kfifo学习及其使用示例
内核代码中有许多值得借鉴的地方,kfifo设计的非常巧妙,代码很精简,对于入队和出对处理的出人意料。当只有一个读线程和一个写线程并发操作时,可以确保是线程安全的,不用添加额外的锁来使用这些功能。kfifo的这一特性,提高了kernel的并发效率。所以kfifo适用于一个线程存数据,一个线程取数据的应用场景。
kfifo结构体:
struct kfifo
{
unsigned char *buffer; / *保存数据的缓冲区* /
unsigned int size; / *分配的缓冲区的大小* /
unsigned int in; / *数据以偏移量(in%size)添加* /
unsigned int out; / *数据从off中提取。(out%size)* /
};kfifo.h
#ifndef _KFIFO_H
#define _KFIFO_H
#include
struct kfifo {
unsigned char *buffer; /* the buffer holding the data */
unsigned int size; /* the size of the allocated buffer */
unsigned int in; /* data is added at offset (in % size) */
unsigned int out; /* data is extracted from off. (out % size) */
};
/*
* Macros for declaration and initialization of the kfifo datatype
*/
extern void kfifo_init(struct kfifo *fifo, void *buffer,
unsigned int size);
extern unsigned int kfifo_in(struct kfifo *fifo,
const void *from, unsigned int len);
extern unsigned int kfifo_out(struct kfifo *fifo,
void *to, unsigned int len);
/**
* kfifo_initialized - Check if kfifo is initialized.
* @fifo: fifo to check
* Return %true if FIFO is initialized, otherwise %false.
* Assumes the fifo was 0 before.
*/
static inline int kfifo_initialized(struct kfifo *fifo)
{
return fifo->buffer != NULL;
}
/**
* kfifo_reset - removes the entire FIFO contents
* @fifo: the fifo to be emptied.
*/
static inline void kfifo_reset(struct kfifo *fifo)
{
fifo->in = fifo->out = 0;
}
/**
* kfifo_reset_out - skip FIFO contents
* @fifo: the fifo to be emptied.
*/
static inline void kfifo_reset_out(struct kfifo *fifo)
{
fifo->out = fifo->in;
}
/**
* kfifo_size - returns the size of the fifo in bytes
* @fifo: the fifo to be used.
*/
static inline unsigned int kfifo_size(struct kfifo *fifo)
{
return fifo->size;
}
/**
* kfifo_len - returns the number of used bytes in the FIFO
* @fifo: the fifo to be used.
*/
static inline unsigned int kfifo_len(struct kfifo *fifo)
{
register unsigned int out;
out = fifo->out;
return fifo->in - out;
}
/**
* kfifo_is_empty - returns true if the fifo is empty
* @fifo: the fifo to be used.
*/
static inline int kfifo_is_empty(struct kfifo *fifo)
{
return fifo->in == fifo->out;
}
/**
* kfifo_is_full - returns true if the fifo is full
* @fifo: the fifo to be used.
*/
static inline int kfifo_is_full(struct kfifo *fifo)
{
return kfifo_len(fifo) == kfifo_size(fifo);
}
/**
* kfifo_avail - returns the number of bytes available in the FIFO
* @fifo: the fifo to be used.
*/
static inline unsigned int kfifo_avail(struct kfifo *fifo)
{
return kfifo_size(fifo) - kfifo_len(fifo);
}
extern void kfifo_skip(struct kfifo *fifo, unsigned int len);
/*
* __kfifo_add_out internal helper function for updating the out offset
*/
static inline void __kfifo_add_out(struct kfifo *fifo,
unsigned int off)
{
fifo->out += off;
}
/*
* __kfifo_add_in internal helper function for updating the in offset
*/
static inline void __kfifo_add_in(struct kfifo *fifo,
unsigned int off)
{
fifo->in += off;
}
/*
* __kfifo_off internal helper function for calculating the index of a
* given offeset
*/
static inline unsigned int __kfifo_off(struct kfifo *fifo, unsigned int off)
{
return off & (fifo->size - 1);
}
#endif /* _KFIFO_H */ kfifo.c
#include "kfifo.h"
#include
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
/* is x a power of 2? */
#define is_power_of_2(x) ((x) != 0 && (((x) & ((x) - 1)) == 0))
/**
* kfifo_init - initialize a FIFO using a preallocated buffer
* @fifo: the fifo to assign the buffer
* @buffer: the preallocated buffer to be used.
* @size: the size of the internal buffer, this has to be a power of 2.
*
*/
void kfifo_init(struct kfifo *fifo, void *buffer, unsigned int size)
{
/* TODO: size must be a power of 2? */
fifo->buffer = buffer;
fifo->size = size;
kfifo_reset(fifo);
}
static inline void __kfifo_in_data(struct kfifo *fifo,
const void *from, unsigned int len, unsigned int off)
{
unsigned int l;
/*
* Ensure that we sample the fifo->out index -before- we
* start putting bytes into the kfifo.
*/
off = __kfifo_off(fifo, fifo->in + off);
/* first put the data starting from fifo->in to buffer end */
l = min(len, fifo->size - off);
memcpy(fifo->buffer + off, from, l);
/* then put the rest (if any) at the beginning of the buffer */
memcpy(fifo->buffer, from + l, len - l);
}
static inline void __kfifo_out_data(struct kfifo *fifo,
void *to, unsigned int len, unsigned int off)
{
unsigned int l;
/*
* Ensure that we sample the fifo->in index -before- we
* start removing bytes from the kfifo.
*/
off = __kfifo_off(fifo, fifo->out + off);
/* first get the data from fifo->out until the end of the buffer */
l = min(len, fifo->size - off);
memcpy(to, fifo->buffer + off, l);
/* then get the rest (if any) from the beginning of the buffer */
memcpy(to + l, fifo->buffer, len - l);
}
unsigned int __kfifo_in_n(struct kfifo *fifo,
const void *from, unsigned int len, unsigned int recsize)
{
if (kfifo_avail(fifo) < len + recsize)
return len + 1;
__kfifo_in_data(fifo, from, len, recsize);
return 0;
}
/**
* kfifo_in - puts some data into the FIFO
* @fifo: the fifo to be used.
* @from: the data to be added.
* @len: the length of the data to be added.
*
* This function copies at most @len bytes from the @from buffer into
* the FIFO depending on the free space, and returns the number of
* bytes copied.
*
* Note that with only one concurrent reader and one concurrent
* writer, you don't need extra locking to use these functions.
*/
unsigned int kfifo_in(struct kfifo *fifo, const void *from,
unsigned int len)
{
len = min(kfifo_avail(fifo), len);
__kfifo_in_data(fifo, from, len, 0);
__kfifo_add_in(fifo, len);
return len;
}
unsigned int __kfifo_out_n(struct kfifo *fifo,
void *to, unsigned int len, unsigned int recsize)
{
if (kfifo_len(fifo) < len + recsize)
return len;
__kfifo_out_data(fifo, to, len, recsize);
__kfifo_add_out(fifo, len + recsize);
return 0;
}
/**
* kfifo_out - gets some data from the FIFO
* @fifo: the fifo to be used.
* @to: where the data must be copied.
* @len: the size of the destination buffer.
*
* This function copies at most @len bytes from the FIFO into the
* @to buffer and returns the number of copied bytes.
*
* Note that with only one concurrent reader and one concurrent
* writer, you don't need extra locking to use these functions.
*/
unsigned int kfifo_out(struct kfifo *fifo, void *to, unsigned int len)
{
len = min(kfifo_len(fifo), len);
__kfifo_out_data(fifo, to, len, 0);
__kfifo_add_out(fifo, len);
return len;
} use_example.c
#include
#include
#include "kfifo.h"
#define BUFF_SIZE 256
char queue_buff[BUFF_SIZE]={0};
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
struct kfifo *pkfifo;
pkfifo = malloc(sizeof(struct kfifo));
if(pkfifo == NULL)
{
printf("malloc queue_buffer error!\n");
return 0;
}
//param1 分配缓冲区的fifo
//param2 要使用的预分配缓冲区
//param3 内部缓冲区的大小必须是2的幂
kfifo_init(pkfifo, queue_buff, BUFF_SIZE);
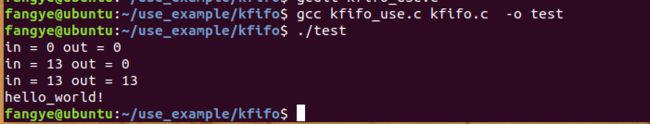
printf("in = %d out = %d\n",pkfifo->in,pkfifo->out);
char str[]={"hello_world!"};
//将一些数据放入FIFO
//param1 要使用的fifo
//param2 要添加的数据
//param3 要添加的数据的长度
kfifo_in(pkfifo,str,sizeof(str)); //一个线程专门负责添加数据,返回值为添加数据的字节数
printf("in = %d out = %d\n",pkfifo->in,pkfifo->out);
char rcv_data[256]={0};
kfifo_out(pkfifo,rcv_data,sizeof(rcv_data)); //一个线程专门负责取出数据,返回值为取出数据的字节数
printf("in = %d out = %d\n",pkfifo->in,pkfifo->out);
printf("%s\n",rcv_data);
return 0;
} 测试结果: