MiniGUI源码分析:GDI(1)-- GDI概览及Surface
上一篇:MiniGUI源码分析--Helloworld(3):消息概览
从本章开始,将逐步介绍MiniGUI部分GDI
GDI(Graphics Device Interface)是对绘图接口的描述,是MiniGUI的核心组成部分之一。
GDI虽然是GUI的基础,但是,它实际上不太适合作为GUI的组成部分之一的。因为GUI的核心功能在用户交互上,而不是如何绘制上。对MiniGUI来说,GDI是成也萧何败萧何:MiniGUI内置的GDI使得MiniGUI更紧凑和高效,但是由于其功能受限,使得MiniGUI在绘图精细度上,以及和其他优秀的界面库结合上,存在巨大的缺陷。由此也造成MiniGUI发展受限,无法赶上时代的潮流。
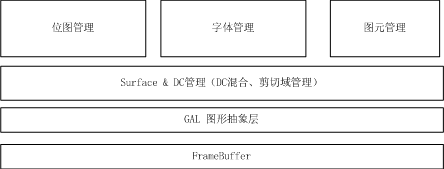
MiniGUI的GDI分成GAL、DC和Surface、位图管理、字体管理以及图元绘制(包括矩形、圆形的绘制和填充),可以用示意图表示:
GDI中涉及很多绘图的算法,这些可以通过查阅计算机图形学相关的书籍就可以了解,这不是我们的重点。我们的重点,在于了解他对显存的管理和操作。
所以,我们从Surface和DC说起。
Surface是管理显存的一个重要对象。它负责管理显存的大小、色深等信息。而且,可以把一块普通的内存看做一个显存,这样,我们就可以在内存中首先构造出该对象。
首先,看它的定义:(src/include/newgal.h)
typedef struct GAL_Surface {
Uint32 flags; /* Read-only */
GAL_PixelFormat *format; /* Read-only */
void *video; /* Read-only */
int w, h; /* Read-only */
Uint32 pitch; /* Read-only */
void *pixels; /* Read-write */
int offset; /* Private */
/* Hardware-specific surface info */
struct private_hwdata *hwdata;
/* clipping information */
GAL_Rect clip_rect; /* Read-only */
/* info for fast blit mapping to other surfaces */
struct GAL_BlitMap *map; /* Private */
/* format version, bumped at every change to invalidate blit maps */
unsigned int format_version; /* Private */
/* Reference count -- used when freeing surface */
int refcount; /* Read-mostly */
} GAL_Surface有几个重要的成员:
format:表示像素的格式,是非常重要的成员
pxiels:是像素的地址指针
map:这是对像素做合并的时候,使用的合并方法。
其中,flags变量来标记surface的一些属性,例如,是硬件surface(surface的pixel指向的内存是显存)或者是软surface(pixel指向普通的内存)等。
由于硬surface和软surface没有太大的区别,所以我们可以先忽略这一部分。
Surface的重要的操作有:创建、删除、Surface的像素合并(BitBlt)。
Surface相关的操作都在src/newgal/surface.c中
首先,看Surface的创建过程。Surface的创建,主要是通过GAL_CreateRGBSurface函数创建的。它初始化一个Surface对象。先看下该函数的实现。
GAL_Surface * GAL_CreateRGBSurface (Uint32 flags,
int width, int height, int depth,
Uint32 Rmask, Uint32 Gmask, Uint32 Bmask, Uint32 Amask)
{
GAL_VideoDevice *video = current_video;
GAL_VideoDevice *this = current_video;
GAL_Surface *screen;
GAL_Surface *surface;
/* Check to see if we desire the surface in video memory */
if ( video ) {
screen = GAL_PublicSurface;
} else {
screen = NULL;
}
if ( screen && ((screen->flags&GAL_HWSURFACE) == GAL_HWSURFACE) ) {
if ( (flags&(GAL_SRCCOLORKEY|GAL_SRCALPHA)) != 0 ) {
flags |= GAL_HWSURFACE;
}
if ( (flags & GAL_SRCCOLORKEY) == GAL_SRCCOLORKEY ) {
if ( ! current_video->info.blit_hw_CC ) {
flags &= ~GAL_HWSURFACE;
}
}
if ( (flags & GAL_SRCALPHA) == GAL_SRCALPHA ) {
if ( ! current_video->info.blit_hw_A ) {
flags &= ~GAL_HWSURFACE;
}
}
} else {
flags &= ~GAL_HWSURFACE;
}
/* Allocate the surface */
surface = (GAL_Surface *)malloc(sizeof(*surface));
if ( surface == NULL ) {
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
if ((flags & GAL_HWSURFACE) == GAL_HWSURFACE)
surface->video = current_video;
else
surface->video = NULL;
surface->flags = GAL_SWSURFACE;
if ( (flags & GAL_HWSURFACE) == GAL_HWSURFACE ) {
depth = screen->format->BitsPerPixel;
Rmask = screen->format->Rmask;
Gmask = screen->format->Gmask;
Bmask = screen->format->Bmask;
Amask = screen->format->Amask;
}
surface->format = GAL_AllocFormat(depth, Rmask, Gmask, Bmask, Amask);
if ( surface->format == NULL ) {
free(surface);
return(NULL);
}
if ( Amask ) {
surface->flags |= GAL_SRCALPHA;
}
surface->w = width;
surface->h = height;
surface->pitch = GAL_CalculatePitch(surface);
surface->pixels = NULL;
surface->offset = 0;
surface->hwdata = NULL;
surface->map = NULL;
surface->format_version = 0;
GAL_SetClipRect(surface, NULL);
/* Get the pixels */
if ( ((flags&GAL_HWSURFACE) == GAL_SWSURFACE) ||
(video->AllocHWSurface(this, surface) < 0) ) {
if ( surface->w && surface->h ) {
surface->pixels = malloc(surface->h*surface->pitch);
if ( surface->pixels == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeSurface(surface);
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
/* This is important for bitmaps */
memset(surface->pixels, 0, surface->h*surface->pitch);
surface->flags &= ~GAL_HWSURFACE;
}
}
/* Allocate an empty mapping */
surface->map = GAL_AllocBlitMap();
if ( surface->map == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeSurface(surface);
return(NULL);
}
/* The surface is ready to go */
surface->refcount = 1;
#ifdef CHECK_LEAKS
++surfaces_allocated;
#endif
return(surface);
}对format成员,它调用了GAL_AllocFormat函数。首先,看下GAL_PixelFormat的定义:
typedef struct GAL_PixelFormat {
GAL_Palette *palette;
BOOL DitheredPalette;
Uint8 BitsPerPixel;
Uint8 BytesPerPixel;
Uint8 Rloss;
Uint8 Gloss;
Uint8 Bloss;
Uint8 Aloss;
Uint8 Rshift;
Uint8 Gshift;
Uint8 Bshift;
Uint8 Ashift;
Uint32 Rmask;
Uint32 Gmask;
Uint32 Bmask;
Uint32 Amask;
/* RGB color key information */
gal_pixel colorkey;
/* Alpha value information (per-surface alpha) */
gal_uint8 alpha;
} GAL_PixelFormat;
BitsPerPixel是一个像素占用的位数,可以选择的是1,2,4,8,16,24,32
BytesPerPixel是一个像素占用的字节数,可以是,1,2,4等
下面的成员,按照R、G、B、A分成loss, shift, mask三组,它是相对于一个分量8位来说的,分别表示RGBA分量所丢失的位数、在像素中的偏移位数和掩码值
例如,对于16位以565格式保存的RGB像素格式来说,其高6位被R分量占用,Rloss为3,Rshift为11,Rmask则为0xF800; 中间6位被G分量占用,Gloss为2,GShift为5,Gmask为0x07E0;B分量占用剩余的5位,其中Bloss为3,Bshift为0,Bmask为0x001F,表示如下:
RRRR RGGG GGGB BBBB
用这些信息,就可以通过RGB分量计算出一个像素的值,如:
Uint32 pixv = (r >> format->Rloss) << format->Rshift
| (g >> format->Gloss) << format->Gshift
| (b >> format->Bloss) << format->Bshift
| ((a >> format->Aloss) << format->Ashift & format->Amask);然后我们看下 GAL_AllocFormat函数的实现:
GAL_PixelFormat *GAL_AllocFormat(int bpp,
Uint32 Rmask, Uint32 Gmask, Uint32 Bmask, Uint32 Amask)
{
GAL_PixelFormat *format;
Uint32 mask;
/* Allocate an empty pixel format structure */
format = malloc(sizeof(*format));
if ( format == NULL ) {
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
memset(format, 0, sizeof(*format));
format->alpha = GAL_ALPHA_OPAQUE;
/* Set up the format */
format->BitsPerPixel = bpp;
format->BytesPerPixel = (bpp+7)/8;
format->DitheredPalette = FALSE;
switch (bpp) {
case 1:
/* Create the 2 color black-white palette */
format->palette = (GAL_Palette *)malloc(
sizeof(GAL_Palette));
if ( format->palette == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeFormat(format);
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
(format->palette)->ncolors = 2;
(format->palette)->colors = (GAL_Color *)malloc(
(format->palette)->ncolors*sizeof(GAL_Color));
if ( (format->palette)->colors == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeFormat(format);
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
format->palette->colors[0].r = 0xFF;
format->palette->colors[0].g = 0xFF;
format->palette->colors[0].b = 0xFF;
format->palette->colors[1].r = 0x00;
format->palette->colors[1].g = 0x00;
format->palette->colors[1].b = 0x00;
format->Rloss = 8;
format->Gloss = 8;
format->Bloss = 8;
format->Aloss = 8;
format->Rshift = 0;
format->Gshift = 0;
format->Bshift = 0;
format->Ashift = 0;
format->Rmask = 0;
format->Gmask = 0;
format->Bmask = 0;
format->Amask = 0;
break;
case 4:
/* Create the 16 color VGA palette */
format->palette = (GAL_Palette *)malloc(
sizeof(GAL_Palette));
if ( format->palette == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeFormat(format);
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
(format->palette)->ncolors = 16;
(format->palette)->colors = (GAL_Color *)malloc(
(format->palette)->ncolors*sizeof(GAL_Color));
if ( (format->palette)->colors == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeFormat(format);
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
/* Punt for now, will this ever be used? */
memset((format->palette)->colors, 0,
(format->palette)->ncolors*sizeof(GAL_Color));
/* Palettized formats have no mask info */
format->Rloss = 8;
format->Gloss = 8;
format->Bloss = 8;
format->Aloss = 8;
format->Rshift = 0;
format->Gshift = 0;
format->Bshift = 0;
format->Ashift = 0;
format->Rmask = 0;
format->Gmask = 0;
format->Bmask = 0;
format->Amask = 0;
break;
case 8:
/* Create an empty 256 color palette */
format->palette = (GAL_Palette *)malloc(
sizeof(GAL_Palette));
if ( format->palette == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeFormat(format);
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
(format->palette)->ncolors = 256;
(format->palette)->colors = (GAL_Color *)malloc(
(format->palette)->ncolors*sizeof(GAL_Color));
if ( (format->palette)->colors == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeFormat(format);
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
memset((format->palette)->colors, 0,
(format->palette)->ncolors*sizeof(GAL_Color));
/* Palettized formats have no mask info */
format->Rloss = 8;
format->Gloss = 8;
format->Bloss = 8;
format->Aloss = 8;
format->Rshift = 0;
format->Gshift = 0;
format->Bshift = 0;
format->Ashift = 0;
format->Rmask = 0;
format->Gmask = 0;
format->Bmask = 0;
format->Amask = 0;
break;
default:
/* No palette, just packed pixel info */
format->palette = NULL;
format->Rshift = 0;
format->Rloss = 8;
if ( Rmask ) {
for ( mask = Rmask; !(mask&0x01); mask >>= 1 )
++format->Rshift;
for ( ; (mask&0x01); mask >>= 1 )
--format->Rloss;
}
format->Gshift = 0;
format->Gloss = 8;
if ( Gmask ) {
for ( mask = Gmask; !(mask&0x01); mask >>= 1 )
++format->Gshift;
for ( ; (mask&0x01); mask >>= 1 )
--format->Gloss;
}
format->Bshift = 0;
format->Bloss = 8;
if ( Bmask ) {
for ( mask = Bmask; !(mask&0x01); mask >>= 1 )
++format->Bshift;
for ( ; (mask&0x01); mask >>= 1 )
--format->Bloss;
}
format->Ashift = 0;
format->Aloss = 8;
if ( Amask ) {
for ( mask = Amask; !(mask&0x01); mask >>= 1 )
++format->Ashift;
for ( ; (mask&0x01); mask >>= 1 )
--format->Aloss;
}
format->Rmask = Rmask;
format->Gmask = Gmask;
format->Bmask = Bmask;
format->Amask = Amask;
break;
}
/* Calculate some standard bitmasks, if necessary
* Note: This could conflict with an alpha mask, if given.
*/
if ( (bpp > 8) && !format->Rmask && !format->Gmask && !format->Bmask ) {
/* R-G-B */
if ( bpp > 24 )
bpp = 24;
format->Rloss = 8-(bpp/3);
format->Gloss = 8-(bpp/3)-(bpp%3);
format->Bloss = 8-(bpp/3);
format->Rshift = ((bpp/3)+(bpp%3))+(bpp/3);
format->Gshift = (bpp/3);
format->Bshift = 0;
format->Rmask = ((0xFF>>format->Rloss)<Rshift);
format->Gmask = ((0xFF>>format->Gloss)<Gshift);
format->Bmask = ((0xFF>>format->Bloss)<Bshift);
}
return(format);
} default分支的代码,注意通过Rmask、Gmask、Bmask和Amask的值,计算得到loss和shift的,算法很简单。不再赘述。
另外一部分重要的代码是map成员变量的初始化。因为它关系到两个surface的混合。首先看下GAL_BitMap结构的定义
/* Blit mapping definition */
typedef struct GAL_BlitMap {
GAL_Surface *dst;
int identity;
Uint8 *table;
GAL_blit hw_blit;
GAL_blit sw_blit;
struct private_hwaccel *hw_data;
struct private_swaccel *sw_data;
/* the version count matches the destination; mismatch indicates
an invalid mapping */
unsigned int format_version;
} GAL_BlitMap;这里需要关注的重点是hw_blit和sw_blit变量,它们是主要指向blit的操作的回调。GAL_blit的定义是:
typedef int (*GAL_blit)(struct GAL_Surface *src, GAL_Rect *srcrect,
struct GAL_Surface *dst, GAL_Rect *dstrect);
GAL_BlitMap *GAL_AllocBlitMap(void)
{
GAL_BlitMap *map;
/* Allocate the empty map */
map = (GAL_BlitMap *)malloc(sizeof(*map));
if ( map == NULL ) {
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
memset(map, 0, sizeof(*map));
/* Allocate the software blit data */
map->sw_data = (struct private_swaccel *)malloc(sizeof(*map->sw_data));
if ( map->sw_data == NULL ) {
GAL_FreeBlitMap(map);
GAL_OutOfMemory();
return(NULL);
}
memset(map->sw_data, 0, sizeof(*map->sw_data));
/* It's ready to go */
return(map);
}Surface的另外一个重要操作,就是做层之间的混合。它是通过GAL_LowerBlit来实现的(lower表示更接近于设备底层的实现),其代码如下:
int GAL_LowerBlit (GAL_Surface *src, GAL_Rect *srcrect,
GAL_Surface *dst, GAL_Rect *dstrect)
{
GAL_blit do_blit;
/* Check to make sure the blit mapping is valid */
if ( (src->map->dst != dst) ||
(src->map->dst->format_version != src->map->format_version) ) {
if ( GAL_MapSurface(src, dst) < 0 ) {
return(-1);
}
}
/* Figure out which blitter to use */
if ( (src->flags & GAL_HWACCEL) == GAL_HWACCEL ) {
do_blit = src->map->hw_blit;
} else {
do_blit = src->map->sw_blit;
}
return(do_blit(src, srcrect, dst, dstrect));
}
hw_blit是用硬件加速实现的函数,所以,它是由GAL层实现和设置的。每种不同的开发板有字节的实现方法,所以,这不是我们讨论的重点。
sw_blit只软件实现的混合函数,由MiniGUI自己提供,它的确定,是在GAL_MapSurface函数中确定。
当第一次调用GAL_LowerBlit的时候,src->map->dst必定为NULL所以,就会调用到该函数。
GAL_MapSurface会调用到GAL_CalculateBlit函数,还选择一个正确的sw_blit,该函数会计算并填充hw_blit和sw_blit函数。这是一个比较复杂的过程。不过最终,sw_blit大部分情况下,会得到GAL_SoftBlit函数的指针。
关于这部分的详细情况,可以查看相关代码。