opencv 实现任意角度的透视变换
opencv中提供了getPerspectiveTransform函数来获取由四对点间的转换矩阵,输出矩阵为3*3, 同时也提供了warpPerspective函数来对通过变换矩阵来对图像进行透视变换的操作,同时还提供了perspectiveTransform来提供对点的转换:
getPerspectiveTransform:
Calculates a perspective transform from four pairs of the corresponding points.
C++: Mat getPerspectiveTransform(InputArray src, InputArray dst)
C++: Mat getPerspectiveTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[])
Python: cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst) → retval
perspectiveTransform:
Performs the perspective matrix transformation of vectors.
C++: void perspectiveTransform(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, InputArray m)
Python: cv2.perspectiveTransform(src, m[, dst]) → dst
C: void cvPerspectiveTransform(const CvArr* src, CvArr* dst, const CvMat* mat)
Parameters:
src – input two-channel or three-channel floating-point array; each element is a 2D/3D vector to be transformed.
dst – output array of the same size and type as src.
m – 3x3 or 4x4 floating-point transformation matrix.
warpPerspective:
Applies a perspective transformation to an image.
C++: void warpPerspective(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, InputArray M, Size dsize, int flags=INTER_LINEAR, int borderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar())
Python: cv2.warpPerspective(src, M, dsize[, dst[, flags[, borderMode[, borderValue]]]]) → dst
C: void cvWarpPerspective(const CvArr* src, CvArr* dst, const CvMat* map_matrix, int flags=CV_INTER_LINEAR+CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS, CvScalar fillval=cvScalarAll(0) )
Parameters:
src – input image.
dst – output image that has the size dsize and the same type as src .
M – 3\times 3 transformation matrix.
dsize – size of the output image.
flags – combination of interpolation methods (INTER_LINEAR or INTER_NEAREST) and the optional flag WARP_INVERSE_MAP, that sets M as the inverse transformation ( \texttt{dst}\rightarrow\texttt{src} ).
borderMode – pixel extrapolation method (BORDER_CONSTANT or BORDER_REPLICATE).
borderValue – value used in case of a constant border; by default, it equals 0.
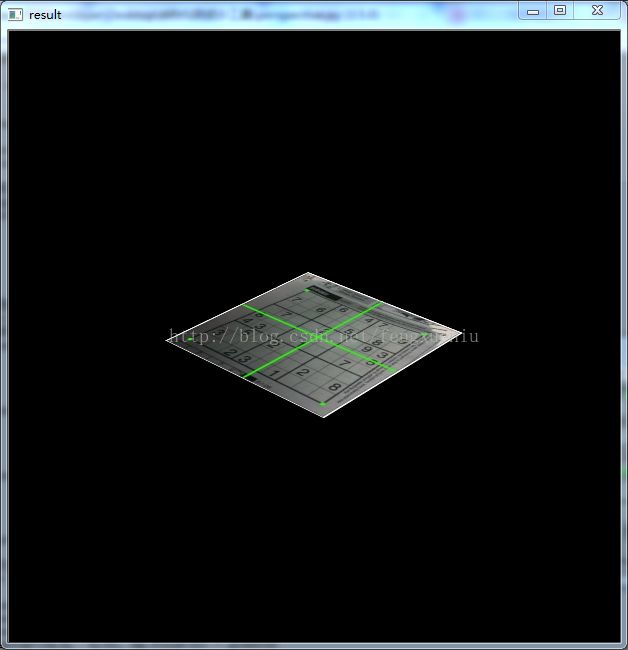
本文为方便,采用的python + opencv 实现,代码及效果如下
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as np
def rad(x):
return x*np.pi/180
img = cv2.imread("b.jpg")
cv2.imshow("original", img)
#扩展图像,保证内容不超出可视范围
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img,200,200,200,200,cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,0)
w,h=img.shape[0:2]
anglex=45
angley = 45
anglez = 0
fov = 42
while 1:
#镜头与图像间的距离,21为半可视角,算z的距离是为了保证在此可视角度下恰好显示整幅图像
z=np.sqrt(w**2 + h**2)/2/np.tan(rad(fov/2))
#齐次变换矩阵
rx = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(rad(anglex)), -np.sin(rad(anglex)), 0],
[0, -np.sin(rad(anglex)), np.cos(rad(anglex)), 0,],
[0, 0, 0, 1]], np.float32)
ry = np.array([[np.cos(rad(angley)), 0, np.sin(rad(angley)), 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[-np.sin(rad(angley)),0, np.cos(rad(angley)), 0,],
[0, 0, 0, 1]], np.float32)
rz = np.array([[np.cos(rad(anglez)), np.sin(rad(anglez)), 0, 0],
[-np.sin(rad(anglez)), np.cos(rad(anglez)), 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]], np.float32)
r = rx.dot(ry).dot(rz)
#四对点的生成
pcenter = np.array([h/2, w/2, 0, 0], np.float32)
p1 = np.array([0,0, 0,0], np.float32) - pcenter
p2 = np.array([w,0, 0,0], np.float32) - pcenter
p3 = np.array([0,h, 0,0], np.float32) - pcenter
p4 = np.array([w,h, 0,0], np.float32) - pcenter
dst1 = r.dot(p1)
dst2 = r.dot(p2)
dst3 = r.dot(p3)
dst4 = r.dot(p4)
list_dst = [dst1, dst2, dst3, dst4]
org = np.array([[0,0],
[w,0],
[0,h],
[w,h]], np.float32)
dst = np.zeros((4,2), np.float32)
#投影至成像平面
for i in range(4):
dst[i,0] = list_dst[i][0]*z/(z-list_dst[i][2]) + pcenter[0]
dst[i,1] = list_dst[i][1]*z/(z-list_dst[i][2]) + pcenter[1]
warpR = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(org, dst)
result = cv2.warpPerspective(img, warpR, (h,w))
cv2.imshow("result", result)
c=cv2.waitKey(30)
#anglex += 3 #auto rotate
#anglez += 1 #auto rotate
#angley += 2 #auto rotate
#键盘控制
if 27 == c: #Esc quit
break;
if c == ord('w'):
anglex += 1
if c == ord('s'):
anglex -= 1
if c == ord('a'):
angley += 1
#dx=0
if c == ord('d'):
angley -= 1
if c == ord('u'):
anglez += 1
if c == ord('p'):
anglez -= 1
if c == ord('t'):
fov +=1
if c == ord('r'):
fov -=1
if c == ord(' '):
anglex=angley=anglez=0
if c == ord('q'):
print("======================================")
print( '旋转矩阵:\n',r)
print("angle alpha: ",anglex, 'angle beta: ',angley, "dz: ",anglez, ": ",z)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()效果图:
原图: