C++读取STL模型文件
数据格式
二进制的数据格式:
二进制STL文件用固定的字节数来给出三角面片的几何信息。
- 【80】80个字节的文件头,用于存贮文件名
- 【4】 4 个字节的int描述模型的三角面片个数(小端存储)
- 【50*n】一个三角面片占用固定的50个字节(小端存储),依次是:
- 【12】3个4字节浮点数(角面片的法矢量)
- 【12】3个4字节浮点数(1个顶点的坐标)
- 【12】3个4字节浮点数(2个顶点的坐标)
- 【12】3个4字节浮点数(3个顶点的坐标)个
- 【2】三角面片的最后2个字节用来描述三角面片的属性信息。
一个完整二进制STL文件的大小为三角形面片数乘以 50再加上84个字节。
ASCII的数据格式
solid name
//一个三角面
facet normal ni nj nk
outer loop
vertex v1x v1y v1z
vertex v2x v2y v2z
vertex v3x v3y v3z
endloop
endfacet
//更多三角面···
endsolid name例子
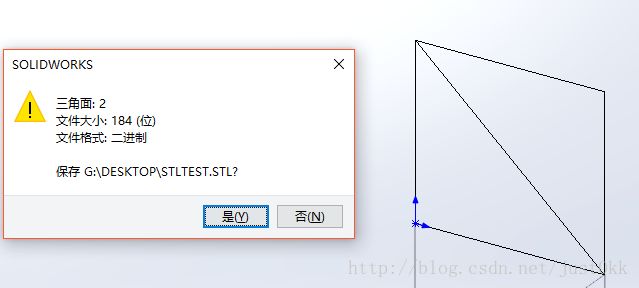
此处将完整展示将一个二进制格式STL文件导入到程序中的过程。
利用solidworks建立了一个10X10mm²的方形面片,并将其导出为二进制STL
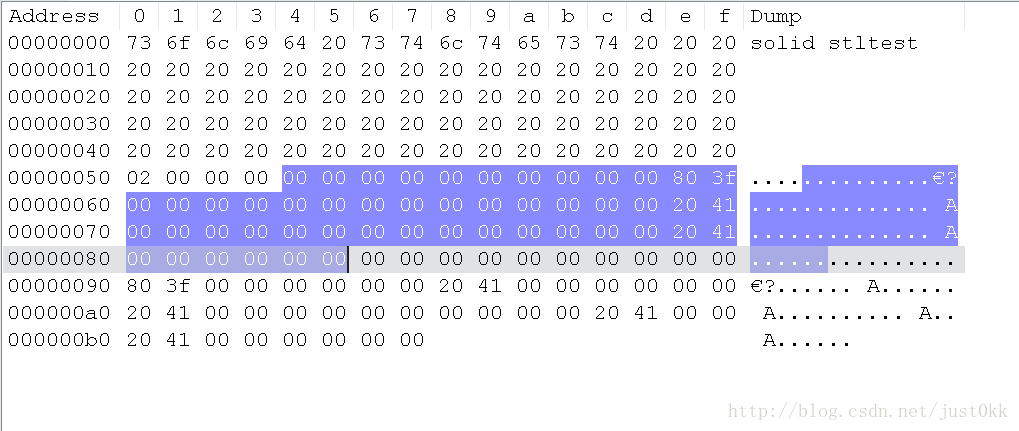
利用notepad++的HEX-Editor插件查看二进制文件
选中的二进制段落就是第一个三角面的全部信息
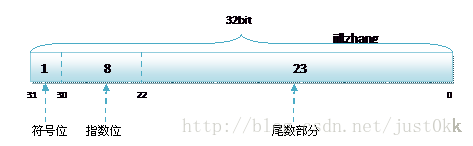
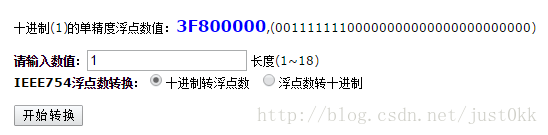
STL中的浮点数格式符合IEEE制定的float格式,并且是小端存储,在x86系统中编译可以直接利用memcpy函数拷贝到C++的float中
在线浮点数转换
表1 三角面1
| 表项 | X | Y | Z | 坐标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 法向量 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 3f800000 | (0,0,1) |
| 点1 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | (0,0,0) |
| 点2 | 41200000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | (10,0,0) |
| 点3 | 00000000 | 41200000 | 00000000 | (0,10,0) |
| 三角面标记 | 0000 |
代码
这段代码的功能是识别一个STL文件是二进制或是ASCII格式,并将内部的三角面存储到vector容器中。
ReadSTLFile.cpp
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;
bool ReadSTLFile::ReadFile(const char *cfilename)
{
FILE * pFile;
long lSize;
char* buffer;
size_t result;
/* 若要一个byte不漏地读入整个文件,只能采用二进制方式打开 */
fopen_s(&pFile,cfilename, "rb");
if (pFile == NULL)
{
fputs("File error", stderr);
exit(1);
}
/* 获取文件大小 */
fseek(pFile, 0, SEEK_END);
lSize = ftell(pFile);
rewind(pFile);
/* 分配内存存储整个文件 */
buffer = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*lSize);
if (buffer == NULL)
{
fputs("Memory error", stderr);
exit(2);
}
/* 将文件拷贝到buffer中 */
result = fread(buffer, 1, lSize, pFile);
if (result != lSize)
{
fputs("Reading error", stderr);
exit(3);
}
/* 结束演示,关闭文件并释放内存 */
fclose(pFile);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if (buffer[79]!='\0')//判断格式
{
ReadASCII(buffer);
}
else
{
ReadBinary(buffer);
}
ios::sync_with_stdio(true);
free(buffer);
return true;
}
bool ReadSTLFile::ReadASCII(const char *buffer)
{
unTriangles = 0;
float x, y, z;
int i;
string name, useless;
stringstream ss(buffer);
ss >> name >> name;
ss.get();
do {
ss >> useless;
if (useless != "facet")
break;
getline(ss, useless);
getline(ss, useless);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
ss >> useless >> x >> y >> z;
pointList.push_back(Point3f(x, y, z));
}
unTriangles++;
getline(ss, useless);
getline(ss, useless);
getline(ss, useless);
} while (1);
return true;
}
bool ReadSTLFile::ReadBinary(const char *buffer)
{
const char* p = buffer;
char name[80];
int i, j;
memcpy(name, p, 80);
p += 80;
unTriangles= cpyint(p);
for (i = 0; i < unTriangles; i++)
{
p += 12;//跳过头部法向量
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)//读取三顶点
pointList.push_back(Point3f(cpyfloat(p), cpyfloat(p), cpyfloat(p)));
p += 2;//跳过尾部标志
}
return true;
}
int ReadSTLFile::NumTri()
{
return unTriangles;
}
vectorReadSTLFile.h
#pragma once
#includePoint3f.cpp
#pragma once
#include"Point3f.h"
Point3f::Point3f():x(0),y(0),z(0)
{
}
Point3f::Point3f(float _x, float _y, float _z) :x(_x), y(_y), z(_z)
{
}
int Point3f::SetParam(float _x, float _y, float _z)
{
x = _x;
y = _y;
z = _z;
return 0;
}Point3f.h
#pragma once
#include效果
方形面片读取
上述内存为:
00000000 00000000 00000000
00000000 00000000 00002041
00000000 00002041 00000000
00000000 00002041 00000000
00000000 00000000 00002041
00000000 00002041 00002041即方形面片的STL数据