Swagger2 关于Map参数在API文档中展示详细参数以及参数说明
前言
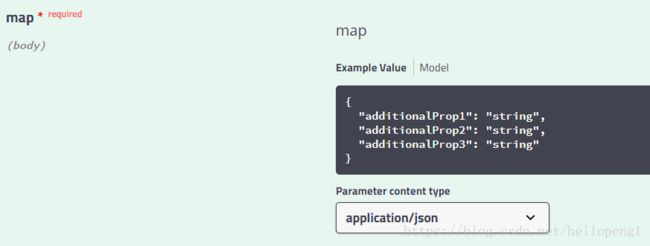
本文主要解决的问题是 Swagger2 (SpringFox)关于Map参数生成的API文档中没有详细Json结构说明,问题如下图所示:
此种方式生成的Api文档中的请求参数如下:
如果是这样的参数类型的会让查看API的人员无法清晰的知道如何请求API文档。当然Swagger2 根据这种情况也给出了解决方案:
@ApiOperation(value = "not use")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "params" , paramType = "body",examples = @Example({
@ExampleProperty(value = "{'user':'id'}", mediaType = "application/json")
}))
@PostMapping("/xxx")
public void test(Map params){} 但是这种写法在SpringFox版本2.8.0至2.9.0之间好像没有实现@ApiImplicitParam的examples的用法,还是属于issue的状态,下面是关于这两个issue的说明:
http://springfox.github.io/springfox/docs/current/#changing-how-generic-types-are-named
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41861164/how-can-i-manually-describe-an-example-input-for-a-java-requestbody-mapstring
解决方法
SpringFox 提供给我们了一个ParameterBuilderPlugin接口,通过这个接口我们可以在SpringFox构造Map参数映射的ModelRef时使用javassist动态的生成类,并把这个map参数的modelRef对象指向我们动态生成的具体Class对象(通过自定义注解在Map参数上生成可表示JSON结构的类),具体实现如下(求方便的同学可以把下面3个类直接Copy到自己的代码中即可):
package com.telepay.service.controller.agent;
import com.fasterxml.classmate.TypeResolver;
import com.google.common.base.Optional;
import com.telepay.service.controller.agent.annotation.ApiJsonObject;
import com.telepay.service.controller.agent.annotation.ApiJsonProperty;
import javassist.*;
import javassist.bytecode.AnnotationsAttribute;
import javassist.bytecode.ConstPool;
import javassist.bytecode.annotation.Annotation;
import javassist.bytecode.annotation.IntegerMemberValue;
import javassist.bytecode.annotation.StringMemberValue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import springfox.documentation.schema.ModelRef;
import springfox.documentation.service.ResolvedMethodParameter;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spi.service.ParameterBuilderPlugin;
import springfox.documentation.spi.service.contexts.ParameterContext;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
@Order //plugin加载顺序,默认是最后加载
public class MapApiReader implements ParameterBuilderPlugin {
@Autowired
private TypeResolver typeResolver;
@Override
public void apply(ParameterContext parameterContext) {
ResolvedMethodParameter methodParameter = parameterContext.resolvedMethodParameter();
if (methodParameter.getParameterType().canCreateSubtype(Map.class) || methodParameter.getParameterType().canCreateSubtype(String.class)) { //判断是否需要修改对象ModelRef,这里我判断的是Map类型和String类型需要重新修改ModelRef对象
Optional optional = methodParameter.findAnnotation(ApiJsonObject.class); //根据参数上的ApiJsonObject注解中的参数动态生成Class
if (optional.isPresent()) {
String name = optional.get().name(); //model 名称
ApiJsonProperty[] properties = optional.get().value();
parameterContext.getDocumentationContext().getAdditionalModels().add(typeResolver.resolve(createRefModel(properties, name))); //像documentContext的Models中添加我们新生成的Class
parameterContext.parameterBuilder() //修改Map参数的ModelRef为我们动态生成的class
.parameterType("body")
.modelRef(new ModelRef(name))
.name(name);
}
}
}
private final static String basePackage = "com.xx.xxx.in.swagger.model."; //动态生成的Class名
/**
* 根据propertys中的值动态生成含有Swagger注解的javaBeen
*/
private Class createRefModel(ApiJsonProperty[] propertys, String name) {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass(basePackage + name);
try {
for (ApiJsonProperty property : propertys) {
ctClass.addField(createField(property, ctClass));
}
return ctClass.toClass();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 根据property的值生成含有swagger apiModelProperty注解的属性
*/
private CtField createField(ApiJsonProperty property, CtClass ctClass) throws NotFoundException, CannotCompileException {
CtField ctField = new CtField(getFieldType(property.type()), property.key(), ctClass);
ctField.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC);
ConstPool constPool = ctClass.getClassFile().getConstPool();
AnnotationsAttribute attr = new AnnotationsAttribute(constPool, AnnotationsAttribute.visibleTag);
Annotation ann = new Annotation("io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty", constPool);
ann.addMemberValue("value", new StringMemberValue(property.description(), constPool));
if (ctField.getType().subclassOf(ClassPool.getDefault().get(String.class.getName())))
ann.addMemberValue("example", new StringMemberValue(property.example(), constPool));
if (ctField.getType().subclassOf(ClassPool.getDefault().get(Integer.class.getName())))
ann.addMemberValue("example", new IntegerMemberValue(Integer.parseInt(property.example()), constPool));
attr.addAnnotation(ann);
ctField.getFieldInfo().addAttribute(attr);
return ctField;
}
private CtClass getFieldType(String type) throws NotFoundException {
CtClass fileType = null;
switch (type) {
case "string":
fileType = ClassPool.getDefault().get(String.class.getName());
break;
case "int":
fileType = ClassPool.getDefault().get(Integer.class.getName());
break;
}
return fileType;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(DocumentationType delimiter) {
return true;
}
}
这里是ApiJsonObject注解和ApiJsonProperty注解的实现:
package com.telepay.service.controller.agent.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ApiJsonObject {
ApiJsonProperty[] value(); //对象属性值
String name(); //对象名称
}
package com.telepay.service.controller.agent.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ApiJsonProperty {
String key(); //key
String example() default "";
String type() default "string"; //支持string 和 int
String description() default "";
}
在这里我需要特殊说明一下,我们每一个ApiOperation都是按一个RequestMapping来加载的每一个RequestMapping在加载的时候都会经过许多不同类型的Plugin的处理,而负责管理全局的ModelRef的Plugin是OperationModelsProviderPlugin这个处理RequestMapping时会检测有没有还没有被放到全局的ModelRef对象(而我们放到DocumentContext的对象就是此时被加载的),但是OperationModelsProviderPlugin类型的执行顺序是优先于ParameterBuilderPlugin类型的 ,所以这里就有了一个小问题,如果我们新建的ModelRef是最后一个被处理的RequestMapping那我们新建的ModelRef就没有机会被OperationModelsProviderPlugin放到全局的ModelRef中了,所以解决方法就是在这个Controller中添加一个无用的方法但是这个方法名要足够的长(这个Document范围内即可)保证这个方法才是被SpringFox最后解析的,让我们每个ModelRef都能被OperationModelsProviderPlugin装载进来,如果想看SpringFox这部分具体实现的可以关注下DocumentationPluginsManager这个类,打个断点(断点在OperationModelsProviderPlugin和ParameterBuilderPlugin这两个plugin的调用地方)应该就能理解了:
Ok做完准备工作,来看下我们在controller层如何使用我们新开发的功能:
@ApiOperation(value = "Login", tags = "login")
@PutMapping
public void auth(@ApiJsonObject(name = "login_model", value = {
@ApiJsonProperty(key = "mobile", example = "18614242538", description = "user mobile"),
@ApiJsonProperty(key = "password", example = "123456", description = "user password")
})
@RequestBody Map params) {
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx
}
@ApiOperation(value = "none")
@GetMapping
public void authaaaa(){
} 效果图:
总结
我这个解决方法是比较繁琐的,但是也实现了在Api文档中展示Map参数应要接收的详细对象。如果你并没有很多Map参数需要表明结构,建议你新建个Class做ModelRef就可以了,或者新建个ModelRequestVo也是好的。最后如果同学们发现有更好的解决方法请告知,以免误导其他人,谢谢~
补充:这个只是个DEMO并没有经过完善的测试,不建议生产使用,个人建议还是新建个对象来做参数接收,代码可读性也要高些,好维护,也好进行参数校验等。