剑指Offer面试题6(Java版):重建二叉树
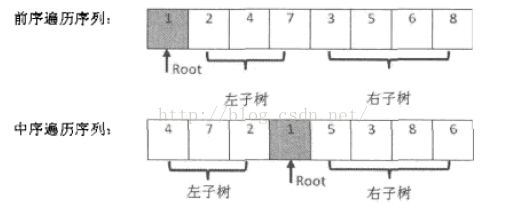
题目:输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重新构造出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中不包含重复的数字。例如输入的前序遍历序列为{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历为{4,7,2,1,5,3,6,8},则重建出二叉树并输出它的头结点。
在二叉树的前序遍历序列中,第一个数字总是树的根节点的值。但在中序遍历中,根节点的值在序列的中间,左子树的结点的值位于根节点的值的左边,而右子树的结点的值位于根节点的右边。因此我们需要扫描中序遍历序列,才能找到根节点的值。
如图所示,前序遍历序列的第一个数字1就是根节点的值。扫描中序遍历序列,就能确定根节点的值的位置。根据中序遍历的特点,在根节点的值1前面3个数字都是左子树结点的值,位于1后面的数字都是右子树结点的值。
由于中序遍历序列中,有3个数字是左子树结点的值,因此左子树总共有3个左子结点。同样,在前序遍历的序列中,根节点后面的3个数字就是3个左子树结点的值,再后面的所有数字都是右子树结点的值。这样我们就在前序遍历和中序遍历两个序列中,分别找到了左右子树对应的子序列。
既然我们已经分别找到了左、右子树的前序遍历序列和中序遍历序列,我们可以用同样的方法分别去构建左右子树。也就是说,接下来的事情可以用递归的方法去完成。
我们使用Java语言来实现上面的代码:
首先构建二叉树代码:
package utils;
public class BinaryTreeNode {
public int value;
public BinaryTreeNode leftNode;
public BinaryTreeNode rightNode;
public BinaryTreeNode(){
}
public BinaryTreeNode(int value){
this.value = value ;
this.leftNode = null;
this.rightNode = null;
}
}
重建二叉树代码:
package swordForOffer;
/**
* @author JInShuangQi
*
* 2015年7月25日
*/
import utils.BinaryTreeNode;
public class E06ConstructBinaryTree {
/**
*
* @param preOrder 前序遍历数组
* @param inOrder 中序遍历数组
* @param length 数组长度
* @return 根结点
*/
public static BinaryTreeNode Construct(int[] preOrder, int[] inOrder,int length){
if (preOrder == null || inOrder == null || length <= 0) {
return null;
}
try {
return ConstructCore(preOrder, 0, preOrder.length - 1, inOrder, 0,inOrder.length - 1);
} catch (InvalidPutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
*
* @param PreOrder
* 前序遍历序列
* @param startPreIndex
* 前序序列开始位置
* @param endPreIndex
* 前序序列结束位置
* @param InOrder
* 中序遍历序列
* @param startInIndex
* 中序序列开始位置
* @param endInIndex
* 中序序列结束位置
* @return 根结点
* @throws InvalidPutException
*/
public static BinaryTreeNode ConstructCore(int[] preOrder,int startPreIndex, int endPreIndex,
int[] inOrder,int startInIndex, int endInIndex) throws InvalidPutException {
int rootValue = preOrder[startPreIndex];
System.out.println("rootValue = " + rootValue);
BinaryTreeNode root = new BinaryTreeNode(rootValue);
// 只有一个元素
if (startPreIndex == endPreIndex) {
if (startInIndex == endInIndex
&& preOrder[startPreIndex] == inOrder[startInIndex]) {
System.out.println("only one element");
return root;
} else {
throw new InvalidPutException();
}
}
// 在中序遍历中找到根结点的索引
int rootInIndex = startInIndex;
while (rootInIndex <= endInIndex && inOrder[rootInIndex] != rootValue) {
++rootInIndex;
}
if (rootInIndex == endInIndex && inOrder[rootInIndex] != rootValue) {
throw new InvalidPutException();
}
int leftLength = rootInIndex - startInIndex;
int leftPreOrderEndIndex = startPreIndex + leftLength;
if (leftLength > 0) {
// 构建左子树
root.leftNode = ConstructCore(preOrder, startPreIndex + 1,
leftPreOrderEndIndex, inOrder, startInIndex,
rootInIndex - 1);
}
if (leftLength < endPreIndex - startPreIndex) {
// 右子树有元素,构建右子树
root.rightNode = ConstructCore(preOrder, leftPreOrderEndIndex + 1,
endPreIndex, inOrder, rootInIndex + 1, endInIndex);
}
return root;
}
static class InvalidPutException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
public static void printPreOrder(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
} else {
System.out.print(root.value + " ");
}
if (root.leftNode != null) {
printPreOrder(root.leftNode);
}
if (root.rightNode != null) {
printPreOrder(root.rightNode);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
E06ConstructBinaryTree test=new E06ConstructBinaryTree();
int[] preOrder={1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8};
int[] inOrder={4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6};
printPreOrder(Construct(preOrder, inOrder, preOrder.length));
}
}