pytorch 机器翻译 seq2seq 模型和注意力机制
序列到序列(seq2seq)的模型图示:

在很多任务场景中,我们需要处理变长序列,并输出另一个变长序列,如:机器翻译、文本摘要、语音识别等。
例:
input: 我是你爸爸
output: i m your father
seq2seq 是处理这种问题的通用模型,如上图所示:用一个 RNN 将输入序列编码成一个 context (上下文)向量,然后从这个 context 向量解码出需要生成的序列,因而这个模型亦可成为 Encoder-Decoder (编码-解码)模型。
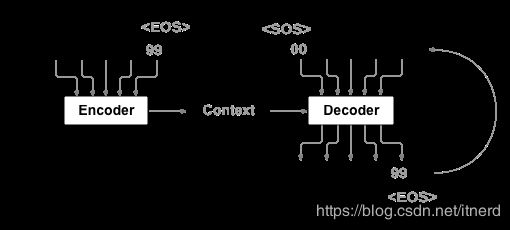
下面用机器翻译的模型来理解 seq2seq 的机理。
pytorch 实战
数据集
下载 pytorch_tutorial_data,其中文件 eng-fra.txt 内容如下,为 tab 间隔的英-法短句。
...
Tom passed away last year. Tom est décédé l'année dernière.
Tom pulled the fire alarm. Tom a tiré l'alarme d'incendie.
Tom raised his right hand. Tom leva sa main droite.
Tom raised his right hand. Tom a levé sa main droite.
Tom read the letter aloud. Tom lut la lettre à voix haute.
Tom reads to his daughter. Tom lit à sa fille.
Tom realized he was alone. Tom réalisa qu'il était seul.
Tom really needs our help. Tom a vraiment besoin de notre aide.
Tom refused to talk to me. Tom a refusé de me parler.
Tom remembered everything. Tom se souvenait de tout.
Tom rolled up his sleeves. Tom retroussa ses manches.
Tom said he wasn't hungry. Tom a dit qu'il n'avait pas faim.
Tom said he would be here. Tom a dit qu'il serait ici.
Tom said that he liked me. Tom a dit qu'il m'appréciait.
Tom said that he liked me. Tom a dit qu'il m'aimait bien.
Tom said that he was busy. Tom a dit qu'il était occupé.
Tom sat down next to Mary. Tom s'assit à côté de Mary.
Tom sat down on the couch. Tom s'assit sur le canapé.
Tom seemed very impressed. Tom avait l'air très impressionné.
Tom seldom makes mistakes. Tom fait rarement des erreurs.
Tom should have paid Mary. Tom aurait dû payer Marie.
Tom should've been in bed. Tom aurait dû être au lit.
...
from __future__ import unicode_literals, print_function, division
from io import open
import unicodedata
import string
import re
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# plt.switch_backend('agg')
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
import numpy as np
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
预处理
给每一种语言定义字典类 Lang,记录
- word2index 单词索引
- index2word 索引单词,其中包含两个特殊符号(Start Of Sentence, End Of Sentence),用于记录句子的起始和终止
- word2count 单词词频
- n_words 单词总数
SOS_token = 0
EOS_token = 1
class Lang:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.word2index = {}
self.word2count = {}
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"}
self.n_words = 2 # Count SOS and EOS
def addSentence(self, sentence):
for word in sentence.split(' '):
self.addWord(word)
def addWord(self, word):
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1
将 unicode 转换成 ASCII码,降低字符的表示维度,因为法语中有些字符可能带帽子,不在26个字母内,如: Ślusàrski
# Turn a Unicode string to plain ASCII, thanks to
# https://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427
def unicodeToAscii(s):
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)
# Lowercase, trim, and remove non-letter characters
def normalizeString(s):
s = unicodeToAscii(s.lower().strip())
s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s)
return s
读取数据文件到列表中
def readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
print("Reading lines...")
# Read the file and split into lines
lines = open('data/data/%s-%s.txt' % (lang1, lang2), encoding='utf-8').\
read().strip().split('\n')
# Split every line into pairs and normalize
pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines]
# Reverse pairs, make Lang instances
if reverse:
pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs]
input_lang = Lang(lang2)
output_lang = Lang(lang1)
else:
input_lang = Lang(lang1)
output_lang = Lang(lang2)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
对语料库中的句子过滤一遍,只用以如下字符开头语句训练模型
MAX_LENGTH = 10
eng_prefixes = (
"i am ", "i m ",
"he is", "he s ",
"she is", "she s ",
"you are", "you re ",
"we are", "we re ",
"they are", "they re "
)
def filterPair(p):
return len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \
len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \
p[1].startswith(eng_prefixes)
def filterPairs(pairs):
return [pair for pair in pairs if filterPair(pair)]
def prepareData(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse)
print("Read %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
pairs = filterPairs(pairs)
print("Trimmed to %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
print("Counting words...")
for pair in pairs:
input_lang.addSentence(pair[0])
output_lang.addSentence(pair[1])
print("Counted words:")
print(input_lang.name, input_lang.n_words)
print(output_lang.name, output_lang.n_words)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = prepareData('eng', 'fra', True)
print(random.choice(pairs))
'''
Reading lines...
Read 135842 sentence pairs
Trimmed to 10599 sentence pairs
Counting words...
Counted words:
fra 4345
eng 2803
['je ne le fais plus .', 'i m not doing it anymore .']
'''
将字符串转换成张量
def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence):
return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence):
indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence)
indexes.append(EOS_token)
return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1)
def tensorsFromPair(pair):
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0])
target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1])
return (input_tensor, target_tensor)
记录时间
import time
import math
def asMinutes(s):
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
def timeSince(since, percent):
now = time.time()
s = now - since
es = s / (percent)
rs = es - s
return '%s (- %s)' % (asMinutes(s), asMinutes(rs))
定义 编码器
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size):
super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
output = embedded
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
定义 解码器
class AttnDecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, dropout_p=0.1, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
super(AttnDecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.dropout_p = dropout_p
self.max_length = max_length
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(self.output_size, self.hidden_size)
self.attn = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.max_length)
self.attn_combine = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(self.dropout_p)
self.gru = nn.GRU(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.output_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden, encoder_outputs):
embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
embedded = self.dropout(embedded)
attn_weights = F.softmax(
self.attn(torch.cat((embedded[0], hidden[0]), 1)), dim=1)
attn_applied = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0),
encoder_outputs.unsqueeze(0))
output = torch.cat((embedded[0], attn_applied[0]), 1)
output = self.attn_combine(output).unsqueeze(0)
output = F.relu(output)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
output = F.log_softmax(self.out(output[0]), dim=1)
return output, hidden, attn_weights
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
这个解码器中加入了注意力机制。
没有加入注意力前,解码器在每一次迭代时都将整个 context 向量作为输入,以下面这个翻译为例:
例:
input: 我是你爸爸
output: i m your father

编码器将 “我是你爸爸
更合理的做法是:翻译出 ‘m’ 时,应该参考 ‘是’ 这个字;翻译出 ‘your’ 时,应该参考 ‘你’ 这个字。
也就是说,解码器的每一步,只需要参考 context 的部分信息,这就是注意力机制。从上面的网络图来看,就是用一个掩码 attn_weights 将编码器的输出 encoder_outputs(context) 过滤一次,得到的 attn_applied 就是在 context 里在当前迭代步值得注意的片段,将其作为当前步的输入信息。
训练
训练单条语句
teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5
def train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
encoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
decoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
input_length = input_tensor.size(0)
target_length = target_tensor.size(0)
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
loss = 0
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(
input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] = encoder_output[0, 0]
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device)
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
use_teacher_forcing = True if random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio else False
if use_teacher_forcing:
# Teacher forcing: Feed the target as the next input
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
decoder_input = target_tensor[di] # Teacher forcing
else:
# Without teacher forcing: use its own predictions as the next input
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() # detach from history as input
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
if decoder_input.item() == EOS_token:
break
loss.backward()
encoder_optimizer.step()
decoder_optimizer.step()
return loss.item() / target_length
训练批量语句
def trainIters(encoder, decoder, n_iters, print_every=1000, plot_every=100, learning_rate=0.01):
start = time.time()
plot_losses = []
print_loss_total = 0 # Reset every print_every
plot_loss_total = 0 # Reset every plot_every
encoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
decoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
training_pairs = [tensorsFromPair(random.choice(pairs))
for i in range(n_iters)]
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
for iter in range(1, n_iters + 1):
training_pair = training_pairs[iter - 1]
input_tensor = training_pair[0]
target_tensor = training_pair[1]
loss = train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder,
decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion)
print_loss_total += loss
plot_loss_total += loss
if iter % print_every == 0:
print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every
print_loss_total = 0
print('%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (timeSince(start, iter / n_iters),
iter, iter / n_iters * 100, print_loss_avg))
if iter % plot_every == 0:
plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every
plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg)
plot_loss_total = 0
showPlot(plot_losses)
def showPlot(points):
plt.figure()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
loc = ticker.MultipleLocator(base=0.2)
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(loc)
plt.plot(points)
训练
hidden_size = 256
encoder = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size).to(device)
attn_decoder1 = AttnDecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words, dropout_p=0.1).to(device)
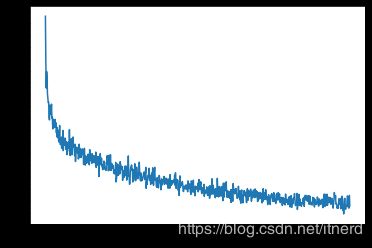
trainIters(encoder, attn_decoder1, 75000, print_every=5000)
'''
2m 55s (- 40m 57s) (5000 6%) 1.7566
5m 49s (- 37m 52s) (10000 13%) 1.2538
8m 41s (- 34m 46s) (15000 20%) 1.0629
11m 37s (- 31m 59s) (20000 26%) 0.9481
14m 30s (- 29m 0s) (25000 33%) 0.8491
17m 22s (- 26m 3s) (30000 40%) 0.7600
20m 14s (- 23m 7s) (35000 46%) 0.6800
23m 7s (- 20m 14s) (40000 53%) 0.6074
26m 1s (- 17m 20s) (45000 60%) 0.5736
28m 54s (- 14m 27s) (50000 66%) 0.5043
31m 48s (- 11m 34s) (55000 73%) 0.4845
34m 42s (- 8m 40s) (60000 80%) 0.4332
37m 34s (- 5m 46s) (65000 86%) 0.4044
40m 28s (- 2m 53s) (70000 93%) 0.3875
43m 23s (- 0m 0s) (75000 100%) 0.3679
'''
测试结果
测评单条语句
def evaluate(encoder, decoder, sentence, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
with torch.no_grad():
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentence)
input_length = input_tensor.size()[0]
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei],
encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] += encoder_output[0, 0]
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) # SOS
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
decoded_words = []
decoder_attentions = torch.zeros(max_length, max_length)
for di in range(max_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
decoder_attentions[di] = decoder_attention.data
topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1)
if topi.item() == EOS_token:
decoded_words.append('' )
break
else:
decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[topi.item()])
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach()
return decoded_words, decoder_attentions[:di + 1]
测评多条语句
def evaluateRandomly(encoder, decoder, n=10):
for i in range(n):
pair = random.choice(pairs)
print('>', pair[0])
print('=', pair[1])
output_words, attentions = evaluate(encoder, decoder, pair[0])
output_sentence = ' '.join(output_words)
print('<', output_sentence)
print('')
evaluateRandomly(encoder1, attn_decoder1)
'''
> ils ne sont pas satisfaits .
= they re not happy .
< they re unhappy .
> nous ne sommes pas ici pour t arreter .
= we are not here to arrest you .
< we are not here to ask you .
> je ne peux pas reparer l ordinateur .
= i m not able to fix the computer .
< i m not able to fix the .
> je suis tres heureux maintenant .
= i m very happy now .
< i m very happy now .
> elle n est pas poete mais romanciere .
= she is not a poet but a novelist .
< she is not a but but a
> elle est sa veritable mere .
= she is his real mother .
< she is her mother mother .
> je suppose que c est votre pere .
= i m assuming this is your father .
< i m assuming this is your father .
> tu es un etre mauvais .
= you are a bad person .
< you are a bad person .
> tu es surmene .
= you re overworked .
< you are overworked .
> je viens de l exterieur de la ville .
= i m from out of town .
< i m from out of town .
'''
注意力可视化
def showAttention(input_sentence, output_words, attentions):
# Set up figure with colorbar
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
cax = ax.matshow(attentions.numpy(), cmap='bone')
fig.colorbar(cax)
# Set up axes
ax.set_xticklabels([''] + input_sentence.split(' ') +
['' ], rotation=90)
ax.set_yticklabels([''] + output_words)
# Show label at every tick
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
plt.show()
def evaluateAndShowAttention(input_sentence):
output_words, attentions = evaluate(
encoder1, attn_decoder1, input_sentence)
print('input =', input_sentence)
print('output =', ' '.join(output_words))
showAttention(input_sentence, output_words, attentions)
evaluateAndShowAttention("elle a cinq ans de moins que moi .")
evaluateAndShowAttention("elle est trop petit .")
evaluateAndShowAttention("je ne crains pas de mourir .")
evaluateAndShowAttention("c est un jeune directeur plein de talent .")
input = elle a cinq ans de moins que moi .
output = she is two years younger than me .

input = elle est trop petit .
output = she s too drunk .

input = je ne crains pas de mourir .
output = i m not scared to die .

input = c est un jeune directeur plein de talent .
output = he is a talented young talented .