OpenCV+yolov2-tiny实现目标检测(C++)
OpenCV+yolov2-tiny实现目标检测(C++)
目标检测算法主要分为两类:一类是基于Region Proposal(候选区域)的算法,如R-CNN系算法(R-CNN,Fast R-CNN, Faster R-CNN),它们是two-stage(两步法)的,需要先使用Selective search或者CNN网络(RPN)产生Region Proposal,然后再在Region Proposal上做分类与回归。而另一类是Yolo,SSD这类one-stage算法(一步法),其仅仅使用一个CNN网络直接预测不同目标的类别与位置。第一类方法是准确度高一些,但是速度慢,而第二类算法是速度快,但是准确性要低一些。
YOLO是一种比SSD还要快的目标检测网络模型,作者在其论文中说FPS是Fast R-CNN的100倍,这里首先简单的介绍一下YOLO网络基本结构,然后通过OpenCV C++调用Darknet的,实现目标检测。OpenCV在3.3.1的版本中开始正式支持Darknet网络框架并且支持YOLO1与YOLO2以及YOLO Tiny网络模型的导入与使用。后面测试,OpenCV3.4.2也支持YOLO3。另外,OpenCV dnn模块目前支持Caffe、TensorFlow、Torch、PyTorch等深度学习框架,关于《OpenCV调用TensorFlow预训练模型》可参考鄙人的另一份博客:https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/80570120
关于《OpenCV+yolov3实现目标检测(C++,Python)》请参考我的另一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/84098461
本博客源码都放在Github上:https://github.com/PanJinquan/opencv-learning-tutorials/tree/master/dnn_tutorial,麻烦给个“Star”哈
参考资料:
《Deep Learning based Object Detection using YOLOv3 with OpenCV ( Python / C++ )》:
《YOLOv3 + OpenCV 实现目标检测(Python / C ++)》:https://blog.csdn.net/haoqimao_hard/article/details/82081285
Github参考源码:https://github.com/spmallick/learnopencv/tree/master/ObjectDetection-YOLO
darknt yolo官网:https://pjreddie.com/darknet/yolo/
目录
目录
OpenCV+yolov2-tiny实现目标检测(C++)
1、YOLOv1网络
(1)YOLOv1网络结构
(2)YOLOv1损失函数
(3)tiny-YOLO网络
2、OpenCV使用YOLO实现目标检测
(1)代码实现过程
(2)完整的代码:
3、YOLO的缺点
4、参考资料:
1、YOLOv1网络
YOLO全称YOU ONLY Look Once表达的意思只要看一眼就能感知识别的物体了。YOLO的核心思想:就是利用整张图作为网络的输入,直接在输出层回归物体的bounding box位置和所属的类别。
(1)YOLOv1网络结构
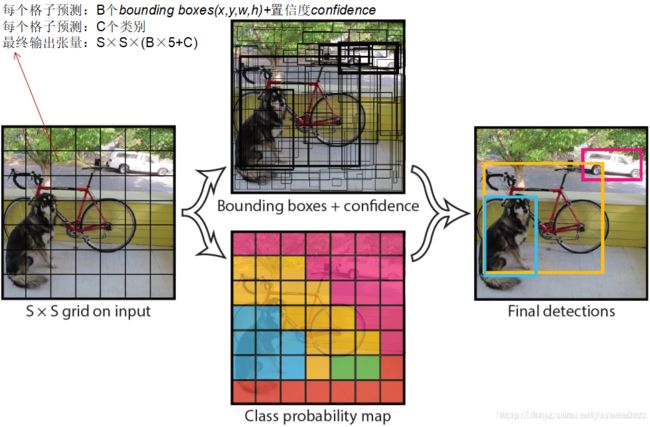
实现过程:首先把输入图像448×448划分成S×S的格子,然后对每个格子都预测B个Bounding Boxes(物体框),每个Bounding Boxes都包含5个预测值:x,y,w,h和confidence(置信度),另外每个格子都预测C个类别的概率分数,但是这个概率分数和物体框的confidence置信度分数是不相关的。这样,每个单元格需要预测(B×5+C)个值。如果将输入图片划分为S×S个网格,那么最终预测值为S×S×(B×5+C)大小的张量。整个模型的预测值结构如下图所示。
- 1、将一幅图像分成SxS个网格(grid cell),如果某个object的中心 落在这个网格中,则这个网格就负责预测这个object。
- 2、每个网格要预测B个bounding box,每个bounding box除了要回归自身的位置(x,y,w,h)之外,还要附带预测一个confidence值(每个bounding box要预测(x, y, w, h)和confidence共5个值)。这个confidence代表了所预测的box中含有object的置信度和这个box预测的有多准两重信息,其值是这样计算的:
说明:如果有object落在一个grid cell里,第一项取1,否则取0。 第二项是预测的bounding box和实际的ground truth之间的IOU值。因此,confidence就是预测的bounding box和ground truth box的IOU值。
- 3、每个网格还要预测一个类别概率信息,记为C类。这样所有网格的类别概率就构成了class probability map
注意:class信息是针对每个网格的,confidence信息是针对每个bounding box的。
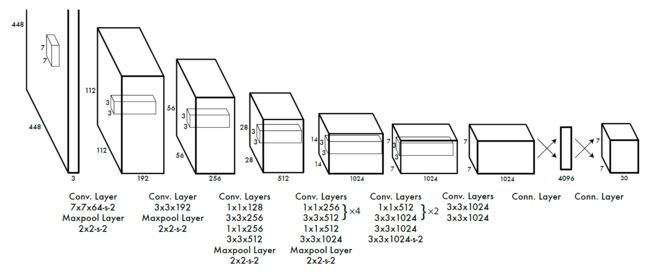
举个栗子:在PASCAL VOC中,图像输入为448x448,取S=7(将图像成7x7个网格(grid cell)),B=2(每个网格要预测2个bounding box),一共有C=20个类别(PASCAL VOC共有20类别)。则输出就是S x S x (5*B+C)=7x7x30的一个张量tensor。整个网络结构如下图所示:
Yolo采用卷积网络来提取特征,然后使用全连接层来得到预测值。网络结构参考GooLeNet模型,包含24个卷积层和2个全连接层,如图所示。对于卷积层,主要使用1x1卷积来做channle reduction,然后紧跟3x3卷积。对于卷积层和全连接层,采用Leaky ReLU激活函数:max(x,0.1x)。但是最后一层却采用线性激活函数。除了上面这个结构,文章还提出了一个轻量级版本Fast Yolo,其仅使用9个卷积层,并且卷积层中使用更少的卷积核。
- 4、在test的时候,每个网格预测的class信息和bounding box预测的confidence信息相乘,就得到每个bounding box的class-specific confidence score:
等式左边第一项就是每个网格预测的类别信息,第二三项就是每个bounding box预测的confidence。这个乘积即encode了预测的box属于某一类的概率,也有该box准确度的信息。
- 5、得到每个box的class-specific confidence score以后,设置阈值,滤掉得分低的boxes,对保留的boxes进行NMS处理,就得到最终的检测结果。
这部分的讲解可以参考资料:https://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/50915317
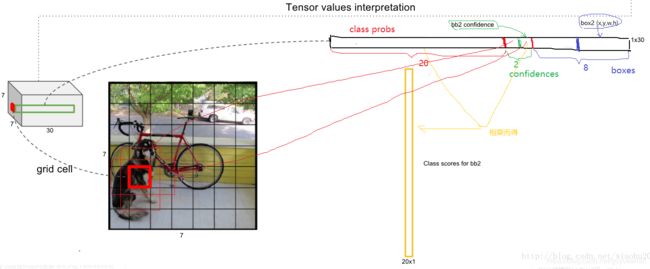
可以看到网络的最后输出为7×7×30大小的张量。这和前面的讨论是一致的。这个张量所代表的具体含义下图所示。对于每一个单元格,前20个元素是类别概率值,然后2个元素是边界框置信度,两者相乘可以得到类别置信度,最后8个元素是边界框的(x,y,w,h)(PS:预测2个BB,所以有2个置信度和8个位置边界元素)。大家可能会感到奇怪,对于边界框为什么把置信度c和(x,y,w,h)都分开排列,而不是按照(x,y,w,h,c)这样排列,其实纯粹是为了计算方便,因为实际上这30个元素都是对应一个单元格,其排列是可以任意的。但是分离排布,可以方便地提取每一个部分。这里来解释一下,首先网络的预测值是一个二维张量P,其shape为[batch,7×7×30]。采用切片,那么
就是类别概率部分,而
是置信度部分,最后剩余部分
是边界框的预测结果。这样,提取每个部分是非常方便的,这会方面后面的训练及预测时的计算。
(2)YOLOv1损失函数
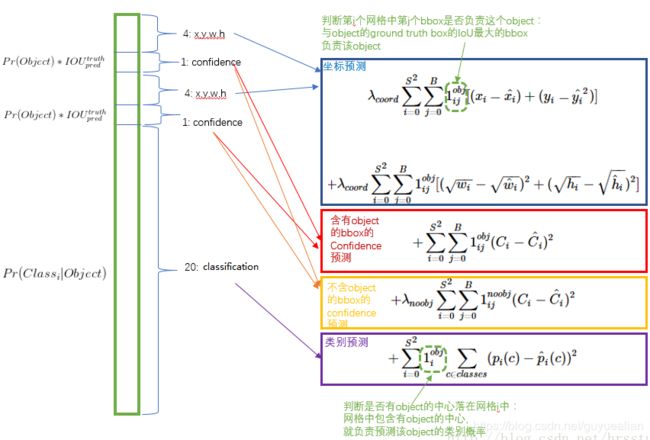
YOLOv1算法将目标检测看成回归问题,所以采用的是均方差损失函数。YOLOv1的损失函数可简单看成是坐标误差+置信度误差+类别误差的组合之和。但是对不同的部分采用了不同的权重值。
坐标误差(定位误差),即边界框坐标预测误差,采用较大的权重λcoord=5。采用均方误差,其同等对待大小不同的边界框,但是实际上较小的边界框的坐标误差应该要比较大的边界框要更敏感。为了保证这一点,将网络的边界框的宽与高预测改为对其平方根的预测,即预测值变为。
置信度误差:对于不包含目标的边界框的confidence误差,采用较小的权重值λnoobj=0.5,而含有目标的边界框的置信度confidence误差权重值为1。
类别误差:权重为1
其中:
第一项是边界框中心坐标的误差项,
指的是第i个单元格存在目标,且该单元格中的第j个边界框负责预测该目标。
第二项是边界框的高与宽的误差项。
第三项是包含目标的边界框的置信度误差项。
第四项是不包含目标的边界框的置信度误差项。
最后一项是包含目标的单元格的分类误差项,
指的是第ii个单元格存在目标。
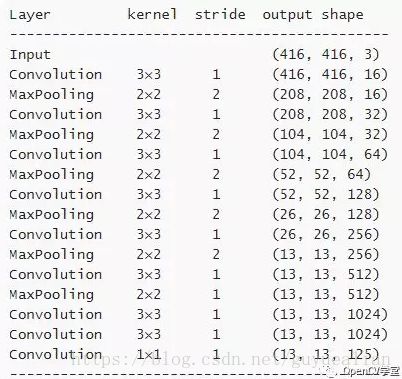
(3)tiny-YOLO网络
tiny-YOLO网络模型是更加轻量级的微型YOLO网络,速度非常快,可以在移动端实时目标检测,但检测效果不算好。tiny-YOLO网络的网络结构如下:
与上面不同的是,tiny-YOLO网络模型每个Cell需要检测5个BOX,对每个BOX来说,包含如下数据
4个位置信息x、y、w、h
1个置信分数
基于VOC数据集的20个目标类别
所以对每个BOX来说,每个BOX有5+20=25个参数,5个BOX共有 5x25=125个参数。所以,tiny-YOLO网络模型最后一层卷积层深度是125。
2、OpenCV使用YOLO实现目标检测
OpenCV使用YOLO实现目标检测的代码如下,注意 OpenCV只是前馈网络,只支持预测,不能训练。
(1)代码实现过程
这里提供图片测试image_detection()和视频测试 video_detection()测试方法:
/**
* @brief YOLO模型视频测试.
* @param cfgFile path to the .cfg file with text description of the network architecture.
* @param weight path to the .weights file with learned network.
* @param clsNames 种类标签文件
* @param video_path 视频文件
* @returns void
*/
void video_detection(string cfgFile, string weight, string clsNames, string video_path);
/**
* @brief YOLO模型图像测试.
* @param cfgFile path to the .cfg file with text description of the network architecture.
* @param weight path to the .weights file with learned network.
* @param clsNames 种类标签文件
* @param image_path 图像文件
* @returns void
*/
void image_detection(string cfgFile, string weight, string clsNames, string image_path);1、需要调用OpenCV DNN模块,所以头文件必须添加:opencv2/dnn.hpp,头文件和命名空间如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::dnn;
2、Main函数以及全局的变量:如confidenceThreshold置信度的阈值,项目根目录,这个参数根据自己的项目改改就好
float confidenceThreshold = 0.25;
string pro_dir = "E:/opencv-learning-tutorials/"; //项目根目录
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
String cfgFile = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov2-tiny-voc/yolov2-tiny-voc.cfg";
String weight = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov2-tiny-voc/yolov2-tiny-voc.weights";
string clsNames = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov2-tiny-voc/voc.names";
string image_path = pro_dir + "data/images/1.jpg";
image_detection(cfgFile, weight, clsNames, image_path);//图片测试
//string video_path = pro_dir + "data/images/lane.avi";
//video_detection(cfgFile, weight, clsNames,video_path);//视频测试
}3、image_detection函数加载网络模型,需要调用DNN的readNetFromDarknet函数
// 加载网络模型
dnn::Net net = readNetFromDarknet(cfgFile, weight);
if (net.empty())
{
printf("Could not load net...\n");
return;
}4、加载分类信息
// 加载分类信息
vector classNamesVec;
ifstream classNamesFile(clsNames);
if (classNamesFile.is_open())
{
string className = "";
while (std::getline(classNamesFile, className))
classNamesVec.push_back(className);
} 5、加载被检测的图像
// 加载图像
Mat frame = imread(image_path);
Mat inputBlob = blobFromImage(frame, 1 / 255.F, Size(416, 416), Scalar(), true, false);
net.setInput(inputBlob, "data");6、进行目标检测:
// 进行目标检测
Mat detectionMat = net.forward("detection_out");
vector layersTimings;
double freq = getTickFrequency() / 1000;
double time = net.getPerfProfile(layersTimings) / freq;
ostringstream ss;
ss << "detection time: " << time << " ms";
putText(frame, ss.str(), Point(20, 20), 0, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255)); 7、检测结果并显示:
// 输出结果
for (int i = 0; i < detectionMat.rows; i++)
{
const int probability_index = 5;
const int probability_size = detectionMat.cols - probability_index;
float *prob_array_ptr = &detectionMat.at(i, probability_index);
size_t objectClass = max_element(prob_array_ptr, prob_array_ptr + probability_size) - prob_array_ptr;
float confidence = detectionMat.at(i, (int)objectClass + probability_index);
if (confidence > confidenceThreshold)
{
float x = detectionMat.at(i, 0);
float y = detectionMat.at(i, 1);
float width = detectionMat.at(i, 2);
float height = detectionMat.at(i, 3);
int xLeftBottom = static_cast((x - width / 2) * frame.cols);
int yLeftBottom = static_cast((y - height / 2) * frame.rows);
int xRightTop = static_cast((x + width / 2) * frame.cols);
int yRightTop = static_cast((y + height / 2) * frame.rows);
Rect object(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom,
xRightTop - xLeftBottom,
yRightTop - yLeftBottom);
rectangle(frame, object, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8);
if (objectClass < classNamesVec.size())
{
ss.str("");
ss << confidence;
String conf(ss.str());
String label = String(classNamesVec[objectClass]) + ": " + conf;
int baseLine = 0;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
rectangle(frame, Rect(Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom),
Size(labelSize.width, labelSize.height + baseLine)),
Scalar(255, 255, 255), CV_FILLED);
putText(frame, label, Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom + labelSize.height),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
}
}
}
imshow("YOLO-Detections", frame);
waitKey(0);
return; (2)完整的代码:
这里提供图片测试image_detection()和视频测试 video_detection()的方法,完整 是项目代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::dnn;
float confidenceThreshold = 0.25;
string pro_dir = "E:/opencv-learning-tutorials/"; //项目根目录
/**
* @brief YOLO模型视频测试.
* @param cfgFile path to the .cfg file with text description of the network architecture.
* @param weight path to the .weights file with learned network.
* @param clsNames 种类标签文件
* @param video_path 视频文件
* @returns void
*/
void video_detection(string cfgFile, string weight, string clsNames, string video_path);
/**
* @brief YOLO模型图像测试.
* @param cfgFile path to the .cfg file with text description of the network architecture.
* @param weight path to the .weights file with learned network.
* @param clsNames 种类标签文件
* @param image_path 图像文件
* @returns void
*/
void image_detection(string cfgFile, string weight, string clsNames, string image_path);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
String cfgFile = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov2-tiny-voc/yolov2-tiny-voc.cfg";
String weight = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov2-tiny-voc/yolov2-tiny-voc.weights";
string clsNames = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov2-tiny-voc/voc.names";
string image_path = pro_dir + "data/images/1.jpg";
image_detection(cfgFile, weight, clsNames, image_path);//图片测试
string video_path = pro_dir + "data/images/lane.avi";
video_detection(cfgFile, weight, clsNames,video_path);//视频测试
}
void video_detection(string cfgFile, string weight,string clsNames, string video_path) {
dnn::Net net = readNetFromDarknet(cfgFile, weight);
if (net.empty())
{
printf("Could not load net...\n");
return;
}
vector classNamesVec;
ifstream classNamesFile(clsNames);
if (classNamesFile.is_open())
{
string className = "";
while (std::getline(classNamesFile, className))
classNamesVec.push_back(className);
}
// VideoCapture capture(0);
VideoCapture capture;
capture.open(video_path);
if (!capture.isOpened()) {
printf("could not open the camera...\n");
return;
}
Mat frame;
while (capture.read(frame))
{
if (frame.empty())
if (frame.channels() == 4)
cvtColor(frame, frame, COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
Mat inputBlob = blobFromImage(frame, 1 / 255.F, Size(416, 416), Scalar(), true, false);
net.setInput(inputBlob, "data");
Mat detectionMat = net.forward("detection_out");
vector layersTimings;
double freq = getTickFrequency() / 1000;
double time = net.getPerfProfile(layersTimings) / freq;
ostringstream ss;
ss << "FPS: " << 1000 / time << " ; time: " << time << " ms";
putText(frame, ss.str(), Point(20, 20), 0, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
for (int i = 0; i < detectionMat.rows; i++)
{
const int probability_index = 5;
const int probability_size = detectionMat.cols - probability_index;
float *prob_array_ptr = &detectionMat.at(i, probability_index);
size_t objectClass = max_element(prob_array_ptr, prob_array_ptr + probability_size) - prob_array_ptr;
float confidence = detectionMat.at(i, (int)objectClass + probability_index);
if (confidence > confidenceThreshold)
{
float x = detectionMat.at(i, 0);
float y = detectionMat.at(i, 1);
float width = detectionMat.at(i, 2);
float height = detectionMat.at(i, 3);
int xLeftBottom = static_cast((x - width / 2) * frame.cols);
int yLeftBottom = static_cast((y - height / 2) * frame.rows);
int xRightTop = static_cast((x + width / 2) * frame.cols);
int yRightTop = static_cast((y + height / 2) * frame.rows);
Rect object(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom,
xRightTop - xLeftBottom,
yRightTop - yLeftBottom);
rectangle(frame, object, Scalar(0, 255, 0));
if (objectClass < classNamesVec.size())
{
ss.str("");
ss << confidence;
String conf(ss.str());
String label = String(classNamesVec[objectClass]) + ": " + conf;
int baseLine = 0;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
rectangle(frame, Rect(Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom),
Size(labelSize.width, labelSize.height + baseLine)),
Scalar(255, 255, 255), CV_FILLED);
putText(frame, label, Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom + labelSize.height),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
}
}
}
imshow("YOLOv3: Detections", frame);
if (waitKey(1) >= 0) break;
}
}
void image_detection(string cfgFile, string weight, string clsNames, string image_path) {
// 加载网络模型
dnn::Net net = readNetFromDarknet(cfgFile, weight);
if (net.empty())
{
printf("Could not load net...\n");
return;
}
// 加载分类信息
vector classNamesVec;
ifstream classNamesFile(clsNames);
if (classNamesFile.is_open())
{
string className = "";
while (std::getline(classNamesFile, className))
classNamesVec.push_back(className);
}
// 加载图像
Mat frame = imread(image_path);
Mat inputBlob = blobFromImage(frame, 1 / 255.F, Size(416, 416), Scalar(), true, false);
net.setInput(inputBlob, "data");
// 进行目标检测
Mat detectionMat = net.forward("detection_out");
vector layersTimings;
double freq = getTickFrequency() / 1000;
double time = net.getPerfProfile(layersTimings) / freq;
ostringstream ss;
ss << "detection time: " << time << " ms";
putText(frame, ss.str(), Point(20, 20), 0, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
// 输出结果
for (int i = 0; i < detectionMat.rows; i++)
{
const int probability_index = 5;
const int probability_size = detectionMat.cols - probability_index;
float *prob_array_ptr = &detectionMat.at(i, probability_index);
size_t objectClass = max_element(prob_array_ptr, prob_array_ptr + probability_size) - prob_array_ptr;
float confidence = detectionMat.at(i, (int)objectClass + probability_index);
if (confidence > confidenceThreshold)
{
float x = detectionMat.at(i, 0);
float y = detectionMat.at(i, 1);
float width = detectionMat.at(i, 2);
float height = detectionMat.at(i, 3);
int xLeftBottom = static_cast((x - width / 2) * frame.cols);
int yLeftBottom = static_cast((y - height / 2) * frame.rows);
int xRightTop = static_cast((x + width / 2) * frame.cols);
int yRightTop = static_cast((y + height / 2) * frame.rows);
Rect object(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom,
xRightTop - xLeftBottom,
yRightTop - yLeftBottom);
rectangle(frame, object, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8);
if (objectClass < classNamesVec.size())
{
ss.str("");
ss << confidence;
String conf(ss.str());
String label = String(classNamesVec[objectClass]) + ": " + conf;
int baseLine = 0;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
rectangle(frame, Rect(Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom),
Size(labelSize.width, labelSize.height + baseLine)),
Scalar(255, 255, 255), CV_FILLED);
putText(frame, label, Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom + labelSize.height),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
}
}
}
imshow("YOLO-Detections", frame);
waitKey(0);
return;
} 图片物体检测:
3、YOLO的缺点
- YOLO对相互靠的很近的物体,还有很小的群体 检测效果不好,这是因为一个网格中只预测了两个框,并且只属于一类。
- 对测试图像中,同一类物体出现的新的不常见的长宽比和其他情况是。泛化能力偏弱。
- 由于损失函数的问题,定位误差是影响检测效果的主要原因。尤其是大小物体的处理上,还有待加强。
4、参考资料:
[1].《论文阅读笔记:You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection》https://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/50915317
[2]. https://blog.csdn.net/xiaohu2022/article/details/79211732
[3]. https://blog.csdn.net/u014380165/article/details/72616238