Kotlin Lambda表达式
用法:{[参数列表] ->[函数体,最后一行是返回值]}//不实用fun修饰,用法跟匿名函数一样
举例
val sum ={a:Int,b:Int -> a+b}
参数和返回值:
1> ( ) -> Unit //无参数 ,返回值的类型为Unit
2> (Int) -> Int //Int类型的参数,返回值得类型为Int
3> (String,(String) ->String) ->Boolean //两个参数,第一个参数为String,第二个参数为Lambda表达式,返回值为Boolean
使用调用( ),例如sum(1,2)或者sum.invoke(1,2)
Lambda表达式的简化
1>函数参数调用时,最后一个Lambda可以移除去
2>函数参数只有一个Lambda,调用小括号可以省略
3>Lambda只有一个参数,可以默认使用it
4>入参,返回值与形参一致的函数可以使用引用的方式作为实参传入
package com.testlambda
/**
* Created by jingwen on 19/4/14.
*/
fun main(args: Array) {//Array -> Unit
var a:Int = 1;
var b:Int = 2;
var sum1 = sum(a,b)
var sum2 = sum.invoke(a,b)
println("$a+$b=$sum1")
println("$a+$b=$sum2")
}
val sum = {a:Int,b:Int -> a+b}//Int,Int -> Int
执行结果:
1+2=3
1+2=3
Process finished with exit code 0
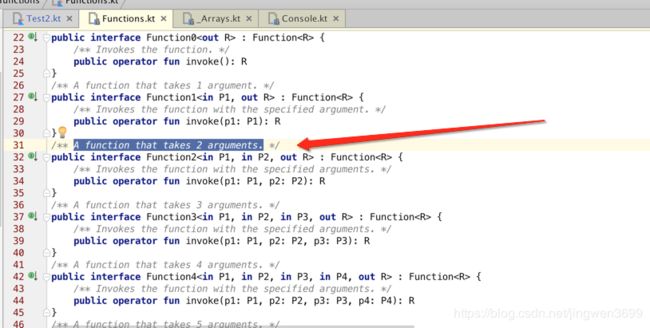
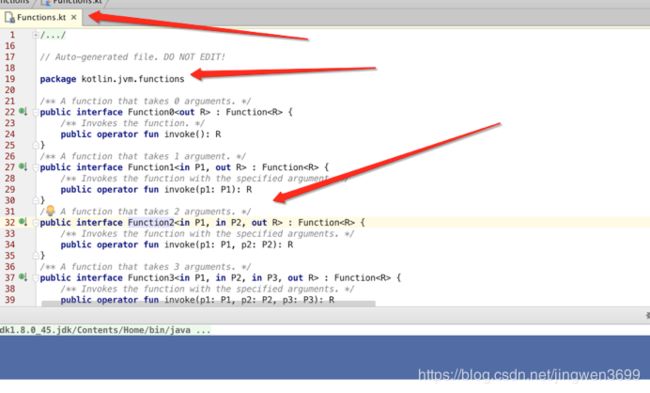
sum.invoke(1,2)//是function里面的function2,总共有23个,不能多于23个参数
Functions.kt package kotlin.jvm.functions
/** A function that takes 2 arguments. */
public interface Function2 : Function {
/** Invokes the function with the specified arguments. */
public operator fun invoke(p1: P1, p2: P2): R
}
/** A function that takes 22 arguments. */
public interface Function22 : Function {
/** Invokes the function with the specified arguments. */
public operator fun invoke(p1: P1, p2: P2, p3: P3, p4: P4, p5: P5, p6: P6, p7: P7, p8: P8, p9: P9, p10: P10, p11: P11, p12: P12, p13: P13, p14: P14, p15: P15, p16: P16, p17: P17, p18: P18, p19: P19, p20: P20, p21: P21, p22: P22): R
}
package com.com.pkg.test
/**
* Created by jingwen on 19/4/14.
*/
fun main(args: Array) {
//调用方法1
printSay();
//调用方法2
printSay.invoke()
var studentNames:Array = arrayOf("jingwen","chengcheng","zhulina")
//方法1
println("学生的名字(方法1):")
for(name in studentNames){
println(name)
}
//forEach是Array的扩展方法
// /**
// * Performs the given [action] on each element.
// */
// public inline fun Array.forEach(action: (T) -> Unit): Unit {
// for (element in this) action(element)
// }
//方法2
println("学生的名字(方法2):")
studentNames.forEach({ it ->
println(it)
})
//方法3
println("学生的名字(方法3):")
studentNames.forEach() {
println(it)
}
//方法4
println("学生的名字(方法4):")
studentNames.forEach {
println(it)
}
//方法5
println("学生的名字(方法5):")
studentNames.forEach(::println)
//方法6
println("学生的名字(方法6):")//参数的名字可以修改的哈
studentNames.forEach { ss ->
println(ss)
}
//参数和类型
println(::printSay)
println("end")
}
//无参数 Lambda表但是 ()->Unit
val printSay = {
println("jingwen: hello world!")
}
jingwen: hello world!
jingwen: hello world!
学生的名字(方法1):
jingwen
chengcheng
zhulina
学生的名字(方法2):
jingwen
chengcheng
zhulina
学生的名字(方法3):
jingwen
chengcheng
zhulina
学生的名字(方法4):
jingwen
chengcheng
zhulina
学生的名字(方法5):
jingwen
chengcheng
zhulina
学生的名字(方法6):
jingwen
chengcheng
zhulina
val printSay: () -> kotlin.Unit
end