UNIX环境高级编程-系统数据文件和信息
相关函数列表
//passwd结构体 /etc/passwd
struct passwd {
char *pw_name; //用户名
char *pw_passwd; //加密口令
uid_t pw_uid; //数值用户ID
gid_t pw_gid; //数值组ID
char *pw_gecos; //注释字段
char *pw_dir; //初始化工作目录
char *pw_shell; //初始shell(用户程序)
char *pw_class; //用户访问类
time_t pw_change //下次更改口令时间
time_t pw_expire //账户有效期时间
};
//阴影口令结构体 /etc/shadow
struct spwd {
char *sp_namp; //用户登录名
char *sp_pwdp; //加密口令
int sp_lstchg; //上次更改口令以来经过的时间
int sp_min; //经多少天后允许更改
int sp_max; //要求更改尚余天数
int sp_warn; //超期警告天数
int sp_inact; //账户不活动之前尚余天数
int sp_expire; //账户超期天数
unisgned int sp_flag; //保留
};
//组文件结构体 /etc/group
struct group {
char *gr_name; //组名
char *gr_paswd; //加密口令
int gr_gid; //数值组ID
char **gr_mem; //指向各用户名指针的数组
};
//两个获取口令文件项的函数
#include
struct passwd *getpwuid(uid_t uid);
struct passwd *getpwnam(const char *name);
//查看整个口令文件,调用getpwent时,返回口令文件中的下一个记录项
#include
struct passwd *getpwent(void);
void setpwent(void); //反绕所使用的文件
void endpwent(void); //关闭这些文件
//访问口令文件的相关函数
#include
struct spwd *getspnam(const char *name);
struct spwd *getspent(void);
void setspent(void);
void endspent(void);
//访问组相关函数
#include
struct group *getgrgid(gid_t gid);
struct group *getgrnam(const char *name);
//类似于获取所有口令文件和关闭文件
#include
struct group *getgrent(void);
void setgrent(void);
void endgrent(void);
//获取和设置附属组ID
#include
int getgroups(int gidsetsize, gid_t grouplist[]); //若成功返回附属组ID,出错返回-1
#include //on linux
#include //on freeBSD
int setgroups(int ngroups, const gid_t grouplist[]);
#include //on linux
#include //on freeBSD
int initgroups(const char *username, gid_t basegid);
//大多数UNIX系统都提供了下列两个数据文件
//utmp文件记录当前登录到系统的各个用户
//wtmp文件跟踪各个登录和注销事件
struct utmp {
char ut_line[8]; //tty line, tty0,tty1,tty2
char ut_name[8]; //login name
long ut_time; //seconds since Epoch
};
//返回主机和操作系统有关的信息
#include
int uname(struct utsname *name);
//utsname结构体
struct utsname {
char sysname[]; //操作系统名称
char nodename[]; //节点的名称
char release[]; //当前release的操作系统版本
char version[]; //当前release的版本
char machine[]; //硬件类型
};
//BSD派生的系统提供了gethostname函数,它只返回主机名
#include
int gethostname(char *name, int namelen);
//返回当前时间和日志
#include
time_t time(time_t *calptr);
//可获取指定时钟的时间,把时间表示为秒和纳秒
#include
int clock_gettime(clockid_t clock_id, struct timespec *tsp);
//此函数把参数tsp指向的timespec结构初始化为与clock_id参数对应的时钟精度
#include
int clock_getres(clockid_t clock_id, const struct timespec *tsp);
//精确到微秒
#include
int gettimeofday(struct timeval *restrict tp, void *restrict tzp);
//两个函数的localtime和gmtime将日历时间转换成分解的时间,并将这些放在一个tm结构中
struct tm{
int tm_sec;
int tm_min;
int tm_hour;
int tm_mday;
int tm_mon;
int tm_year;
int tm_wday;
int tm_yday;
int tm_isdst;
};
//将日历时间转换成本地时间
#include
struct tm *gettime(const time_t *calptr);
//将日历时间转换成协调统一时间的年、月、日、时、分、秒
#include
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *calptr);
//以本地时间的年、月、日等作为参数,将其转换成time_t值
#include
time_t mktime(struct tm *tmptr);
//类似于printf的时间函数,非常复杂, 可以通过可用的多个参数来定制产生的字符串
#include
size_t strftime(char *restrict buf, size_t maxsize, const char *restrict format,
const struct tm *restrict tmptr);
size_t strftime_1(char *restrict buf, size_t maxsize, const char *restrict format,
const struct tm *restrict tmptr, locale_t locale);
//strptime函数是strftime的反过来版本,把字符串时间转换成分解时间
#include
char *strptime(const char *restrict buf, const char *restrict format,
struct tm *restrict tmptr);
访问系统数据文件的一些历程
| 说明 | 数据文件 | 头文件 | 结构 | 附加的键搜索函数 |
| 口令 | /etc/passwd | passwd | getpwnam,getpwuid | |
| 组 | /etc/group | group | getgrnam,getgrgid | |
| 阴影 | /etc/shadow | spwd | getspnam | |
| 主机 | /etc/hosts | hostent | getnameinfo,getaddrinfo | |
| 网络 | /etc/networks | netent | getnetbyname,getnetbyaddr | |
| 协议 | /etc/protocols | protoent | getprotobyname,getprotobynumber | |
| 服务 | /etc/services | servent | getservbyname,getservbyport |
| 标识符 | 选项 | 说明 |
| CLOCCK_REALTIME | 实时系统时间 | |
| CLOCK_MONOTONIC | _POSIX_MONOTONIC_CLOCK | 不带负跳的实时系统时间 |
| CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID | _POSIX_CPUTIME | 调用进程的CPU时间 |
| CLOCK_THREAD_CPUTIME_ID | _POSIX_THREAD_CPUTIME | 调用线程的CPU时间 |
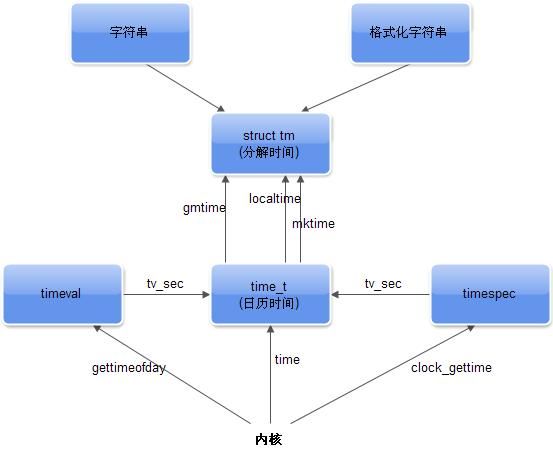
各个时间函数之间的关系如下
读取/etc/passwd,/etc/shadow,/etc/group文件中的某个指定用户信
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char *name = "mysql";
if(argc > 1) {
name = argv[1];
}
struct passwd *pwd;
if((pwd=getpwnam(name)) == NULL) {
printf("getpwnam error\r\n");
}
printf("name=%s\n",pwd->pw_name);
printf("passwd=%s\n",pwd->pw_passwd);
printf("uid=%d\n",pwd->pw_uid);
printf("gid=%d\n",pwd->pw_gid);
printf("gencos=%s\n",pwd->pw_gecos);
printf("init dir=%s\n",pwd->pw_dir);
printf("init shell=%s\n",pwd->pw_shell);
struct spwd *sp;
if((sp=getspnam(name)) == NULL) {
printf("getspnam error\r\n");
}
printf("\nspwd passwod = %s\n",sp->sp_pwdp);
struct group *gp;
//gp = getgrnam(name);
if((gp=getgrgid(pwd->pw_gid)) == NULL) {
printf("getgrgid error\r\n");
}
printf("\ngroup gr_name = %s\n",gp->gr_name);
printf("group passwrd = %s\n",gp->gr_passwd);
printf("group gid = %d\n",gp->gr_gid);
return 0;
} 迭代/etc/passwd中的内容(/etc/shadow和/etc/group的迭代方式跟下面类似)
读取uname相关信息
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
struct passwd *ptr;
setpwent();
while((ptr=getpwent()) != NULL) {
printf("%s\n",ptr->pw_name);
}
endpwent();
struct utsname name;
if(uname(&name) < 0) {
printf("uname error\r\n");
}
printf("sysname = %s\n",name.sysname);
printf("nodename = %s\n",name.nodename);
printf("release = %s\n",name.release);
printf("version = %s\n",name.version);
printf("machine = %s\n",name.machine);
return 0;
}
时间格式转换
#include
#include
int main() {
time_t time_T;
time_T = time(NULL);
printf("time_T -> %d\n", time_T);
struct tm *tmTime;
//long time_long = 1537866136L;
//tmTime = localtime(&time_long);
tmTime = localtime(&time_T);
printf("Now Time is: %d:%d:%d\n", (*tmTime).tm_hour, (*tmTime).tm_min, (*tmTime).tm_sec);
char* format = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S";
char strTime[100];
strftime(strTime, sizeof(strTime), format, tmTime);
printf("Time is :%s\n", strTime);
return 0;
}