -m shell -a 'touch a' #该命令会在root家目录下创建
ansible all -m shell -a 'touch /opt/a' #必须使用绝对路径才可以在你指定的地方创建
还有一种方式,使用chdir参数
ansible all -m shell -a 'chdir=/opt touch a'
使用''单引号和""双引号输出的变量结果不同,单引号将显示托管机的变量值,而双引号会输出本机的值
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible web -m shell -a 'echo ${HOSTNAME}' #单引号显示托管机的名称
web2 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
web2
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
web1
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible web -m shell -a "echo ${HOSTNAME}" #双引号显示管理机的名称
web2 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
ansible
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
ansible
正常来说你只需要单引号即可,但是如果你执意要使用双引号,请在变量前加\转义
这是因为ansible执行两次解析,第一次解析在本机(""),第二次解析在托管机(''),在变量前加\加入一次转义
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible web -m shell -a "echo \${HOSTNAME}"
web2 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
web2
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
web1
4.script模块
这是一个脚本执行模块,比如你想在一批托管机上执行某个脚本,常规思路是将脚本拷贝过去,然后依次执行.
使用script模块的好处就是只需要执行一条命令,就可以在一批托管机上执行,并且不需要将脚本拷贝到每台机上
ansible 托管机名 -m script -a '脚本路径/脚本名'
5.yum模块
顾名思义,就是使用yum批量安装软件的模块.
-name:要进行操作的软件包名字
-state:动作(installed,removed)
与常规使用yum不一样,正常使用的话是yum install 包名,而这里需要在每个命令后面加ed
例子:
ansible web -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=installed' #安装http
ansible web -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=removed' #卸载http
6.copy模块
顾名思义,就是复制文件到远程主机的模块
-src:复制本地文件到远程主机,绝对路径和相对路径都可(相对路径需要在该目录下),路径为目录是会递归复制,若路径以'/'结尾,则复制目录里所有内容,若不以'/'结尾,则复制整个目录过去
-dest:远程主机的绝对路径(取决于你想拷贝到哪).如果当前路径下存在你要拷贝的文件,则覆盖整个文件,如不存在则创建
-force:强制复制,当目标主机包含该文件,但内容不同,若设置为yes,则覆盖,若为no,则不覆盖.默认为yes.
例子:
ansible web -m copy -a 'src=/opt/hello.txt dest=/opt/' #将hello.txt文件拷贝到opt下
ansible web -m copy -a 'src=/opt/dir dest=/opt/' #将dir目录拷贝到opt下
ansible web -m copy -a 'src=/opt/dir/ dest=/opt/' #将dir目录下的所有文件拷贝到opt下
7.service模块
启动服务的命令,相当于systemctl start 服务名,开启某项服务
-name:必选项,服务名称
-enabled:是否开启启动,yes|or
-state:开启,停止,重启,重新加载 started | stoped | restarted | reloaded
例子:
ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd enable=yes state=started' #开启httpd服务,设置为开启自启
8.lineinfile模块(重要)
类似sed的一种编辑替换模块,替换某行
-path:目录文件名
-regexp:正则表达式,要修改的行
-line:最终修改的结果
例子:
若所有托管机的某个文件内容如下:
binlog-format=bin #我要将其修改为binlog-format=row
#注意双引号和单引号,使用单引号包起全部,然后在其下使用双引号,注意这里会替换一整行,所以查找条件你不需要打全,用^匹配以某字符开头即可
ansible db -m lineinfile -a 'path="/etc/my.cnf" regexp="^binlog-format" line="binlog-format=row"'
9.replace模块
类似sed的一种字符串替换模块
-path:目录文件名
-regexp:正则表达式,要修改的行
-replace:替换后的结果
例子:
若所有托管机的某个文件内容如下:
binlog-format=bin #我要将bin替换成row
#注意双引号和单引号,使用单引号包起全部,然后在其下使用双引号,注意这里会替换一整行,所以查找条件你不需要打全,用^匹配以某字符开头即可
ansible db -m replace -a 'path="/etc/my.cnf" regexp="bin" replace="row"'
与lineinfile不同,匹配的条件需要区分开,replace是替换某串字符,所以匹配条件以字符为主,lineinfile替换某行,所以只要找到某行开头的几个字符即可