MongoDB 基础(五)备份还原与导出导入
参考官方文档 : MongoDB Backup Methods
原本使用操作系统的快照进行备份还原,备份成功后,还原没有成功(参考:Backup and Restore with Filesystem Snapshots)
所以这个方法就先不记录到这里了。
当前测试以下?种备份还原方法(个人初学理解):
1. 使用拷贝和替换数据库文件进行备份还原
2. 使用mongodump和mongorestore
3. 使用mongoimport 和 mongoexport
1. 使用拷贝和替换数据库文件进行备份还原(有些危险又不好)
1.1 备份
a. 在mongodb中执行db.fsyncLock(),刷新数据写入磁盘并锁住整个实例:
>db.fsyncLock()[root@localhost ~]# tar -cvzf /root/mongodb_20150505.tar.gz /var/lib/mongo
>db.fsyncUnlock()a. 在mongodb中关闭服务(或者在操作系统层面关闭mongod服务):
>use admin
>db.shutdownServer()b. 将mongo数据文件删除!注意确认备份存在且正常!~否则回天无力!
[root@localhost ~]# rm -rf /var/lib/mongo/*[root@localhost ~]# tar -xvzf /root/mongodb_20150505.tar.gz -C /[root@localhost ~]# rm -f /var/lib/mongo/mongod.lock[root@localhost ~]# service mongod start2. 使用 mongodump和 mongorestore
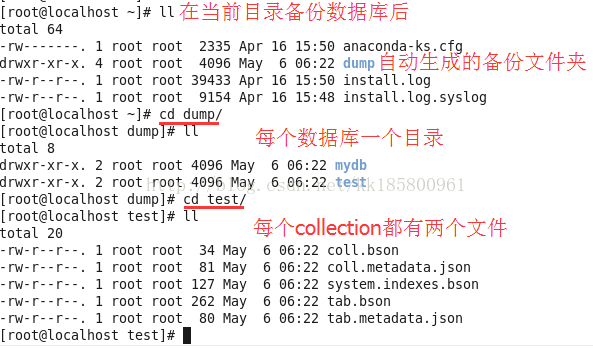
a. 简单备份还原本地数据库的的方法,备份所有及还原所有:
mongodump
mongorestore /root/dump
备份完成后在当前目录将生成一个文件夹”dump“:
b. 还原单个数据库时,指定要还原的数据库及其备份目录:
mongorestore --db test /root/dump/testmongodump --host localhost.localdomain --port 27017 --out /root/mongodump-2015-05-05
mongorestore --port 27017 --db test /root/mongodump-2015-05-05/testmongodump --host mongodb1.example.net --port 3017 --username user --password pass --out /opt/backup/mongodump-2013-10-24
mongorestore --host mongodb1.example.net --port 3017 --username user --password pass /opt/backup/mongodump-2013-10-24
c. 更多参考:执行 # mongorestore --help
# mongorestore --help
general options:
--help print usage
--version print the tool version and exit
verbosity options:
-v, --verbose more detailed log output (include multiple times for more verbosity, e.g. -vvvvv)
--quiet hide all log output
connection options:
-h, --host= mongodb host to connect to (setname/host1,host2 for replica sets)
--port= server port (can also use --host hostname:port)
ssl options:
--ssl connect to a mongod or mongos that has ssl enabled
--sslCAFile= the .pem file containing the root certificate chain from
the certificate authority
--sslPEMKeyFile= the .pem file containing the certificate and key
--sslPEMKeyPassword= the password to decrypt the sslPEMKeyFile, if necessary
--sslCRLFile= the .pem file containing the certificate revocation list
--sslAllowInvalidCertificates bypass the validation for server certificates
--sslAllowInvalidHostnames bypass the validation for server name
--sslFIPSMode use FIPS mode of the installed openssl library
authentication options:
-u, --username= username for authentication
-p, --password= password for authentication
--authenticationDatabase= database that holds the user's credentials
--authenticationMechanism= authentication mechanism to use
namespace options:
-d, --db= database to use
-c, --collection= collection to use
input options:
--objcheck validate all objects before inserting
--oplogReplay replay oplog for point-in-time restore
--oplogLimit= only include oplog entries before the provided Timestamp(seconds[:ordinal])
--restoreDbUsersAndRoles restore user and role definitions for the given database
--dir= input directory, use '-' for stdin
restore options:
--drop drop each collection before import
--writeConcern= write concern options e.g. --writeConcern majority,
--writeConcern '{w: 3, wtimeout: 500, fsync: true, j:true}' (defaults to 'majority')
--noIndexRestore don't restore indexes
--noOptionsRestore don't restore collection options
--keepIndexVersion don't update index version
--maintainInsertionOrder preserve order of documents during restoration
-j, --numParallelCollections= number of collections to restore in parallel (4 by default)
--numInsertionWorkersPerCollection= number of insert operations to run concurrently per collection (1 by default)
--stopOnError stop restoring if an error is encountered on insert (off bydefault)
3. 使用mongoimport 和 mongoexport
3.1 mongoexport导出
--type: 为json 或 csv
--fields: 选择导出的列
#导出列{_id,id,size}为csv的格式
mongoexport --db test --collection tab --type=csv --fields _id,id,size --out /root/test_tab.csv
#导出json格式
mongoexport --db test --collection tab --type=json --out /root/test_tab.json
#输出到shell中,查询id=2 并按name升序输出
mongoexport --db test --collection tab --query '{"id": 2}' --sort '{"name": 1}'
#查询导出
mongoexport --db test --collection tab --type=csv --query '{"id": 2}' --fields _id,id --out /root/test_tab.csv
#简写选项[--db]和[--collection],使用跳过和限制函数输出
mongoexport -d test -c tab --sort '{"name": -1}' --limit 2 --skip 2 --out /root/test_tab.json
#若是远程,需要添加参数:host,port,username,password
--host servername_or_ip --port 37017 --username user --password pass
查看帮助:mongoexport --help
general options:
--help print usage
--version print the tool version and exit
verbosity options:
-v, --verbose more detailed log output (include multiple times for more verbosity, e.g. -vvvvv)
--quiet hide all log output
connection options:
-h, --host= mongodb host to connect to (setname/host1,host2 for replica sets)
--port= server port (can also use --host hostname:port)
ssl options:
--ssl connect to a mongod or mongos that has ssl enabled
--sslCAFile= the .pem file containing the root certificate chain from the certificate authority
--sslPEMKeyFile= the .pem file containing the certificate and key
--sslPEMKeyPassword= the password to decrypt the sslPEMKeyFile, if necessary
--sslCRLFile= the .pem file containing the certificate revocation list
--sslAllowInvalidCertificates bypass the validation for server certificates
--sslAllowInvalidHostnames bypass the validation for server name
--sslFIPSMode use FIPS mode of the installed openssl library
authentication options:
-u, --username= username for authentication
-p, --password= password for authentication
--authenticationDatabase= database that holds the user's credentials
--authenticationMechanism= authentication mechanism to use
namespace options:
-d, --db= database to use
-c, --collection= collection to use
output options:
-f, --fields= comma separated list of field names (required for exporting CSV) e.g. -f "name,age"
--fieldFile= file with field names - 1 per line
--type= the output format, either json or csv (defaults to 'json')
-o, --out= output file; if not specified, stdout is used
--jsonArray output to a JSON array rather than one object per line
--pretty output JSON formatted to be human-readable
querying options:
-q, --query= query filter, as a JSON string, e.g., '{x:{$gt:1}}'
-k, --slaveOk allow secondary reads if available (default true)
--forceTableScan force a table scan (do not use $snapshot)
--skip= number of documents to skip
--limit= limit the number of documents to export
--sort= sort order, as a JSON string, e.g. '{x:1}'
3.2 mongoimport 导入
#列"_id"也会导入,注意重复键
mongoimport --db mydb --collection tab --file /root/test_tab.json
mongoimport --db mydb --collection tab --type csv --headerline --file /root/test_tab.csv
#若是远程,需要添加参数:host,port,username,password
--host servername_or_ip --port 37017 --username user --password pass
查看帮助: mongoimport --help
general options:
--help print usage
--version print the tool version and exit
verbosity options:
-v, --verbose more detailed log output (include multiple times for more verbosity, e.g. -vvvvv)
--quiet hide all log output
connection options:
-h, --host= mongodb host to connect to (setname/host1,host2 for replica sets)
--port= server port (can also use --host hostname:port)
ssl options:
--ssl connect to a mongod or mongos that has ssl enabled
--sslCAFile= the .pem file containing the root certificate chain from the certificate authority
--sslPEMKeyFile= the .pem file containing the certificate and key
--sslPEMKeyPassword= the password to decrypt the sslPEMKeyFile, if necessary
--sslCRLFile= the .pem file containing the certificate revocation list
--sslAllowInvalidCertificates bypass the validation for server certificates
--sslAllowInvalidHostnames bypass the validation for server name
--sslFIPSMode use FIPS mode of the installed openssl library
authentication options:
-u, --username= username for authentication
-p, --password= password for authentication
--authenticationDatabase= database that holds the user's credentials
--authenticationMechanism= authentication mechanism to use
namespace options:
-d, --db= database to use
-c, --collection= collection to use
input options:
-f, --fields= comma separated list of field names, e.g. -f name,age
--fieldFile= file with field names - 1 per line
--file= file to import from; if not specified, stdin is used
--headerline use first line in input source as the field list (CSV and TSV
only)
--jsonArray treat input source as a JSON array
--type= input format to import: json, csv, or tsv (defaults to 'json')
ingest options:
--drop drop collection before inserting documents
--ignoreBlanks ignore fields with empty values in CSV and TSV
--maintainInsertionOrder insert documents in the order of their appearance in the input source
-j, --numInsertionWorkers= number of insert operations to run concurrently (defaults to 1)
--stopOnError stop importing at first insert/upsert error
--upsert insert or update objects that already exist
--upsertFields= comma-separated fields for the query part of the upsert
--writeConcern= write concern options e.g. --writeConcern majority,
--writeConcern '{w: 3, wtimeout: 500, fsync: true, j: true}'
(defaults to 'majority')
由于没有做复制,复制中的备份到时再测试记录吧!~