算法4第5章低位优先/高位优先和三向快速字符串排序算法讲解
前面讲的插入/快速排序等通用排序算法对字符串排序同样有效,但对字符串排序有更加高效的排序算法。
一种是低位优先的字符串排序算法(LSD),从右往左检查字符串的每个字符。
一种是高位优先的字符串排序算法(MSD),从左往右检查字符串的每个字符。
这两种算法都是基于一种叫做键索引计数法的排序方法实现的。
低位优先的字符串排序
首先看低位优先的字符串排序算法,LSD从字符串的右边开始,先按右边第1个字符的大小把字符串排序,再按第2个字符的大小进行排序,直到左边第1个字符,
LSD只适用字符串长度都相同的字符串进行排序,轨迹图如下
代码如下
public class LSD {
private static final int BITS_PER_BYTE = 8;
// do not instantiate
private LSD() { }
/**
* Rearranges the array of W-character strings in ascending order.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param w the number of characters per string
*/
public static void sort(String[] a, int w) {
int n = a.length;
int R = 256; // extend ASCII alphabet size
String[] aux = new String[n];
for (int d = w-1; d >= 0; d--) {
// sort by key-indexed counting on dth character
// compute frequency counts
//计算第d列每个字符出现的个数,+1表示下一个字符在数组中相对这个字符的距离
//比如若a对应索引0,第d个字符中a出现2个,则a+1=b在数组中相对a排在索引2的位置
int[] count = new int[R+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[a[i].charAt(d) + 1]++;
// compute cumulates
//计算按第d个字符进行排序每个字符串在数组中的索引位置
//比如a有2个,b有1个,则a对应的索引是0,b对应2,c对应3
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// move data
//按索引位置把字符串调整到辅助数组
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
aux[count[a[i].charAt(d)]++] = a[i];
// copy back
//回写
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = aux[i];
}
}
/**
* Rearranges the array of 32-bit integers in ascending order.
* This is about 2-3x faster than Arrays.sort().
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(int[] a) {
final int BITS = 32; // each int is 32 bits
final int R = 1 << BITS_PER_BYTE; // each bytes is between 0 and 255
final int MASK = R - 1; // 0xFF
final int w = BITS / BITS_PER_BYTE; // each int is 4 bytes
int n = a.length;
int[] aux = new int[n];
for (int d = 0; d < w; d++) {
// compute frequency counts
int[] count = new int[R+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int c = (a[i] >> BITS_PER_BYTE*d) & MASK;
count[c + 1]++;
}
// compute cumulates
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// for most significant byte, 0x80-0xFF comes before 0x00-0x7F
if (d == w-1) {
int shift1 = count[R] - count[R/2];
int shift2 = count[R/2];
for (int r = 0; r < R/2; r++)
count[r] += shift1;
for (int r = R/2; r < R; r++)
count[r] -= shift2;
}
// move data
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int c = (a[i] >> BITS_PER_BYTE*d) & MASK;
aux[count[c]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = aux[i];
}
}
/**
* Reads in a sequence of fixed-length strings from standard input;
* LSD radix sorts them;
* and prints them to standard output in ascending order.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
int n = a.length;
// check that strings have fixed length
int w = a[0].length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
assert a[i].length() == w : "Strings must have fixed length";
// sort the strings
sort(a, w);
// print results
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac MSD.java
* Execution: java MSD < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/51radix/words3.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/51radix/shells.txt
*
* Sort an array of strings or integers using MSD radix sort.
*
* % java MSD < shells.txt
* are
* by
* sea
* seashells
* seashells
* sells
* sells
* she
* she
* shells
* shore
* surely
* the
* the
*
******************************************************************************/
/**
* The {@code MSD} class provides static methods for sorting an
* array of extended ASCII strings or integers using MSD radix sort.
*
* For additional documentation,
* see Section 5.1 of
* Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
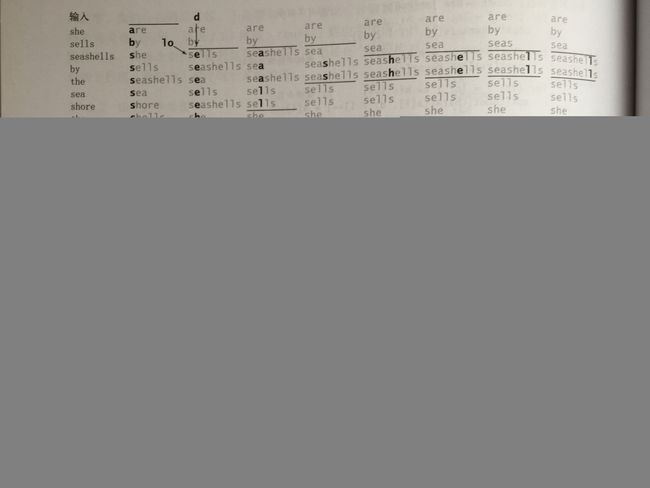
高位优先的字符串排序
高位优先的字符串排序思路更容易理解,从字符串左边开始,先按第1个字符进行排序,再对第1个字符相同的每个子数组按第2个字符进行排序,直到每个字符串所有字符遍历完
虽然思路比较容易理解,代码也很简洁,但理解起来真不太容易,下面代码是按ASCII字母表进行编写的,R=256.
我们按小写字母表来进行理解,R=26, 即a的索引是0,z的索引是25,为了处理第d列已经为空的字符串,代码中讲索引的位置加1,即a的索引是1,z的索引是26,索引0代表空字符
轨迹图如下:
public class MSD {
private static final int BITS_PER_BYTE = 8;
private static final int BITS_PER_INT = 32; // each Java int is 32 bits
private static final int R = 256; // extended ASCII alphabet size
private static final int CUTOFF = 15; // cutoff to insertion sort
// do not instantiate
private MSD() { }
/**
* Rearranges the array of extended ASCII strings in ascending order.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(String[] a) {
int n = a.length;
String[] aux = new String[n];
sort(a, 0, n-1, 0, aux);
}
// return dth character of s, -1 if d = length of string
private static int charAt(String s, int d) {
assert d >= 0 && d <= s.length();
if (d == s.length()) return -1;
return s.charAt(d);
}
// sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth character
private static void sort(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d, String[] aux) {
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
//将小型子数组切换到插入排序效率会提高很多
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) {
insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
// compute frequency counts
int[] count = new int[R+2];
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
//假设c=0代表a,则c+1如上边所说代表a的索引位置,c+2跟LSD一样代表b相对a在数组中索引位置
//c=-1代表第d行的字母为空,c+1代表空字母,c+2就代表a相对空字母在数组中索引位置,比如空字母2个,则a排在2的位置
int c = charAt(a[i], d);
count[c+2]++;
}
// transform counts to indicies
for (int r = 0; r < R+1; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// distribute
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = charAt(a[i], d);
//c+1才代表字母的索引位置,比如c=0,则count[c+1]代表字母a在数组中排的位置
aux[count[c+1]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
a[i] = aux[i - lo];
// recursively sort for each character (excludes sentinel -1)
//对第1个字母相同的每个子数组分别按第2个字母进行排序
//假设r=0,则r+1是a的索引,通过上面的叠加,此时count[r+1]代表字母a结束的索引位置,count[r]代表空字母结束的索引位置
//则从lo + count[r]到 lo + count[r+1] - 1,就代表第1个字母都为a的子数组在原数组中的开始结束索引,对这个子数组按第2个字母进行排序
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
sort(a, lo + count[r], lo + count[r+1] - 1, d+1, aux);
}
// insertion sort a[lo..hi], starting at dth character
private static void insertion(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && less(a[j], a[j-1], d); j--)
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
// exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(String[] a, int i, int j) {
String temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
// is v less than w, starting at character d
private static boolean less(String v, String w, int d) {
// assert v.substring(0, d).equals(w.substring(0, d));
for (int i = d; i < Math.min(v.length(), w.length()); i++) {
if (v.charAt(i) < w.charAt(i)) return true;
if (v.charAt(i) > w.charAt(i)) return false;
}
return v.length() < w.length();
}
/**
* Rearranges the array of 32-bit integers in ascending order.
* Currently assumes that the integers are nonnegative.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length;
int[] aux = new int[n];
sort(a, 0, n-1, 0, aux);
}
// MSD sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth byte
private static void sort(int[] a, int lo, int hi, int d, int[] aux) {
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) {
insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
// compute frequency counts (need R = 256)
int[] count = new int[R+1];
int mask = R - 1; // 0xFF;
int shift = BITS_PER_INT - BITS_PER_BYTE*d - BITS_PER_BYTE;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = (a[i] >> shift) & mask;
count[c + 1]++;
}
// transform counts to indicies
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
/************* BUGGGY CODE.
// for most significant byte, 0x80-0xFF comes before 0x00-0x7F
if (d == 0) {
int shift1 = count[R] - count[R/2];
int shift2 = count[R/2];
for (int r = 0; r < R/2; r++)
count[r] += shift1;
for (int r = R/2; r < R; r++)
count[r] -= shift2;
}
************************************/
// distribute
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = (a[i] >> shift) & mask;
aux[count[c]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
a[i] = aux[i - lo];
// no more bits
if (d == 4) return;
// recursively sort for each character
if (count[0] > 0)
sort(a, lo, lo + count[0] - 1, d+1, aux);
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
if (count[r+1] > count[r])
sort(a, lo + count[r], lo + count[r+1] - 1, d+1, aux);
}
// TODO: insertion sort a[lo..hi], starting at dth character
private static void insertion(int[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && a[j] < a[j-1]; j--)
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
// exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
/**
* Reads in a sequence of extended ASCII strings from standard input;
* MSD radix sorts them;
* and prints them to standard output in ascending order.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
int n = a.length;
sort(a);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
}
}
三向字符串快速排序
三向快速字符串排序更前面通用的三向快速排序类似,从左往右按每个字母的大小只把字符串分成三部分,再分别对3个子数组排序,适合含有较长公共前缀的字符串
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac Quick3string.java
* Execution: java Quick3string < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/51radix/words3.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/51radix/shells.txt
*
* Reads string from standard input and 3-way string quicksort them.
*
* % java Quick3string < shell.txt
* are
* by
* sea
* seashells
* seashells
* sells
* sells
* she
* she
* shells
* shore
* surely
* the
* the
*
*
******************************************************************************/
/**
* The {@code Quick3string} class provides static methods for sorting an
* array of strings using 3-way radix quicksort.
*
* For additional documentation,
* see Section 5.1 of
* Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class Quick3string {
private static final int CUTOFF = 15; // cutoff to insertion sort
// do not instantiate
private Quick3string() { }
/**
* Rearranges the array of strings in ascending order.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(String[] a) {
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
sort(a, 0, a.length-1, 0);
assert isSorted(a);
}
// return the dth character of s, -1 if d = length of s
private static int charAt(String s, int d) {
assert d >= 0 && d <= s.length();
if (d == s.length()) return -1;
return s.charAt(d);
}
// 3-way string quicksort a[lo..hi] starting at dth character
private static void sort(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) {
insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
int lt = lo, gt = hi;
int v = charAt(a[lo], d);
int i = lo + 1;
while (i <= gt) {
int t = charAt(a[i], d);
if (t < v) exch(a, lt++, i++);
else if (t > v) exch(a, i, gt--);
else i++;
}
// a[lo..lt-1] < v = a[lt..gt] < a[gt+1..hi].
sort(a, lo, lt-1, d);
if (v >= 0) sort(a, lt, gt, d+1);
sort(a, gt+1, hi, d);
}
// sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth character
private static void insertion(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && less(a[j], a[j-1], d); j--)
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
// exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(String[] a, int i, int j) {
String temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
// is v less than w, starting at character d
// DEPRECATED BECAUSE OF SLOW SUBSTRING EXTRACTION IN JAVA 7
// private static boolean less(String v, String w, int d) {
// assert v.substring(0, d).equals(w.substring(0, d));
// return v.substring(d).compareTo(w.substring(d)) < 0;
// }
// is v less than w, starting at character d
private static boolean less(String v, String w, int d) {
assert v.substring(0, d).equals(w.substring(0, d));
for (int i = d; i < Math.min(v.length(), w.length()); i++) {
if (v.charAt(i) < w.charAt(i)) return true;
if (v.charAt(i) > w.charAt(i)) return false;
}
return v.length() < w.length();
}
// is the array sorted
private static boolean isSorted(String[] a) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
if (a[i].compareTo(a[i-1]) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
/**
* Reads in a sequence of fixed-length strings from standard input;
* 3-way radix quicksorts them;
* and prints them to standard output in ascending order.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// read in the strings from standard input
String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
int n = a.length;
// sort the strings
sort(a);
// print the results
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
}
}