windows下ini配置文件的读写
最近在看传奇客户端的源代码,里面有对ini文件的读写。特此记录一下使用方法
对ini文件进行写操作用到函数
BOOL
WINAPI
WritePrivateProfileStringA(
__in_opt LPCSTR lpAppName,
__in_opt LPCSTR lpKeyName,
__in_opt LPCSTR lpString,
__in_opt LPCSTR lpFileName
);
其中lpAppName为分节名字,lpKeyName为键的名字,lpString为对应键的字符串的值,lpFileName为完整的文件名,这个文件可以存在,也可以不存在,不存在则会创建,如果存在则会覆盖原来的内容
另外还有其他的函数
// 写入结构体
BOOL WritePrivateProfileStruct(
LPCTSTR lpszSection, // pointer to section name
LPCTSTR lpszKey, // pointer to key name
LPVOID lpStruct, // 要写入的数据缓冲区
UINT uSizeStruct, // 缓冲区的大小
LPCTSTR szFile // pointer to initialization filename
);
// 写入整个键值,lpString 为“key=value”的格式
BOOL WritePrivateProfileSection(
LPCTSTR lpAppName, // pointer to string with section name
LPCTSTR lpString, // 写入的字符串
LPCTSTR lpFileName // pointer to string with filename
);
这个为只写入分节名
对ini文件读操作有一组函数:
读取字符串:
DWORD
WINAPI
GetPrivateProfileStringA(
__in_opt LPCSTR lpAppName,
__in_opt LPCSTR lpKeyName,
__in_opt LPCSTR lpDefault,
__out_ecount_part_opt(nSize, return + 1) LPSTR lpReturnedString,
__in DWORD nSize,
__in_opt LPCSTR lpFileName
);
lpAppName,lpKeyName,lpFileName这三个参数和上面的一样,lpDefault为取不到指定的键值时默认返回的字符串,lpReturnedString为接收字符串的缓存区,nSize为缓冲区的最大长度
读取整型值,需要用到下面的函数:
UINT
WINAPI
GetPrivateProfileIntA(
__in LPCSTR lpAppName,
__in LPCSTR lpKeyName,
__in INT nDefault,
__in_opt LPCSTR lpFileName
);
函数返回即需要读取的值,nDefault为取不到指定键值时默认返回的整型值。
//读取结构体
BOOL
WINAPI
GetPrivateProfileStructA(
__in LPCSTR lpszSection,
__in LPCSTR lpszKey,
__out_bcount_opt(uSizeStruct) LPVOID lpStruct,
__in UINT uSizeStruct,
__in_opt LPCSTR szFile
);
代码示例:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include //这个头文件一定要添加,否则GetPrivateProfileString(...)函数无法使用
using namespace std;
struct A
{
int n;
char ch;
};
void main() {
char temp[20] = {0};
char name[20] = {0};
A a;
a.n = 600;
a.ch = 'a';
sprintf_s(temp, 20,"%d", 100);
// 在配置文件中写入字符串
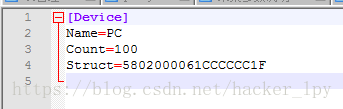
WritePrivateProfileString("Device", "Name", "PC", "C:\\Users\\mycomputer\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\test2.ini");
// 在配置文件中写入整型数,需要将整型转换成字符串
WritePrivateProfileString("Device", "Count", temp, "C:\\Users\\mycomputer\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\test2.ini");
// 写入结构体
WritePrivateProfileStruct("Device", "Struct", &a, sizeof(a), "C:\\Users\\mycomputer\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\test2.ini");
// 读取配置文件中的字符串
GetPrivateProfileString("Device", "Name", "", name, sizeof(name), "C:\\Users\\mycomputer\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\test2.ini");
// 读取一个整型值
int count = GetPrivateProfileInt("Device", "Count", 0, "C:\\Users\\mycomputer\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\test2.ini");
// 读取结构体
A aa = {0};
GetPrivateProfileStruct("Device", "Struct", &aa, sizeof(aa), "C:\\Users\\mycomputer\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\test2.ini");
cout << "Name:" << name << endl;
cout << "Count:" << count << endl;
cout << "Struct.n:" << aa.n << endl;
cout << "Struct.ch:" << aa.ch << endl;
system("pause");
}
在文件中的格式为: