使用python写神经网络模型之分类器
http://blog.csdn.net/eric_doug/article/details/51769644
使用python写神经网络模型之分类器
分类:
机器学习
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,原文链接地址: http://blog.csdn.net/eric_doug
目录(?)[+]
最近在尝试将所有的机器学习与深度学习的模型用Python来实现,大致的学习思路如下:
- 分类器
- 回归与预测
- 时间序列
所有的模型先用 Python语言实现,然后用Tensorflow的实现。
1 数据集
本文开始以UCI中的Iris数据集作为训练数据集和测试时间集。该数据集给出了花萼(sepal)的长度和宽度以及花瓣(petal)的长度和宽度,根据这4个特征训练模型,预测花的类别(Iris Setosa,Iris Versicolour,Iris Virginica)。
# 包引入
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
df = pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/iris.data', header=None)
df.head(10)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
1.1 数据处理
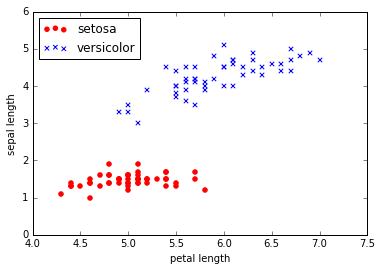
我们提取前100个样本(50个Iris Setosa和50个Iris Versicolour),并将不同的样本类别标注为1(Iris Versicolour)和-1(Iris Setosa);然后,将花萼的长度和花瓣的长度作为特征。大致处理如下:
y = df.iloc[0:100, 4].values # 预测标签向量
y = np.where(y == 'Iris-setosa', -1, 1)
X = df.iloc[0:100, [0,2]].values # 输入特征向量
# 使用散点图可视化样本
plt.scatter(X[:50, 0], X[:50,1], color='red', marker='o', label='setosa')
plt.scatter(X[50:100, 0], X[50:100, 1], color='blue', marker='x', label='versicolor')
plt.xlabel('petal length')
plt.ylabel('sepal length')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2 模型
2.1 神经网络模型
2.1.1 模型实现
我们可以将该问题转化为一个二分类的任务,因此,可以将1与-1作为类别标签。从而激活函数可以表示如下:
ϕ(z) ={1−1 , z≥ 0 , z< 0
大致的模型结构如下:
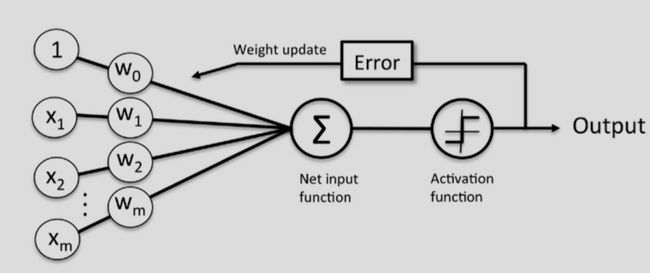
class Perceptron(object):
"""
Parameters
------------
eta : float
学习率 (between 0.0 and 1.0)
n_iter : int
迭代次数
Attributes
-----------
w_ : 1d-array
权重
errors_ : list
误差
"""
def __init__(self, eta=0.01, n_iter=10):
self.eta = eta
self.n_iter = n_iter
def fit(self, X, y):
self.w_ = np.zeros(1 + X.shape[1])
self.errors_ = []
for _ in range(self.n_iter):
errors = 0
for xi, target in zip(X, y):
update = self.eta * (target - self.predict(xi))
self.w_[1:] += update * xi
self.w_[0] += update
errors += int(update != 0.0)
self.errors_.append(errors)
return self
def net_input(self, X):
return np.dot(X, self.w_[1:]) + self.w_[0]
def predict(self, X):
return np.where(self.net_input(X) >= 0.0, 1, -1)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
2.1.2 模型训练
ppn = Perceptron(eta=0.1, n_iter=10)
ppn.fit(X, y)- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
2.1.3 模型验证
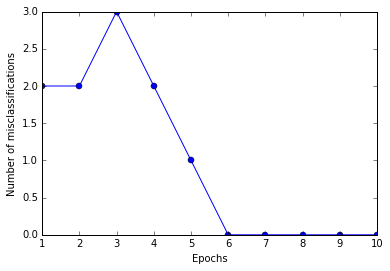
- 误差分析
plt.plot(range(1, len(ppn.errors_) + 1), ppn.errors_, marker='o')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Number of misclassifications')
plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 可视化分类器
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, resolution=0.01):
"""
可视化分类器
:param X: 样本特征向量
:param y: 样本标签向量
:param classifier: 分类器
:param resolution: 残差
:return:
"""
markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v')
colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution), np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
Z = Z.reshape(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0], y=X[y == cl, 1], alpha=0.8, c=cmap(idx), marker=markers[idx], label=cl)
# 调用可视化分类器函数
plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier=ppn)
plt.xlabel('sepal length [cm]')
plt.ylabel('petal length [cm]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35