学习笔记之HOUGH变换
霍夫变换(Hough Transform)是图像处理中的一种特征提取技术,它通过一种投票算法检测具有特定形状的物体。该过程在一个参数空间中通过计算累计结果的局部最大值得到一个符合该特定形状的集合作为霍夫变换结果。经典霍夫变换用来检测图像中的直线,后来霍夫变换扩展到任意形状物体的识别,多为圆和椭圆。
霍夫变换运用两个坐标空间之间的变换将在一个空间中具有相同形状的曲线或直线映射到另一个坐标空间的一个点上形成峰值,从而把检测任意形状的问题转化为统计峰值问题,下面介绍hough变换检测直线的原理和检测结果。
我们知道,一条直线在直角坐标系下可以用y=kx+b表示, 霍夫变换的主要思想是将该方程的参数和变量交换,即用x,y作为已知量k,b作为变量坐标,所以直角坐标系下的直线y=kx+b在参数空间表示为点(k,b),而一个点(x1,y1)在直角坐标系下表示为一条直线y1=x1·k+b,其中(k,b)是该直线上的任意点。为了计算方便,我们将参数空间的坐标表示为极坐标下的γ和θ。因为同一条直线上的点对应的(γ,θ)是相同的,因此可以先将图片进行边缘检测,然后对图像上每一个非零像素点,在参数坐标下变换为一条直线,那么在直角坐标下属于同一条直线的点便在参数空间形成多条直线并内交于一点。因此可用该原理进行直线检测。
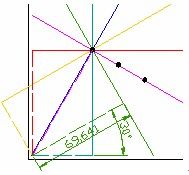
4-13 参数空间变换结果
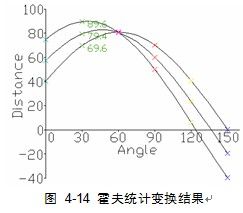
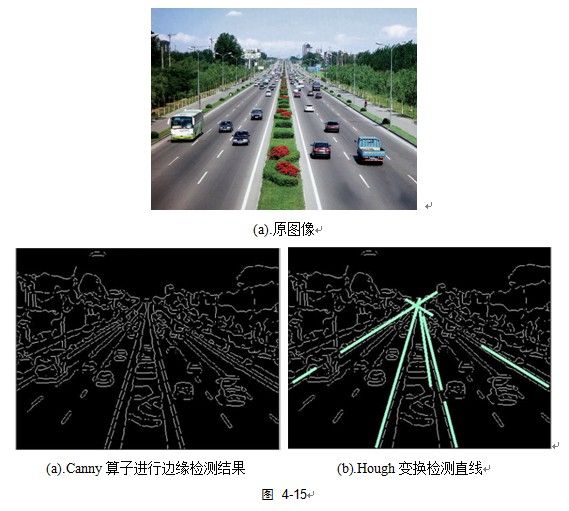
如图 4‑13. 所示,对于原图内任一点(x,y)都可以在参数空间形成一条直线,以图中一条直线为例有参数(γ,θ)=(69.641,30°),所有属于同一条直线上的点会在参数空间交于一点,该点即为对应直线的参数。由该图中所有直线所得到的(γ,θ)在参数空间中得到一系列对应曲线见图 4‑14 霍夫统计变换结果。由霍夫变换检测结果见图 4‑15(c)所示。
hough变换是如何检测出直线和圆的?
(I)直线篇
1 直线是如何表示的?
对于平面中的一条直线,在笛卡尔坐标系中,常见的有点斜式,两点式两种表示方法。然而在hough变换中,考虑的是另外一种表示方式:使用(r,theta)来表示一条直线。其中r为该直线到原点的距离,theta为该直线的垂线与x轴的夹角。如下图所示。
使用hough变换来检测直线的思想就是:为每一个点假设n个方向的直线,通常n=180,此时检测的直线的角度精度为1°,分别计算这n条直线的(r,theta)坐标,得到n个坐标点。如果要判断的点共有N个,最终得到的(r,theta)坐标有N*n个。有关这N*n个(r,theta)坐标,其中theta是离散的角度,共有180个取值。
最重要的地方来了,如果多个点在一条直线上,那么必有这多个点在theta=某个值theta_i时,这多个点的r近似相等于r_i。也就是说这多个点都在直线(r_i,theta_i)上。
3 下面拿个例子说明:
通过 r0theta 坐标系可以更直观表示这种关系,如下图:图中三个点的(r,theta)曲线汇集在一起,该交点就是同时经过这三个点的直线。
在实际的直线检测情况中,如果超过一定数目的点拥有相同的(r,theta)坐标,那么就可以判定此处有一条直线。在r0theta 坐标系图中,明显的交汇点就标示一条检测出的直线。
如下图,可以判定出平面上的点共构成了两条直线,即检测出两条直线。
继使用hough变换检测出直线之后,顺着坐标变换的思路,提出了一种检测圆的方法。
1 如何表示一个圆?
与使用(r,theta)来表示一条直线相似,使用(a,b,r)来确定一个圆心为(a,b)半径为 r 的圆。
2 如何表示过某个点的所有圆?
某个圆过点(x1,y1),则有:(x1-a1)^2 + (y1-b1)^2 = r1^2 。
那么过点(x1,y1)的所有圆可以表示为(a1(i),b1(i),r1(i)),其中r1∈(0,无穷),每一个 i 值都对应一个不同的圆,(a1(i),b1(i),r1(i))表示了无穷多个过点(x1,y1)的圆。
3 如何确定多个点在同一个圆上?
如(2)中说明,过点(x1,y1)的所有圆可以表示为(a1(i),b1(i),r1(i)),过点(x2,y2)的所有圆可以表示为(a2(i),b2(i),r2(i)),过点(x3,y3)的所有圆可以表示为(a3(i),b3(i),r3(i)),如果这三个点在同一个圆上,那么存在一个值(a0,b0,r0),使得 a0 = a1(k)=a2(k)=a3(k) 且b0 = b1(k)=b2(k)=b3(k) 且r0 = r1(k)=r2(k)=r3(k),即这三个点同时在圆(a0,b0,r0)上。
从下图可以形象的看出:
三个圆锥面的交点A 既是同时过这三个点的圆。
OpenCV中的Hough变换
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc < 2) {
cout<<"Usage: ./hough [image file name]"< lines;
HoughLines(img, lines, 1, CV_PI/360, 200); // 返回直线坐标对
for (size_t i=0; i 在做Hough变换之前,一般都要先使用LOG或Canny先检测边缘,再对边缘图像进行Hough变换操作,上面程序使用Canny算子检测边缘,Canny算子Canny(img, img, 100, 200, 3);的两个阈值100,100选择很重要,间接影响Hough检测的结果,同时HoughLines中的阈值参数也应该细调。用上面程序对道路直线进行检测结果如下,
道路图片1
Canny算子边缘检测结果
Hough直线检测结果
道路图片2
Canny算子边缘检测结果
Hough直线检测结果
Hough变换源码分析
Hough变换的源代码在modules/imgproc/src/hough.cpp中,提供了3种Hough变换源码:直线检测、概率Hough变换检测直线、圆检测,如果要实现其它有解析方程的图形的检测,则要自己动手写了。
Hough变换调用接口函数解释
先看Hough检测直线的代码,cvHoughLines2也只不过是个对不同Hough方法的封装,下面是该函数中的部分代码,选择不同的Hough变换方法,
switch( method )
{
case CV_HOUGH_STANDARD:
icvHoughLinesStandard( img, (float)rho,
(float)theta, threshold, lines, linesMax ); // 标准Hough变换
break;
case CV_HOUGH_MULTI_SCALE:
icvHoughLinesSDiv( img, (float)rho, (float)theta,
threshold, iparam1, iparam2, lines, linesMax ); // 多尺度Hough变换
break;
case CV_HOUGH_PROBABILISTIC:
icvHoughLinesProbabalistic( img, (float)rho, (float)theta,
threshold, iparam1, iparam2, lines, linesMax ); // 概率Hough变换
break;
default:
CV_Error( CV_StsBadArg, "Unrecognized method id" );
}不妨详细看看标准Hough变换的实现代码,
/* 这段注释解释了函数各个参数的作用
Here image is an input raster;
step is it's step; size characterizes it's ROI;
rho and theta are discretization steps (in pixels and radians correspondingly).
threshold is the minimum number of pixels in the feature for it
to be a candidate for line. lines is the output
array of (rho, theta) pairs. linesMax is the buffer size (number of pairs).
Functions return the actual number of found lines.
*/
static void
icvHoughLinesStandard( const CvMat* img, float rho, float theta,
int threshold, CvSeq *lines, int linesMax )
{
cv::AutoBuffer _accum, _sort_buf; // _accum:计数用数组,_sort_buf,排序用数组
cv::AutoBuffer _tabSin, _tabCos; // 提前计算sin与cos值,避免重复计算带来的计算性能下降
const uchar* image;
int step, width, height;
int numangle, numrho;
int total = 0;
float ang;
int r, n;
int i, j;
float irho = 1 / rho; // rho指像素精度,常取1,因此irho常为1
double scale;
CV_Assert( CV_IS_MAT(img) && CV_MAT_TYPE(img->type) == CV_8UC1 );
image = img->data.ptr;
step = img->step;
width = img->cols;
height = img->rows;
numangle = cvRound(CV_PI / theta); // 根据th精度计算th维度的长度
numrho = cvRound(((width + height) * 2 + 1) / rho); // 根据r精度计算r维度的长度
_accum.allocate((numangle+2) * (numrho+2));
_sort_buf.allocate(numangle * numrho);
_tabSin.allocate(numangle);
_tabCos.allocate(numangle);
int *accum = _accum, *sort_buf = _sort_buf;
float *tabSin = _tabSin, *tabCos = _tabCos;
memset( accum, 0, sizeof(accum[0]) * (numangle+2) * (numrho+2) );
for( ang = 0, n = 0; n < numangle; ang += theta, n++ ) // 计算三角函数表,避免重复计算
{
tabSin[n] = (float)(sin(ang) * irho);
tabCos[n] = (float)(cos(ang) * irho);
}
// stage 1. fill accumulator
for( i = 0; i < height; i++ )
for( j = 0; j < width; j++ )
{
if( image[i * step + j] != 0 )
for( n = 0; n < numangle; n++ )
{
r = cvRound( j * tabCos[n] + i * tabSin[n] ); // Hough极坐标变换式
r += (numrho - 1) / 2;
accum[(n+1) * (numrho+2) + r+1]++; // 计数器统计
}
}
// stage 2. find local maximums
for( r = 0; r < numrho; r++ )
for( n = 0; n < numangle; n++ )
{
int base = (n+1) * (numrho+2) + r+1;
if( accum[base] > threshold && // 大于阈值,且是局部极大值
accum[base] > accum[base - 1] && accum[base] >= accum[base + 1] &&
accum[base] > accum[base - numrho - 2] && accum[base] >= accum[base + numrho + 2] )
sort_buf[total++] = base;
}
// stage 3. sort the detected lines by accumulator value
icvHoughSortDescent32s( sort_buf, total, accum );
// stage 4. store the first min(total,linesMax) lines to the output buffer
linesMax = MIN(linesMax, total); // linesMax是输入参数,表示最多输出多少个直线参数
scale = 1./(numrho+2);
for( i = 0; i < linesMax; i++ )
{
CvLinePolar line; // 输出结构,就是(r,theta)
int idx = sort_buf[i];
int n = cvFloor(idx*scale) - 1;
int r = idx - (n+1)*(numrho+2) - 1;
line.rho = (r - (numrho - 1)*0.5f) * rho;
line.angle = n * theta;
cvSeqPush( lines, &line ); // 确定的直线入队列输出
}
} Hough.cpp中对输出结构的定义为:
typedef struct CvLinePolar
{
float rho;
float angle;
} CvLinePolar;其它的Hough变换采用类似的方式逐层可以分析其源码,不妨自己试试?