GraphicsLab Project之基于物理的着色系统(Physical based shading) - 基于图像的光照(Image Based Lighting)(Diffuse篇)
作者:i_dovelemon
日期:2018-01-21
来源:CSDN
主题:PBR, Equrectangular Map, Cube Map, Irradiance Map, HDR Image, Pre-Filtering
引言
前面一篇文章讲述了怎么搭建一个PBS的直接光照系统。但是,想要发挥PBR的强大实力,就需要更加丰富的光照系统,本篇文章将要向大家展示,如何实现一个IBL-Diffuse的光照系统,实现的效果如下所示:
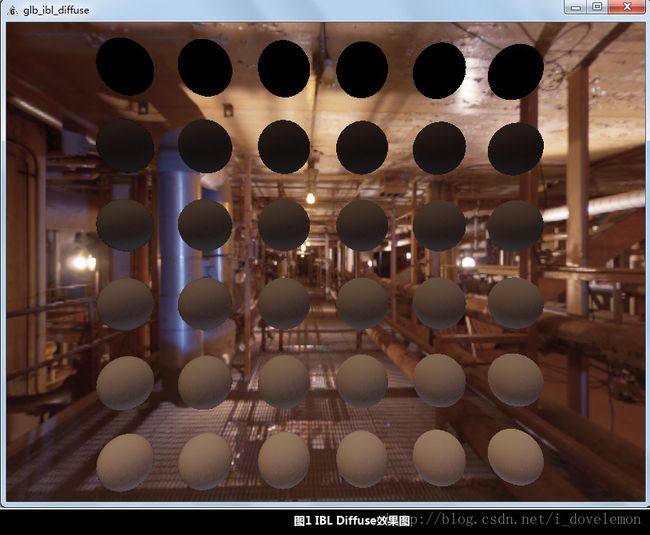
基于图像的光照(Image Based Lighting)
在开始之前,我们先来了解下什么是基于图像的光照(IBL)。一个物体,不会单独的存在一个空空的环境里面,它的周围一定有其他的物体。当光源照射到其他物体上的时候,一定也会反射,其中就有很多反射的光线会反射到该物体上去。上一篇文章中我们模拟的是直接光照。对于直接光照系统,像上面那种其他物体反射过来的光,我们一般就只是使用一个Ambient项来模拟。这种模拟方法只能够模拟单调的环境光照效果,想要更加丰富,更加精细的效果,我们就需要使用更加丰富的环境光照系统,而IBL就是实现它的一种方式。
一般来说,我们通过一张环境贴图(Environment Map)来保存一个物体周围的环境信息,然后通过某种处理,来实现丰富的环境光照效果。本文就是讲述,如何通过对环境贴图进行处理,然后实现丰富的环境光照效果。
从渲染方程解释IBL
还记得前面一篇文章中讲述的渲染方程嘛,这里再次的给出:
根据前面对环境光照的描述,环境光照也应该符合这个公式,只不过相对于直接光照,它需要计算更多的入射光线。
同时从渲染方程可以看出,我们可以把渲染方程拆成两个部分进行处理:
本篇文章集中于处理:
对于这个方程,我们就可以将周围环境的所有光照信息保存在一张环境贴图中,而这个环境贴图就模拟了所有的 Li 。
环境贴图
在图形领域,用于保存周围环境信息的环境贴图有多种形式,如:



现在业界,对于IBL普遍使用的是Cube Map的形式。本篇文章也将主要使用Cube Map来进行IBL。
从前面一篇文章描述中我们知道,HDR对于PBR的重要性,没有了HDR,PBR的效果将大大折扣。所以,对于IBL来说,我们依然需要使用HDR。也就说,对于周围环境光照的描述,需要通过HDR的格式文件来保存。
本文的所有使用的环境光照贴图将从 sIBL中获取,这个网站里面有很多免费使用的HDR光照贴图,我们将从这些图中选择一些进行测试。
需要注意的是,这个网站里面的HDR贴图并不是CubeMap的形式,而是EquirectangularMap的形式进行保存的,所以接下来我们需要解决两个问题:如何读取.hdr文件,如何对这个贴图进行filter。
.hdr文件读取
在sIBL网站上,已经给出了.hdr文件格式的详细描述。我这里为了方便就直接使用了github上开源的stb_image库来读取.hdr文件。这个库里面都是一些单个文件的c代码库,感兴趣的读者可以自行探索。
使用它也很简单,只要简单的将stb_image.h包含到你的工程里面去,然后调用如下的代码:
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true);
int32_t width = 0, height = 0, component = 0;
float* data = stbi_loadf(file_name, &width, &height, &component, 0);
...
stbi_free(data);你就能够得到.hdr文件保存的HDR数据了,然后可以通过图形API创建一个2D的HDR纹理,以便后续使用。
Equirectangular Map Filter
我们前面说过,我们将使用Cube Map来进行IBL。所以,我们需要一种方法来将该Equirectangular Map转换为Cube Map。为此,我们先简单的绘制一个球体,然后将这个Equirectangular Map贴上去,然后使用传统的创建Cube Map的方式产生一张Cube Map。
那么,我们怎么样将Equirectangular Map映射到球体上去了?通过一些简单的计算就能够完成这个操作,代码如下所示:
vec2 sampling_equirectangular_map(vec3 n) {
float u = atan(n.z, n.x);
u = (u + PI) / (2.0 * PI);
float v = asin(n.y);
v = (v * 2.0 + PI) / (2.0 * PI);
return vec2(u, v);
}上面代码中的n表示的是球体上某个点的法线,这个法线需要是归一化(normliaze)的。
通过计算atan(n.z, n.x)就能够得到具有该法线顶点的UV坐标的U值,通过计算asin(n.y)就能够得到具有该法线顶点的UV坐标的V值。同时,由于atan函数返回的结果在 [−π,π] 之间,而asin返回的结果在 [−π2,π2] 之间,所有需要把它们都映射到 [0,1] 之间。
下面是使用该方法得到的映射之后的结果:
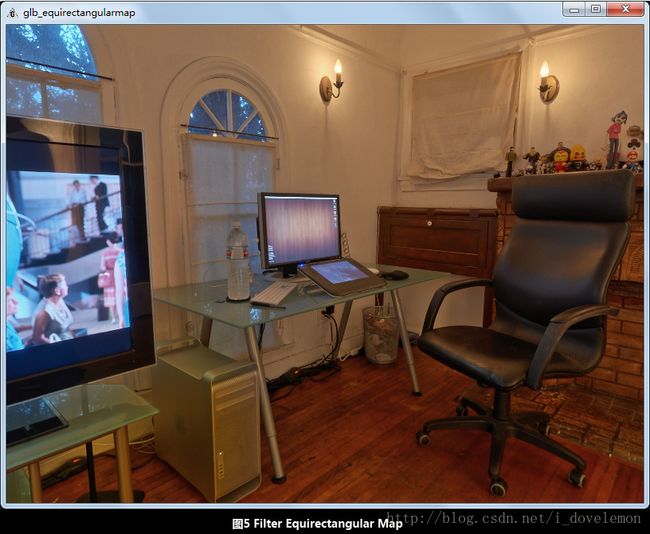
完整的代码可以在 glb_equirectangularmap中查看。
在得到了这个球体之后,我们就可以简单的使用传统的方法来创建CubeMap,主要就是通过设置FOV为90度的摄像机,分别朝着+X,-X,+Y,-Y,+Z,-Z去观察该球体,然后渲染CubeMap的6个面,从而得到一张HDR的CubeMap。该过程在 GraphicsLab Project之Dynamic Environment Mapping中详细的讲述了,这里就不在赘述。
预计算辐射光照贴图
简化积分方程
我们已经能够使用HDR的Cube Map来表示一个物体周围环境的光照信息了,接下来我们就需要计算渲染方程:
对于上面的渲染方程,我们需要求解一个积分运算。理论上,上面的渲染方程定义的积分域是半球空间,所以有无限个入射向量。对于这样的积分,我们没有办法硬解出来。所以在图形领域,一般采用概率和采样的方式来求解积分。常用的积分方法有:Monte Carlo积分,基于Monte Carlo积分改进的Importance Sampling积分,Riemann Sum等。本篇文章将要使用Riemann Sum的方式进行积分的求解,Importance Sampling的方法将在后续求Specular-IBL的时候详细介绍。
在进行实际积分运算之前,我们先来仔细的看下积分方程:
对于Diffuse部分的积分方程,我们知道如下的信息:
也就是说,对于同一个点来说 fd 是一个常量,所以上述的方程可以简化为:
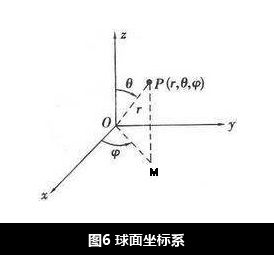
渲染方程球面坐标表示
为了方便进行积分运算,一般都将渲染方程改为球面坐标的积分形式,其中:
所以,方程转变为如下形式:
关于 θ 和 ϕ 定义如下图所示:
Riemann Sum(黎曼和)
Riemann Sum是一种很简单的积分方法,下面简要的介绍下。
我们假设有如下函数,值域在 [0,π] 上,

现在要求该函数与X轴所围图形的面积。对于这样一个不规则的图形,很难直接求出来它的面积,不过我们可以这样转换:肯定有一个长度为 π ,高度为h的矩形的面积,与该图形的面积一致,如下图所示:

所以,现在的问题,就变成了如何去求解这个h。理论上,这个h就应该等于所有在 [0,π] 定义域里面,函数 f(x) 值的平均值。
对于这个平均值的求法,Riemann Sum是这样来求解的:
设定一个步进值step,从函数的定义域 [0,π] 起点出发,一步一步的往终点去移动,计算每一个函数的值,然后将这些值求平均数(除以步进的步数),如下图所示:

这样,当我们的步进值越小的时候,通过这种方法计算出来的h值就越加的接近真实值。
所以上面的渲染方程的Riemann Sum形式变成如下:
其中:
带入得到:
上述公式中,只有 kD 和 c 是未知的,我们不在积分里面计算,剩下的,都是能够通过预先计算得到。把这个过程转换为代码,如下所示:
float samplingStep = 0.025;
int sampler = 0;
vec3 l = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for (float phi = 0.0; phi < 2.0 * PI; phi = phi + samplingStep) {
for (float theta = 0.0; theta < 0.5 * PI; theta = theta + samplingStep) {
vec3 d = calc_cartesian(phi, theta); // Transform spherical coordinate to cartesian coordinate
d = d.x * r + d.y * u + d.z * n; // Transform tangent space coordinate to world space coordinate
l = l + filtering_cube_map(glb_CubeMap, normalize(d)) * cos(theta) * sin(theta); // L * (ndotl) * sin(theta) d(theta)d(phi)
sampler = sampler + 1;
}
}
l = PI * l * (1.0 / sampler);
}预计算操作
我们先仔细的观察下需要积分的渲染方程:
对于单个表面来说,这个积分方程里面,除了 fd 不需要考虑之外,积分里面的 n 也是固定不变的。所以,当我们最终将积分的结果保存在Cube Map里面,并且在实际渲染的时候,我们就是使用这个表面法线 n 来获取对应表面在半球积分里面的结果。所以,当我们在进行预计算的时候,其结果就需要与这样的获取方式相对应。也就说,对于CubeMap的6个面,我们分别使用其上的UV以及面的方向(+X,-X,+Y,-Y,+Z,-Z)来确定一个法线 n ,然后进行预计算。下面的代码,是根据面的方向以及UV确定一个法线 n 的代码:
vec3 calc_normal(int face, vec2 uv) {
// 6 Face(+X,-X,+Y,-Y,+Z,-Z) for [0,5]
uv = (uv - 0.5) * 2.0; // Convert range [0, 1] to [-1, 1]
vec3 n = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
if (face == 0) {
// +X face
n.x = 1.0;
n.zy = uv;
} else if (face == 1) {
// -X face
n.x = -1.0;
n.z = -uv.x;
n.y = uv.y;
} else if (face == 2) {
// +Y face
n.y = 1.0;
n.xz = uv;
} else if (face == 3) {
// -Y face
n.y = -1.0;
n.x = uv.x;
n.z = -uv.y;
} else if (face == 4) {
// +Z face
n.z = 1.0;
n.x = -uv.x;
n.y = uv.y;
} else if (face == 5) {
// -Z face
n.z = -1.0;
n.xy = uv;
}
return n;
}
对于Riemann Sum形式的积分方程:
其中只有 Li 是未知的了,所以我们需要根据 θ 和 ϕ 构造出这个 Li 出来。在每次运算过程中,我们通过步进得到了 θ 和 ϕ 值,不过这是球面坐标系的表示,我们得把它转换成为笛卡尔坐标,如下代码完成该操作:
vec3 calc_cartesian(float phi, float theta) {
return vec3(sin(theta) * cos(phi), sin(theta) * sin(phi), cos(theta));
}同时我们还需要知道一点,我们这里定义的 θ 和 ϕ 都是在 n 为(0,0,1)的空间中定义,所以我们需要将该向量转换到世界空间中去,如下代码:
// Calculate tangent space base vector
vec3 n = calc_normal(faceIndex, uv);
n = normalize(n);
vec3 u = vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
vec3 r = cross(u, n);
r = normalize(r);
u = cross(n, r);
u = normalize(u);
......
vec3 d = calc_cartesian(phi, theta); // Transform spherical coordinate to cartesian coordinate
d = d.x * r + d.y * u + d.z * n; // Transform tangent space coordinate to world space coordinate
l = filtering_cube_map(glb_CubeMap, normalize(d))通过这样的方式,我们就能够得到积分方程里面 Li ,然后带入公式即可。
下面是完整的预计算代码:
#version 330
#extension GL_NV_shadow_samplers_cube : enable
in vec2 vs_TexCoord;
out vec3 oColor;
uniform samplerCube glb_CubeMap;
uniform int glb_FaceIndex;
const float PI = 3.1415926536898;
vec3 filtering_cube_map(samplerCube cube, vec3 n) {
n.yz = -n.yz;
return textureCube(cube, n).xyz;
}
vec3 calc_normal(int face, vec2 uv) {
// 6 Face(+X,-X,+Y,-Y,+Z,-Z) for [0,5]
uv = (uv - 0.5) * 2.0; // Convert range [0, 1] to [-1, 1]
vec3 n = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
if (face == 0) {
// +X face
n.x = 1.0;
n.zy = uv;
} else if (face == 1) {
// -X face
n.x = -1.0;
n.z = -uv.x;
n.y = uv.y;
} else if (face == 2) {
// +Y face
n.y = 1.0;
n.xz = uv;
} else if (face == 3) {
// -Y face
n.y = -1.0;
n.x = uv.x;
n.z = -uv.y;
} else if (face == 4) {
// +Z face
n.z = 1.0;
n.x = -uv.x;
n.y = uv.y;
} else if (face == 5) {
// -Z face
n.z = -1.0;
n.xy = uv;
}
return n;
}
vec3 calc_cartesian(float phi, float theta) {
return vec3(sin(theta) * cos(phi), sin(theta) * sin(phi), cos(theta));
}
vec3 convolution_cube_map(samplerCube cube, int faceIndex, vec2 uv) {
// Calculate tangent space base vector
vec3 n = calc_normal(faceIndex, uv);
n = normalize(n);
vec3 u = vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
vec3 r = cross(u, n);
r = normalize(r);
u = cross(n, r);
u = normalize(u);
// Convolution
float samplingStep = 0.025;
int sampler = 0;
vec3 l = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for (float phi = 0.0; phi < 2.0 * PI; phi = phi + samplingStep) {
for (float theta = 0.0; theta < 0.5 * PI; theta = theta + samplingStep) {
vec3 d = calc_cartesian(phi, theta); // Transform spherical coordinate to cartesian coordinate
d = d.x * r + d.y * u + d.z * n; // Transform tangent space coordinate to world space coordinate
l = l + filtering_cube_map(glb_CubeMap, normalize(d)) * cos(theta) * sin(theta); // L * (ndotl) * sin(theta) d(theta)d(phi)
sampler = sampler + 1;
}
}
l = PI * l * (1.0 / sampler);
return l;
}
void main() {
vec3 color = convolution_cube_map(glb_CubeMap, glb_FaceIndex, vs_TexCoord);
//oColor = color / (1.0 + color);
oColor = color;
}下图给出了预计算前后Cube Map的对比图:

需要注意,我这里预计算的Diffuse图尺寸在32×32。之所以选择较小的图,是因为Diffuse项是一个低频的信号,能够通过插值得到较好的结果,所以为了减少预计算的消耗,就选择了这个大小的尺寸。
IBL光照计算
有了前面的基础,这里的IBL光照计算就十分的简单,回顾下最后的渲染方程:
其中的:
已经通过预计算保存在了Cube Map里面,所以我们只要根据法线 n 获取Cube Map里面对应的值,然后乘上剩下的 kD∗c 就可以了。以下是完整的代码:
vec3 calc_ibl(vec3 n, vec3 v, vec3 albedo, float roughness, float metalic) {
vec3 F0 = mix(vec3(0.04, 0.04, 0.04), albedo, metalic);
vec3 F = calc_fresnel_roughness(n, v, F0, roughness);
vec3 T = vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) - F;
vec3 kD = T * (1.0 - metalic);
vec3 irradiance = filtering_cube_map(glb_IrradianceMap, n);
return kD * albedo * irradiance;
}需要额外说明的是,我们这里计算Fresnel系数的方式和前面直接光照系统的计算方式有所不同。这是因为对于IBL来说,我们没有办法得到一个单一的half向量,所以这里就直接使用了表面法线 n 来代替。但是这样就丢失了表面粗糙度的影响,所以重新设计了新的Fresnel函数,并且将roughness属性考虑进去。以下是考虑了roughness属性的新的Fresnel系数计算函数:
vec3 calc_fresnel_roughness(vec3 n, vec3 v, vec3 F0, float roughness) {
float ndotv = max(dot(n, v), 0.0);
return F0 + (max(vec3(1.0 - roughness), F0) - F0) * pow(1.0 - ndotv, 5.0);
}总结
以上就是本篇文章的全部内容,配套代码放在:
https://github.com/idovelemon/GraphicsLabtory/tree/master/glbcodebase/graphicslab/glb_ibl_diffuse。
参考文献
[1]LearnOpenGL
[2]Article - Physically Based Rendering
[3]ScratchPixel
[4]Adapt a physically based rendering model