算法4第4章加权有向图Dijkstra/BellmanFord最短路径算法关键路径算法讲解
最短路径即从一个顶点到达另一个顶点成本最小的路径,例如利用导航软件获取从一个地方到达另一个地方的路径,顶点对应路口,边对应公路,边的权重对应经过该路段的成本,可以是时间或距离,如果有单行线,那就要考虑加权有向图。
加权有向图的数据结构实现如下
public class EdgeWeightedDigraph {
private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator");
private final int V; // number of vertices in this digraph
private int E; // number of edges in this digraph
private Bag
private int[] indegree; // indegree[v] = indegree of vertex v
/**
* Initializes an empty edge-weighted digraph with {@code V} vertices and 0 edges.
*
* @param V the number of vertices
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code V < 0}
*/
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V) {
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
this.indegree = new int[V];
adj = (Bag
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
adj[v] = new Bag
}
/**
* Initializes a random edge-weighted digraph with {@code V} vertices and E edges.
*
* @param V the number of vertices
* @param E the number of edges
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code V < 0}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code E < 0}
*/
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V, int E) {
this(V);
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = StdRandom.uniform(V);
int w = StdRandom.uniform(V);
double weight = 0.01 * StdRandom.uniform(100);
DirectedEdge e = new DirectedEdge(v, w, weight);
addEdge(e);
}
}
/**
* Initializes an edge-weighted digraph from the specified input stream.
* The format is the number of vertices V,
* followed by the number of edges E,
* followed by E pairs of vertices and edge weights,
* with each entry separated by whitespace.
*
* @param in the input stream
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the endpoints of any edge are not in prescribed range
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the number of vertices or edges is negative
*/
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(In in) {
this(in.readInt());
int E = in.readInt();
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = in.readInt();
int w = in.readInt();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
double weight = in.readDouble();
addEdge(new DirectedEdge(v, w, weight));
}
}
/**
* Initializes a new edge-weighted digraph that is a deep copy of {@code G}.
*
* @param G the edge-weighted digraph to copy
*/
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(EdgeWeightedDigraph G) {
this(G.V());
this.E = G.E();
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
this.indegree[v] = G.indegree(v);
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
// reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original
Stack
for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj[v]) {
reverse.push(e);
}
for (DirectedEdge e : reverse) {
adj[v].add(e);
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the number of vertices in this edge-weighted digraph.
*
* @return the number of vertices in this edge-weighted digraph
*/
public int V() {
return V;
}
/**
* Returns the number of edges in this edge-weighted digraph.
*
* @return the number of edges in this edge-weighted digraph
*/
public int E() {
return E;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
/**
* Adds the directed edge {@code e} to this edge-weighted digraph.
*
* @param e the edge
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless endpoints of edge are between {@code 0}
* and {@code V-1}
*/
public void addEdge(DirectedEdge e) {
int v = e.from();
int w = e.to();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
adj[v].add(e);
indegree[w]++;
E++;
}
/**
* Returns the directed edges incident from vertex {@code v}.
*
* @param v the vertex
* @return the directed edges incident from vertex {@code v} as an Iterable
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public Iterable
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
/**
* Returns the number of directed edges incident from vertex {@code v}.
* This is known as the outdegree of vertex {@code v}.
*
* @param v the vertex
* @return the outdegree of vertex {@code v}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public int outdegree(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
/**
* Returns the number of directed edges incident to vertex {@code v}.
* This is known as the indegree of vertex {@code v}.
*
* @param v the vertex
* @return the indegree of vertex {@code v}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public int indegree(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return indegree[v];
}
/**
* Returns all directed edges in this edge-weighted digraph.
* To iterate over the edges in this edge-weighted digraph, use foreach notation:
* {@code for (DirectedEdge e : G.edges())}.
*
* @return all edges in this edge-weighted digraph, as an iterable
*/
public Iterable
Bag
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
for (DirectedEdge e : adj(v)) {
list.add(e);
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this edge-weighted digraph.
*
* @return the number of vertices V, followed by the number of edges E,
* followed by the V adjacency lists of edges
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
s.append(v + ": ");
for (DirectedEdge e : adj[v]) {
s.append(e + " ");
}
s.append(NEWLINE);
}
return s.toString();
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code EdgeWeightedDigraph} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in);
StdOut.println(G);
}
}
public class DirectedEdge {
private final int v;
private final int w;
private final double weight;
/**
* Initializes a directed edge from vertex {@code v} to vertex {@code w} with
* the given {@code weight}.
* @param v the tail vertex
* @param w the head vertex
* @param weight the weight of the directed edge
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if either {@code v} or {@code w}
* is a negative integer
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code weight} is {@code NaN}
*/
public DirectedEdge(int v, int w, double weight) {
if (v < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vertex names must be nonnegative integers");
if (w < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vertex names must be nonnegative integers");
if (Double.isNaN(weight)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Weight is NaN");
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
this.weight = weight;
}
/**
* Returns the tail vertex of the directed edge.
* @return the tail vertex of the directed edge
*/
public int from() {
return v;
}
/**
* Returns the head vertex of the directed edge.
* @return the head vertex of the directed edge
*/
public int to() {
return w;
}
/**
* Returns the weight of the directed edge.
* @return the weight of the directed edge
*/
public double weight() {
return weight;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of the directed edge.
* @return a string representation of the directed edge
*/
public String toString() {
return v + "->" + w + " " + String.format("%5.2f", weight);
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code DirectedEdge} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
DirectedEdge e = new DirectedEdge(12, 34, 5.67);
StdOut.println(e);
}
}
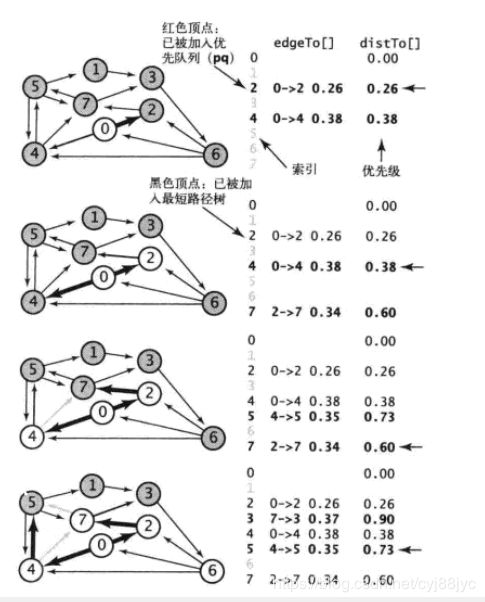
Dijkstra算法能够解决边权重非负的加权有向图的单起点最短路径问题,Dijkstra算法的过程类似Prim算法,对于起点s首先标记distTo[s] = 0.0;其他顶点v标记distTo[v]是无穷大,distTo[v]表示起点s到v的距离,首先将s的领边加入最短路径树,并将s相邻的顶点按distTo[v]的大小加入优先队列,然后从队列中取一个顶点,把该顶点相领顶点加入优先队列,领边加入最短路径树,加入的过程中如果某个顶点已经在树中或优先队列中但新的边会使s到这个点更近,则更换s到这个顶点的路径,直到所有顶点遍历完成,Dijkstra算法的时间复杂度是Elog(V)
轨迹图如下
public class DijkstraSP {
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = distance of shortest s->v path
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest s->v path
private IndexMinPQ
/**
* Computes a shortest-paths tree from the source vertex {@code s} to every other
* vertex in the edge-weighted digraph {@code G}.
*
* @param G the edge-weighted digraph
* @param s the source vertex
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an edge weight is negative
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= s < V}
*/
public DijkstraSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) {
for (DirectedEdge e : G.edges()) {
if (e.weight() < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("edge " + e + " has negative weight");
}
distTo = new double[G.V()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()];
validateVertex(s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// relax vertices in order of distance from s
pq = new IndexMinPQ
pq.insert(s, distTo[s]);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int v = pq.delMin();
for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v))
relax(e);
}
// check optimality conditions
assert check(G, s);
}
// relax edge e and update pq if changed
private void relax(DirectedEdge e) {
int v = e.from(), w = e.to();
if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.weight()) {
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
if (pq.contains(w)) pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo[w]);
else pq.insert(w, distTo[w]);
}
}
/**
* Returns the length of a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}.
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return the length of a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v};
* {@code Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY} if no such path
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public double distTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return distTo[v];
}
/**
* Returns true if there is a path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}.
*
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return {@code true} if there is a path from the source vertex
* {@code s} to vertex {@code v}; {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
}
/**
* Returns a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}.
*
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}
* as an iterable of edges, and {@code null} if no such path
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public Iterable
validateVertex(v);
if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()]) {
path.push(e);
}
return path;
}
// check optimality conditions:
// (i) for all edges e: distTo[e.to()] <= distTo[e.from()] + e.weight()
// (ii) for all edge e on the SPT: distTo[e.to()] == distTo[e.from()] + e.weight()
private boolean check(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) {
// check that edge weights are nonnegative
for (DirectedEdge e : G.edges()) {
if (e.weight() < 0) {
System.err.println("negative edge weight detected");
return false;
}
}
// check that distTo[v] and edgeTo[v] are consistent
if (distTo[s] != 0.0 || edgeTo[s] != null) {
System.err.println("distTo[s] and edgeTo[s] inconsistent");
return false;
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (v == s) continue;
if (edgeTo[v] == null && distTo[v] != Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY) {
System.err.println("distTo[] and edgeTo[] inconsistent");
return false;
}
}
// check that all edges e = v->w satisfy distTo[w] <= distTo[v] + e.weight()
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
int w = e.to();
if (distTo[v] + e.weight() < distTo[w]) {
System.err.println("edge " + e + " not relaxed");
return false;
}
}
}
// check that all edges e = v->w on SPT satisfy distTo[w] == distTo[v] + e.weight()
for (int w = 0; w < G.V(); w++) {
if (edgeTo[w] == null) continue;
DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[w];
int v = e.from();
if (w != e.to()) return false;
if (distTo[v] + e.weight() != distTo[w]) {
System.err.println("edge " + e + " on shortest path not tight");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
int V = distTo.length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code DijkstraSP} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in);
int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
// compute shortest paths
DijkstraSP sp = new DijkstraSP(G, s);
// print shortest path
for (int t = 0; t < G.V(); t++) {
if (sp.hasPathTo(t)) {
StdOut.printf("%d to %d (%.2f) ", s, t, sp.distTo(t));
for (DirectedEdge e : sp.pathTo(t)) {
StdOut.print(e + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
else {
StdOut.printf("%d to %d no path\n", s, t);
}
}
}
}
对于无环加权有向图计算最短路径有更快更简单的算法,首先将顶点进行拓扑排序,然后按拓扑排序的顺序遍历每个顶点,将顶点的领边加入最小路径树,该算法可以在线性时间内计算最短路径并且可以有负权重的边,稍做修改就可以计算最长路径
代码如下
public class AcyclicSP {
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = distance of shortest s->v path
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest s->v path
/**
* Computes a shortest paths tree from {@code s} to every other vertex in
* the directed acyclic graph {@code G}.
* @param G the acyclic digraph
* @param s the source vertex
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the digraph is not acyclic
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= s < V}
*/
public AcyclicSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) {
distTo = new double[G.V()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()];
validateVertex(s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// visit vertices in topological order
Topological topological = new Topological(G);
if (!topological.hasOrder())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Digraph is not acyclic.");
for (int v : topological.order()) {
for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v))
relax(e);
}
}
// relax edge e
private void relax(DirectedEdge e) {
int v = e.from(), w = e.to();
if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.weight()) {
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
}
}
/**
* Returns the length of a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}.
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return the length of a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v};
* {@code Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY} if no such path
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public double distTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return distTo[v];
}
/**
* Is there a path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}?
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return {@code true} if there is a path from the source vertex
* {@code s} to vertex {@code v}, and {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
}
/**
* Returns a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}.
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}
* as an iterable of edges, and {@code null} if no such path
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public Iterable
validateVertex(v);
if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()]) {
path.push(e);
}
return path;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
int V = distTo.length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code AcyclicSP} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in);
// find shortest path from s to each other vertex in DAG
AcyclicSP sp = new AcyclicSP(G, s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (sp.hasPathTo(v)) {
StdOut.printf("%d to %d (%.2f) ", s, v, sp.distTo(v));
for (DirectedEdge e : sp.pathTo(v)) {
StdOut.print(e + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
else {
StdOut.printf("%d to %d no path\n", s, v);
}
}
}
}
关键路径
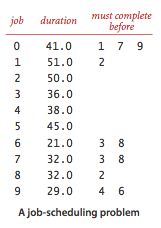
给定一组待完成的任务,以及一组关于任务完成先后顺序的优先级限制,在满足优先级限制的前提下,如何在若干相同的服务器下安排任务并在最短的时间完成所有任务,假设服务器数量不限
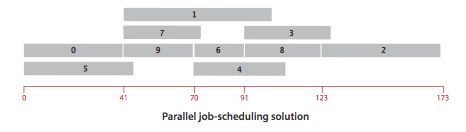
例如0-9个任务按优先级限制排列后如下图所示,其中0-9-6-8-2这条路径的总时间决定了所有任务的完成时间,这条路径叫做关键路径。
寻找关键路径的方法与计算无环加权有向图的最长路径是等价的,根据任务的优先级限制构造无环加权有向图,计算机出最长路径树就可以解决这个问题
实现步骤如下

代码如下
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac CPM.java
* Execution: java CPM < input.txt
* Dependencies: EdgeWeightedDigraph.java AcyclicDigraphLP.java StdOut.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/44sp/jobsPC.txt
*
* Critical path method.
*
* % java CPM < jobsPC.txt
* job start finish
* --------------------
* 0 0.0 41.0
* 1 41.0 92.0
* 2 123.0 173.0
* 3 91.0 127.0
* 4 70.0 108.0
* 5 0.0 45.0
* 6 70.0 91.0
* 7 41.0 73.0
* 8 91.0 123.0
* 9 41.0 70.0
* Finish time: 173.0
*
******************************************************************************/
/**
* The {@code CPM} class provides a client that solves the
* parallel precedence-constrained job scheduling problem
* via the critical path method. It reduces the problem
* to the longest-paths problem in edge-weighted DAGs.
* It builds an edge-weighted digraph (which must be a DAG)
* from the job-scheduling problem specification,
* finds the longest-paths tree, and computes the longest-paths
* lengths (which are precisely the start times for each job).
*
* This implementation uses {@link AcyclicLP} to find a longest
* path in a DAG.
* The running time is proportional to V + E,
* where V is the number of jobs and E is the
* number of precedence constraints.
*
* For additional documentation,
* see Section 4.4 of
* Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class CPM {
// this class cannot be instantiated
private CPM() { }
/**
* Reads the precedence constraints from standard input
* and prints a feasible schedule to standard output.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// number of jobs
int n = StdIn.readInt();
// source and sink
int source = 2*n;
int sink = 2*n + 1;
// build network
EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(2*n + 2);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
double duration = StdIn.readDouble();
G.addEdge(new DirectedEdge(source, i, 0.0));
G.addEdge(new DirectedEdge(i+n, sink, 0.0));
G.addEdge(new DirectedEdge(i, i+n, duration));
// precedence constraints
int m = StdIn.readInt();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int precedent = StdIn.readInt();
G.addEdge(new DirectedEdge(n+i, precedent, 0.0));
}
}
// compute longest path
AcyclicLP lp = new AcyclicLP(G, source);
// print results
StdOut.println(" job start finish");
StdOut.println("--------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
StdOut.printf("%4d %7.1f %7.1f\n", i, lp.distTo(i), lp.distTo(i+n));
}
StdOut.printf("Finish time: %7.1f\n", lp.distTo(sink));
}
}
BellmanFord算法可以计算有环和负权重边的加权有向图的最短路径,但不能有负权重环(总权重为负的环)
BellmanFord算法和Dijkstra算法代码比较像,Dijkstra用的优先队列,BellmanFord用的一般FIFO队列并且检查是否有负权重环
BellmanFord算法时间复杂度O(EV)
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac BellmanFordSP.java
* Execution: java BellmanFordSP filename.txt s
* Dependencies: EdgeWeightedDigraph.java DirectedEdge.java Queue.java
* EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/44sp/tinyEWDn.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/44sp/mediumEWDnc.txt
*
* Bellman-Ford shortest path algorithm. Computes the shortest path tree in
* edge-weighted digraph G from vertex s, or finds a negative cost cycle
* reachable from s.
*
* % java BellmanFordSP tinyEWDn.txt 0
* 0 to 0 ( 0.00)
* 0 to 1 ( 0.93) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39 3->6 0.52 6->4 -1.25 4->5 0.35 5->1 0.32
* 0 to 2 ( 0.26) 0->2 0.26
* 0 to 3 ( 0.99) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39
* 0 to 4 ( 0.26) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39 3->6 0.52 6->4 -1.25
* 0 to 5 ( 0.61) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39 3->6 0.52 6->4 -1.25 4->5 0.35
* 0 to 6 ( 1.51) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39 3->6 0.52
* 0 to 7 ( 0.60) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34
*
* % java BellmanFordSP tinyEWDnc.txt 0
* 4->5 0.35
* 5->4 -0.66
*
*
******************************************************************************/
/**
* The {@code BellmanFordSP} class represents a data type for solving the
* single-source shortest paths problem in edge-weighted digraphs with
* no negative cycles.
* The edge weights can be positive, negative, or zero.
* This class finds either a shortest path from the source vertex s
* to every other vertex or a negative cycle reachable from the source vertex.
*
* This implementation uses the Bellman-Ford-Moore algorithm.
* The constructor takes time proportional to V (V + E)
* in the worst case, where V is the number of vertices and E
* is the number of edges.
* Each call to {@code distTo(int)} and {@code hasPathTo(int)},
* {@code hasNegativeCycle} takes constant time;
* each call to {@code pathTo(int)} and {@code negativeCycle()}
* takes time proportional to length of the path returned.
*
* For additional documentation,
* see Section 4.4 of
* Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class BellmanFordSP {
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = distance of shortest s->v path
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest s->v path
private boolean[] onQueue; // onQueue[v] = is v currently on the queue?
private Queue
private int cost; // number of calls to relax()
private Iterable
/**
* Computes a shortest paths tree from {@code s} to every other vertex in
* the edge-weighted digraph {@code G}.
* @param G the acyclic digraph
* @param s the source vertex
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= s < V}
*/
public BellmanFordSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) {
distTo = new double[G.V()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()];
onQueue = new boolean[G.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// Bellman-Ford algorithm
queue = new Queue
queue.enqueue(s);
onQueue[s] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty() && !hasNegativeCycle()) {
int v = queue.dequeue();
onQueue[v] = false;
relax(G, v);
}
assert check(G, s);
}
// relax vertex v and put other endpoints on queue if changed
private void relax(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int v) {
for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
int w = e.to();
if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.weight()) {
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
if (!onQueue[w]) {
queue.enqueue(w);
onQueue[w] = true;
}
}
if (cost++ % G.V() == 0) {
findNegativeCycle();
if (hasNegativeCycle()) return; // found a negative cycle
}
}
}
/**
* Is there a negative cycle reachable from the source vertex {@code s}?
* @return {@code true} if there is a negative cycle reachable from the
* source vertex {@code s}, and {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean hasNegativeCycle() {
return cycle != null;
}
/**
* Returns a negative cycle reachable from the source vertex {@code s}, or {@code null}
* if there is no such cycle.
* @return a negative cycle reachable from the soruce vertex {@code s}
* as an iterable of edges, and {@code null} if there is no such cycle
*/
public Iterable
return cycle;
}
// by finding a cycle in predecessor graph
private void findNegativeCycle() {
int V = edgeTo.length;
EdgeWeightedDigraph spt = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (edgeTo[v] != null)
spt.addEdge(edgeTo[v]);
EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle finder = new EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle(spt);
cycle = finder.cycle();
}
/**
* Returns the length of a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}.
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return the length of a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v};
* {@code Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY} if no such path
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if there is a negative cost cycle reachable
* from the source vertex {@code s}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public double distTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
if (hasNegativeCycle())
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Negative cost cycle exists");
return distTo[v];
}
/**
* Is there a path from the source {@code s} to vertex {@code v}?
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return {@code true} if there is a path from the source vertex
* {@code s} to vertex {@code v}, and {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
}
/**
* Returns a shortest path from the source {@code s} to vertex {@code v}.
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return a shortest path from the source {@code s} to vertex {@code v}
* as an iterable of edges, and {@code null} if no such path
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if there is a negative cost cycle reachable
* from the source vertex {@code s}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public Iterable
validateVertex(v);
if (hasNegativeCycle())
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Negative cost cycle exists");
if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()]) {
path.push(e);
}
return path;
}
// check optimality conditions: either
// (i) there exists a negative cycle reacheable from s
// or
// (ii) for all edges e = v->w: distTo[w] <= distTo[v] + e.weight()
// (ii') for all edges e = v->w on the SPT: distTo[w] == distTo[v] + e.weight()
private boolean check(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) {
// has a negative cycle
if (hasNegativeCycle()) {
double weight = 0.0;
for (DirectedEdge e : negativeCycle()) {
weight += e.weight();
}
if (weight >= 0.0) {
System.err.println("error: weight of negative cycle = " + weight);
return false;
}
}
// no negative cycle reachable from source
else {
// check that distTo[v] and edgeTo[v] are consistent
if (distTo[s] != 0.0 || edgeTo[s] != null) {
System.err.println("distanceTo[s] and edgeTo[s] inconsistent");
return false;
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (v == s) continue;
if (edgeTo[v] == null && distTo[v] != Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY) {
System.err.println("distTo[] and edgeTo[] inconsistent");
return false;
}
}
// check that all edges e = v->w satisfy distTo[w] <= distTo[v] + e.weight()
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
int w = e.to();
if (distTo[v] + e.weight() < distTo[w]) {
System.err.println("edge " + e + " not relaxed");
return false;
}
}
}
// check that all edges e = v->w on SPT satisfy distTo[w] == distTo[v] + e.weight()
for (int w = 0; w < G.V(); w++) {
if (edgeTo[w] == null) continue;
DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[w];
int v = e.from();
if (w != e.to()) return false;
if (distTo[v] + e.weight() != distTo[w]) {
System.err.println("edge " + e + " on shortest path not tight");
return false;
}
}
}
StdOut.println("Satisfies optimality conditions");
StdOut.println();
return true;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
int V = distTo.length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code BellmanFordSP} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in);
BellmanFordSP sp = new BellmanFordSP(G, s);
// print negative cycle
if (sp.hasNegativeCycle()) {
for (DirectedEdge e : sp.negativeCycle())
StdOut.println(e);
}
// print shortest paths
else {
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (sp.hasPathTo(v)) {
StdOut.printf("%d to %d (%5.2f) ", s, v, sp.distTo(v));
for (DirectedEdge e : sp.pathTo(v)) {
StdOut.print(e + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
else {
StdOut.printf("%d to %d no path\n", s, v);
}
}
}
}
}