传统手工特征--opencv
一,颜色特征:
简单点来说就是将一幅图上的各个像素点颜色统计出来,适用颜色空间:RGB,HSV等颜色空间,
具体操作:量化颜色空间,每个单元(bin)由单元中心代表,统计落在量化单元上的像素数量
量化颜色直方图(HSV空间)
缺点:稀疏,量化问题
聚类颜色直方图:
适用颜色空间:Lab等颜色空间
操作:使用聚类算法对所有像素点颜色向量进行聚类
单元(bin)由聚类中心代表
解决稀疏问题
二,几何特征
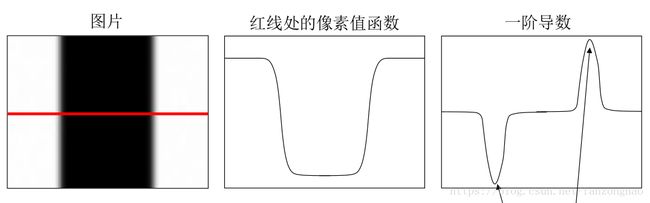
边缘:像素明显变化的区域,含有丰富的语义信息
边缘定义:像素值快速变化的区域
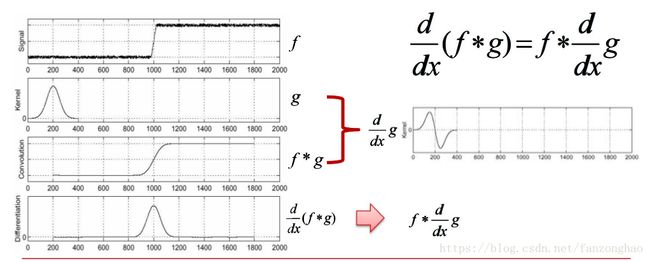
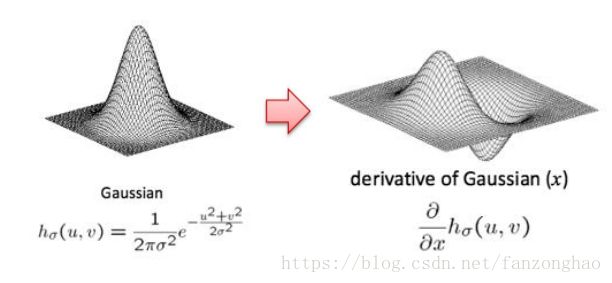
高斯滤波一阶求导:
三,基于特征点的特征描述子
不同的观测方式,物体的大小,形状,明暗会有不同,依然可以判断为同一物体
Harris角点(corner):
在任何方向上移动小观察窗,导致大的像素变动
代码:
def harris_corner():
import numpy as np
import cv2
filename = './data/chessboard.png'
img = cv2.imread(filename)
img=cv2.resize(img,(200,200))
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = np.float32(gray)
dst = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 2, 3, 0.04)
# result is dilated for marking the corners, not important
dst = cv2.dilate(dst, None)
# Threshold for an optimal value, it may vary depending on the image.
img[dst > 0.01 * dst.max()] = [0, 0, 255]
cv2.imshow('dst', img)
if cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff == 27:
cv2.destroyAllWindows()打印结果:
(1)SIFT特征:基于尺度空间不变的特征,4×4网格,8方向直方图,总共128维特征向量
特点:具有良好的不变性,少数物体也能产生大量SIFT特征
代码:
def sift():
import numpy as np
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('./data/home.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
kp = sift.detect(gray, None)
img = cv2.drawKeypoints(gray, kp, img)
cv2.imshow("SIFT", img)
cv2.imwrite('sift_keypoints.jpg', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()结果:
(2)LBP(局部二值模式):每个像素点与周围点大小比较,多个bit组成一个数,统计每个数的直方图,
LBP特征具有灰度不变性和旋转不变性等显著优点。
(3)SURF,为了保证旋转不变性,在SURF中,统计特征点领域内的Harr小波特征。
代码:
def surf():
import numpy as np
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('./data/butterfly.jpg', 0)
surf = cv2.xfeatures2d.SURF_create(400)
# kp, des = surf.detectAndCompute(img,None)
surf.setHessianThreshold(50000)
kp, des = surf.detectAndCompute(img, None)
img2 = cv2.drawKeypoints(img, kp, None, (255, 0, 0), 4)
cv2.imshow('surf', img2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()(4)ORB特征基于FAST角点的特征点检测
def orb():
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img1 = cv.imread('./data/box.png', 0) # queryImage
img2 = cv.imread('./data/box_in_scene.png', 0) # trainImage
# Initiate ORB detector
orb = cv.ORB_create()
# find the keypoints and descriptors with ORB
kp1, des1 = orb.detectAndCompute(img1, None)
kp2, des2 = orb.detectAndCompute(img2, None)
# create BFMatcher object
bf = cv.BFMatcher(cv.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True)
# Match descriptors.
matches = bf.match(des1, des2)
# Sort them in the order of their distance.
matches = sorted(matches, key=lambda x: x.distance)
# Draw first 10 matches.
img3 = cv.drawMatches(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, matches[:20], None, flags=2)
plt.imshow(img3), plt.show()(5)Gabor滤波:用于边缘提取的线性滤波器,三角函数+高斯函数=Gabor滤波器
基于sift拼接:Stitcher.py
import numpy as np
import cv2
class Stitcher:
#拼接函数
def stitch(self, images, ratio=0.75, reprojThresh=4.0,showMatches=False):
#获取输入图片
(imageB, imageA) = images
#检测A、B图片的SIFT关键特征点,并计算特征描述子
(kpsA, featuresA) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageA)
(kpsB, featuresB) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageB)
# 匹配两张图片的所有特征点,返回匹配结果
M = self.matchKeypoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh)
# 如果返回结果为空,没有匹配成功的特征点,退出算法
if M is None:
return None
# 否则,提取匹配结果
# H是3x3视角变换矩阵
(matches, H, status) = M
# 将图片A进行视角变换,result是变换后图片
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, (imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1], imageA.shape[0]))
# 将图片B传入result图片最左端
result[0:imageB.shape[0], 0:imageB.shape[1]] = imageB
# 检测是否需要显示图片匹配
if showMatches:
# 生成匹配图片
vis = self.drawMatches(imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status)
# 返回结果
return (result, vis)
# 返回匹配结果
return result
def detectAndDescribe(self, image):
# 将彩色图片转换成灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 建立SIFT生成器
descriptor = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
# 检测SIFT特征点,并计算描述子
(kps, features) = descriptor.detectAndCompute(image, None)
# 将结果转换成NumPy数组
kps = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kps])
# 返回特征点集,及对应的描述特征
return (kps, features)
def matchKeypoints(self, kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh):
# 建立暴力匹配器
matcher = cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create("BruteForce")
# 使用KNN检测来自A、B图的SIFT特征匹配对,K=2
rawMatches = matcher.knnMatch(featuresA, featuresB, 2)
matches = []
for m in rawMatches:
# 当最近距离跟次近距离的比值小于ratio值时,保留此匹配对
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < m[1].distance * ratio:
# 存储两个点在featuresA, featuresB中的索引值
matches.append((m[0].trainIdx, m[0].queryIdx))
# 当筛选后的匹配对大于4时,计算视角变换矩阵
if len(matches) > 4:
# 获取匹配对的点坐标
ptsA = np.float32([kpsA[i] for (_, i) in matches])
ptsB = np.float32([kpsB[i] for (i, _) in matches])
# 计算视角变换矩阵
(H, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsA, ptsB, cv2.RANSAC, reprojThresh)
# 返回结果
return (matches, H, status)
# 如果匹配对小于4时,返回None
return None
def drawMatches(self, imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status):
# 初始化可视化图片,将A、B图左右连接到一起
(hA, wA) = imageA.shape[:2]
(hB, wB) = imageB.shape[:2]
vis = np.zeros((max(hA, hB), wA + wB, 3), dtype="uint8")
vis[0:hA, 0:wA] = imageA
vis[0:hB, wA:] = imageB
# 联合遍历,画出匹配对
for ((trainIdx, queryIdx), s) in zip(matches, status):
# 当点对匹配成功时,画到可视化图上
if s == 1:
# 画出匹配对
ptA = (int(kpsA[queryIdx][0]), int(kpsA[queryIdx][1]))
ptB = (int(kpsB[trainIdx][0]) + wA, int(kpsB[trainIdx][1]))
cv2.line(vis, ptA, ptB, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 返回可视化结果
return visdef image_stich():
from opencv.Stitcher import Stitcher
import cv2
# 读取拼接图片
imageA = cv2.imread("./data/left_01.png")
imageB = cv2.imread("./data/right_01.png")
# 把图片拼接成全景图
stitcher = Stitcher()
(result, vis) = stitcher.stitch([imageA, imageB], showMatches=True)
# 显示所有图片
cv2.imshow("Image A", imageA)
cv2.imshow("Image B", imageB)
cv2.imshow("Keypoint Matches", vis)
cv2.imshow("Result", result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()