Linux 多线程编程—线程池 实现
Linux 多线程编程—线程池 实现
1. 线程池介绍
- 池是一组资源的集合,这组资源在服务器启动之初就完全被创建并初始化,这称为静态资源分配。当服务器进入正式运行阶段,即开始处理客户请求的时候,如果它需要相关的资源,就可以直接从池中获取,无需动态分配。很显然,直接从池中取得所需资源比动态分配资源的速度要快得多,因为分配系统资源的系统调用都是很耗时的。当服务器处理完一个客户连接后,可以把相关的资源放回池中,无需执行系统调用来释放资源。
- 程序中需要频繁的进行内存申请释放,进程、线程创建销毁等操作时,通常会使用内存池、进程池、线程池技术来提升程序的性能。
- 线程池流程如下:先启动若干数量的线程,并让这些线程都处于睡眠状态,当需要一个开辟一个线程去做具体的工作时,就会唤醒线程池中的某一个睡眠线程,让它去做具体工作,当工作完成后,线程又处于睡眠状态,而不是将线程销毁。
- 线程池优点:
1)需要大量的线程来完成任务,且完成任务的时间比较短。线程池的好处是避免了繁琐的创建和结束线程的时间,有效的利用了CPU资源。 比如WEB服务器完成网页请求这样的任务,使用线程池技术是非常合适的。因为单个任务小,而任务数量巨大>但对于长时间的任务,比如一个Telnet连接请求,线程池的优点就不明显了。因为Telnet会话时间比线程的创建时间大多了。
2)对性能要求苛刻的应用,比如要求服务器迅速响应客户请求。
3)接受突发性的大量请求,但不至于使服务器因此产生大量线程的应用。
2. 线程池模型
2.1 线程池常见三种模型:
- 任务队列控制的线程池模型
- 工作线程控制的线程池模型
- 主控线程控制的线程池模型
2.2 任务队列控制的线程池模型
- 通过任务队列来对线程池进行并发调度,如下图所示.
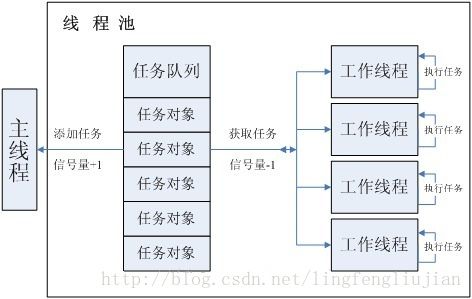
- 线程池是由预创建的一个任务队列和一组工作线程组成,其中任务队列中存放工作对象.线程池启动后,工作线程将采用轮询的方式从任务队列中获取任务对象,任务队列包含一个信号量(当工作队列中有任务时,该信号量有信号),所有工作线程等待该信号量,从而控制(通知)工作线程的执行状态。由于初始化时任务队列中不存在任务对象,这时的信号量为0,所有的工作线程都处于阻塞状态.主控线程将任务对象放入任务队列中(通常用链表或队列来实现),并将信号量加1,这样信号量就会唤醒一个阻塞中的工作线程(操作系统层面决定唤醒哪个阻塞的工作线程).工作线程唤醒后从任务队列中获取一个任务对象并执行该任务,执行完后,工作线程将再次访问信号量,如果信号信号量大于0,那么工作线程将继续从任务队列中获取任务对象并执行,直到信号量等于0,这时的工作线程将再次被阻塞.
- 任务队列控制的线程模型主要是通过任务队列上的信号来控制线程池中的线程调度.
3. 线程池数据结构设计
- 任务
/* Job */
typedef struct job{
struct job* prev; /* pointer to previous job 下一个任务 */
void (*function)(void* arg); /* function pointer 任务函数接口 */
void* arg; /* function's argument 函数参数 */
} job;- 信号量(用于任务队列)
/* Binary semaphore */
//用互斥锁和条件变量实现二元信号量机制。
typedef struct bsem {
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁
pthread_cond_t cond; //条件变量
int v; //信号量的值
} bsem;- 任务队列
/* Job queue */
typedef struct jobqueue{
//该互斥锁实现外部调用对工作(任务)队列的互斥读写操作,访问任务队列前,先要获得该互斥锁。
pthread_mutex_t rwmutex; /* used for queue r/w access */
job *front; //队首 /* pointer to front of queue */
job *rear; //队尾 /* pointer to rear of queue */
bsem *has_jobs; //指示任务队列是否为空的信号 /* flag as binary semaphore */
int len; /* number of jobs in queue */
} jobqueue;- 工作线程
/* Thread */
typedef struct thread{
int id; /* friendly id 人为赋予的线程标识 */
pthread_t pthread; /* pointer to actual thread 线程文件描述符 */
struct thpool_* thpool_p; /* access to thpool 所对应的线程池 */
} thread;- 线程池接口
/* Threadpool */
typedef struct thpool_{
thread** threads; /* pointer to threads 该线程池拥有的工作线程 */
volatile int num_threads_alive; /* threads currently 当前启动的线程总数*/
volatile int num_threads_working; /* threads currently working (正在执行的线程)*/
pthread_mutex_t thcount_lock; /* used for thread count etc 对线程池的互斥访问*/
//当num_threads_working为0时,当前所有线程均为空闲状态;条件变量threads_all_idle触发,
//发送信号给thpool_wait()*/
pthread_cond_t threads_all_idle; /* signal to thpool_wait */
jobqueue jobqueue; /* job queue 任务队列 */
} thpool_;
>alive(当前启动的线程数目)=阻塞(睡眠)线程 + 正在执行的(working)线程
- 线程状态控制变量(全局变量)
//控制所有线程是否终止,结束运行。 0,终止所有正在运行的线程;1,使能所有线程能够正常运行。
//初始化情况下为1
static volatile int threads_keepalive;
//控制所有线程是否暂停运行(而不是挂起)。0,不暂停;1,暂停。
//初始化情况下为0
static volatile int threads_on_hold; (1) threads_keepalive:
thpool_destro()[销毁线程池]将threads_keepalive置为0,使得工作线程退出死循环。
(2) threads_on_hold:
调用thpool_pause()【暂停所有线程】,该函数内部对所有启动的线程,调用pthread_kill()函数,触发在thread_do( )[线程函数]中的SIGUSR1消息,消息处理函数为thread_hold( ),该函数将threads_on_hold=1,并且进入死循环,一直调用sleep()函数,不断地睡眠。从而使得所有工作线程thread_do( )被暂停。
4. 线程池架构流程
初始化线程池、任务队列和工作线程 ——> 向任务队列中提交任务 ——> 将等候在信号(任务队列上有任务)上的线程唤醒,唤醒的线程轮询地从该任务队列队取出第一个任务(取出的任务将从队首删除)给该线程执行 ——> 等待任务队列中所有任务执行完毕 ——> 关闭线程池。
4.1 初始化线程池 —— thpool_* thpool_init(int num_threads)
1.线程池状态位和控制位初始化
threads_on_hold = 0; //工作线程持续正常运行,不暂停。 threads_keepalive = 1; //工作线程函数体执行死循环,表明线程将一直运行,不会执行完就退出。 thpool_p->num_threads_alive = 0; //当前线程数目为0 thpool_p->num_threads_working = 0; //正在执行的线程数目为空 pthread_mutex_init(&(thpool_p->thcount_lock), NULL); pthread_cond_init(&thpool_p->threads_all_idle, NULL);2.任务队列初始化 —— int jobqueue_init(jobqueue* jobqueue_p)
//任务队列为空 jobqueue_p->len = 0; jobqueue_p->front = NULL; jobqueue_p->rear = NULL; pthread_mutex_init(&(jobqueue_p->rwmutex), NULL); //读写锁释放 bsem_init(jobqueue_p->has_jobs, 0); //无任务,信号量has_jobs的值为0,状态位无信号。3.初始化所有工作线程 —— int thread_init (thpool_* thpool_p,thread** thread_p, int id)
(*thread_p)->thpool_p = thpool_p; //指向对应线程池 (*thread_p)->id = id; //人为指定的线程标识编号(并非系统返回的线程id) //创建工作线程,线程函数为thread_do(),传入参数为(*thread_p) pthread_create(&(*thread_p)->pthread, NULL, (void *)thread_do, (*thread_p)); pthread_detach((*thread_p)->pthread);函数实现: thpool_* thpool_init(int num_threads)
struct thpool_* thpool_init(int num_threads){
if (num_threads < 0){
num_threads = 0;
}
/* Make new thread pool */
thpool_* thpool_p;
thpool_p = (struct thpool_*)malloc(sizeof(struct thpool_));
if (thpool_p == NULL){
err("thpool_init(): Could not allocate memory for thread pool\n");
return NULL;
}
threads_on_hold = 0;
threads_keepalive = 1;
thpool_p->num_threads_alive = 0;
thpool_p->num_threads_working = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&(thpool_p->thcount_lock), NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&thpool_p->threads_all_idle, NULL);
/* Initialise the job queue */
if (jobqueue_init(&thpool_p->jobqueue) == -1){
err("thpool_init(): Could not allocate memory for job queue\n");
free(thpool_p);
return NULL;
}
/* Make threads in pool */
thpool_p->threads = (struct thread**)malloc(num_threads * sizeof(struct thread *));
if (thpool_p->threads == NULL){
err("thpool_init(): Could not allocate memory for threads\n");
jobqueue_destroy(&thpool_p->jobqueue);
free(thpool_p);
return NULL;
}
/* Thread init */
int n;
for (n=0; nthreads[n], n);
#if THPOOL_DEBUG
printf("THPOOL_DEBUG: Created thread %d in pool \n", n);
#endif
}
/* Wait for threads to initialize */
while (thpool_p->num_threads_alive != num_threads) {}
return thpool_p;
} 4.2 向任务队列提交任务 —— thpool_add_work(thpool_* thpool_p, void (func_job)(void), void* arg)
—提交任务后,has_jobs信号量发出信号,唤醒其中一个阻塞的工作线程,取出队首任务并执行。
- 1.编写每个任务要执行的函数体func_job
void func_job(void* arg)
{
ARG* arg_ptr = (ARG*)arg;//强制类型转换,获取所指定格式的参数。例如 int* arg_ptr=(int*) arg;
//通过arg_ptr读取所需参数,进行操作
do_something();
return;
}- 2.创建一个新任务结构newjob,将要执行的函数func和对应参数arg绑定到该job中。
job* newjob=(struct job*)malloc(sizeof(struct job));
/* add function and argument */
newjob->function=func_job;
newjob->arg=arg;- 3.将新建的任务插入到任务队列jobqueue的队尾
jobqueue_push(&thpool_p->jobqueue, newjob);–函数:void jobqueue_push(jobqueue* jobqueue_p, struct job* newjob)
static void jobqueue_push(jobqueue* jobqueue_p, struct job* newjob){
pthread_mutex_lock(&jobqueue_p->rwmutex);
newjob->prev = NULL;
switch(jobqueue_p->len){
case 0: /* if no jobs in queue */
jobqueue_p->front = newjob;
jobqueue_p->rear = newjob;
break;
default: /* if jobs in queue */
jobqueue_p->rear->prev = newjob;
jobqueue_p->rear = newjob;
}
jobqueue_p->len++;
bsem_post(jobqueue_p->has_jobs); //当前任务队列有任务,has_jobs信号量产生信号,通知并唤醒其中一个阻塞的工作线程,执行对应的任务函数体。
pthread_mutex_unlock(&jobqueue_p->rwmutex);
}4.3 工作线程 —— void* thread_do(struct thread* thread_p)
- 工作线程内部机制
- (1)注册暂停线程的信号SIGUSR1
/* Register signal handler */
struct sigaction act;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
act.sa_handler = thread_hold; //信号处理函数(暂停所有线程)
if (sigaction(SIGUSR1, &act, NULL) == -1) {
err("thread_do(): cannot handle SIGUSR1");
}/* Sets the calling thread on hold */
//信号处理函数(暂停所有线程)
static void thread_hold(int sig_id) {
(void)sig_id;
threads_on_hold = 1;
//不断进入睡眠,直到外部调用thpool_resume( ),将threads_on_hold置为0,
//退出while睡眠,恢复所有暂停的工作线程。
while (threads_on_hold){
sleep(1);
}
}- (2) 从任务队列中取出第一个job —— job* jobqueue_pull(jobqueue* jobqueue_p)
/* Get first job from queue(removes it from queue)
* Notice: Caller MUST hold a mutex
*/
static struct job* jobqueue_pull(jobqueue* jobqueue_p){
pthread_mutex_lock(&jobqueue_p->rwmutex);
job* job_p = jobqueue_p->front;
switch(jobqueue_p->len){
case 0: /* if no jobs in queue */
break;
case 1: /* if one job in queue */
jobqueue_p->front = NULL;
jobqueue_p->rear = NULL;
jobqueue_p->len = 0;
break;
default: /* if >1 jobs in queue */
jobqueue_p->front = job_p->prev;
jobqueue_p->len--;
/* more than one job in queue -> post it */
bsem_post(jobqueue_p->has_jobs);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&jobqueue_p->rwmutex);
return job_p;
}若从任务队列中取走一个job后,队列不为空,表明还有需要处理的任务;则bsem_post(has_jobs),has_jobs有信号,唤醒等待该信号量的某个阻塞的工作线程thread_do( ),执行任务。
- 函数实现:
/* What each thread is doing
*
* In principle this is an endless loop. The only time this loop gets interuppted is once
* thpool_destroy() is invoked or the program exits.
*
* @param thread thread that will run this function
* @return nothing
*/
static void* thread_do(struct thread* thread_p){
/* Set thread name for profiling and debuging */
char thread_name[128] = {0};
sprintf(thread_name, "thread-pool-%d", thread_p->id);
#if defined(__linux__)
/* Use prctl instead to prevent using _GNU_SOURCE flag and implicit declaration */
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, thread_name);
#elif defined(__APPLE__) && defined(__MACH__)
pthread_setname_np(thread_name);
#else
err("thread_do(): pthread_setname_np is not supported on this system");
#endif
/* Assure all threads have been created before starting serving */
thpool_* thpool_p = thread_p->thpool_p;
/* Register signal handler */
struct sigaction act;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
act.sa_handler = thread_hold;
if (sigaction(SIGUSR1, &act, NULL) == -1) {
err("thread_do(): cannot handle SIGUSR1");
}
/* Mark thread as alive (initialized) */
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
thpool_p->num_threads_alive += 1;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
//线程一直死循环运行,有任务就执行任务,无任务就处于阻塞状态(直到有新任务唤醒);直到调用thpool_destroy(),销毁线程池,退出循环。
while(threads_keepalive){
//一直阻塞,直到工作任务队列中有需要执行的任务。
bsem_wait(thpool_p->jobqueue.has_jobs);
if (threads_keepalive){
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
thpool_p->num_threads_working++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
/* Read job from queue and execute it */
void (*func_buff)(void*);
void* arg_buff;
job* job_p = jobqueue_pull(&thpool_p->jobqueue);
if (job_p) {
func_buff = job_p->function;
arg_buff = job_p->arg;
func_buff(arg_buff);
//afer the job is executed, we should remove the resource it owned.
free(job_p);
}
//--afer one job is executed, the total working trheads num decrease 1
//when num_threads_working=0,triger a sigal that indicates that all threads are idle.
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
thpool_p->num_threads_working--;
if (!thpool_p->num_threads_working) {
pthread_cond_signal(&thpool_p->threads_all_idle);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
}
}
//当调用thpool_destroy()时,threads_keepalive=0,退出该线程,故线程总数减1
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
thpool_p->num_threads_alive --;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
return NULL;
}4.4 暂停所有工作线程 —— void thpool_pause(threadpool)
/**
* @brief Pauses all threads immediately
* The threads will be paused no matter if they are idle or working.
*
* The threads return to their previous states once thpool_resume is called.
* While the thread is being paused, new work can be added.
* @param threadpool the threadpool where the threads should be paused
* @return nothing
*/
void thpool_pause(thpool_* thpool_p) {
int n;
for (n=0; n < thpool_p->num_threads_alive; n++){
pthread_kill(thpool_p->threads[n]->pthread, SIGUSR1);
}
}- 实例
void work1(void *){
sleep(1);
puts("Work1");
}
void work2(void *){
sleep(1);
puts("Work2");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int num_threads = 4;
threadpool thpool = thpool_init(num_threads);
for(int ii=0;ii<13;ii++){
thpool_add_work(thpool,work1, NULL);
}
sleep(1);
// Since pool is paused, threads should not start before main's sleep
thpool_pause(thpool);
for(int ii=0;ii<13;ii++){
thpool_add_work(thpool,work2, NULL);
}
sleep(1);
// Now we will start threads in no-parallel with main
thpool_resume(thpool);
thpool_wait(thpool);
thpool_destroy(thpool); // Wait for work to finish
return 0;
}4.5 恢复运行所有暂停的工作线程 —— void thpool_resume(thpool_* thpool_p)
/**
* @brief Unpauses all threads if they are paused
*
* @example
* ..
* thpool_pause(thpool);
* sleep(10); // Delay execution 10 seconds
* thpool_resume(thpool);
* ..
*
* @param threadpool the threadpool where the threads should be unpaused
* @return nothing
*/
void thpool_resume(thpool_* thpool_p) {
// resuming a single threadpool hasn't been
// implemented yet, meanwhile this supresses(阻止) the warnings
(void)thpool_p;
threads_on_hold = 0;
}4.6 等待任务队列中的所有任务全部执行完成 —— void thpool_wait(threadpool)
/**
* @brief Wait for all queued jobs to finish
*
* Will wait for all jobs - both queued and currently running to finish.
* Once the queue is empty and all work has completed, the calling thread
* (probably the main program) will continue.
*
* Smart polling is used in wait. The polling is initially 0 - meaning that
* there is virtually no polling at all. If after 1 seconds the threads
* haven't finished, the polling interval starts growing exponentially
* untill it reaches max_secs seconds. Then it jumps down to a maximum polling
* interval assuming that heavy processing is being used in the threadpool.
*
* @example
*
* ..
* threadpool thpool = thpool_init(4);
* ..
* // Add a bunch of work
* ..
* thpool_wait(thpool);
* puts("All added work has finished");
* ..
*
* @param threadpool the threadpool to wait for
* @return nothing
*/
void thpool_wait(thpool_* thpool_p){
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
//--等待(死循环),直到任务队列为空且当前正在执行的线程数目为0时,退出循环。
while (thpool_p->jobqueue.len || thpool_p->num_threads_working) {
pthread_cond_wait(&thpool_p->threads_all_idle, &thpool_p->thcount_lock);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
}4.7 销毁线程池
/**
* @brief Destroy the threadpool
*
* This will wait for the currently active threads to finish and then 'kill'
* the whole threadpool to free up memory.
*
* @example
* int main() {
* threadpool thpool1 = thpool_init(2);
* threadpool thpool2 = thpool_init(2);
* ..
* thpool_destroy(thpool1);
* ..
* return 0;
* }
*
* @param threadpool the threadpool to destroy
* @return nothing
*/
void thpool_destroy(thpool_* thpool_p){
/* No need to destory if it's NULL */
if (thpool_p == NULL) return ;
volatile int threads_total = thpool_p->num_threads_alive;
/* End each thread 's infinite loop */
//(1) 终止工作线程thread_do( )中的死循环
threads_keepalive = 0;
/* Give one second to kill idle threads */
//规定时间内,Kill所有空闲的工作线程(无任务)
double TIMEOUT = 1.0;
time_t start, end;
double tpassed = 0.0;
time (&start);
while (tpassed < TIMEOUT && thpool_p->num_threads_alive){
//让阻塞在has_jobs信号量上的工作线程继续执行,唤醒。
//唤醒后若该线程无任务可执行,为空闲线程,则直接退出while(threads_keepalive)
//的死循环,整个线程返回。
bsem_post_all(thpool_p->jobqueue.has_jobs);
time (&end);
tpassed = difftime(end,start);
}
/* Poll remaining threads */
//让阻塞在has_jobs信号量上的工作线程继续执行,唤醒。
//唤醒工作线程执行完任务,一直等待直到所有的任务全部完成。
while (thpool_p->num_threads_alive){
bsem_post_all(thpool_p->jobqueue.has_jobs);
sleep(1);
}
/* Job queue cleanup */
jobqueue_destroy(&thpool_p->jobqueue);
/* Deallocs */
int n;
for (n=0; n < threads_total; n++){
thread_destroy(thpool_p->threads[n]);
}
free(thpool_p->threads);
free(thpool_p);
}5. Test实例
- 并行实现累加运算。
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int sum=0;
int dat=0;
void increment(void *) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
dat++;
sum+=dat;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int num_jobs = 100;
int num_threads = 4;
threadpool thpool = thpool_init(num_threads);
int n;
for (n=0; nfor(int ii=0;ii"%d+",ii);
printf("%d=",dat);
printf("%d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
//输出结果:
0+1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10+11+12+13+14+15+16+17+18+19+20+21+22+23+24+25+26+27+28+29+30+31+32+33+34+35+36+37+38+39+40+41+42+43+44+45+46+47+48+49+50+51+52+53+54+55+56+57+58+59+60+61+62+63+64+65+66+67+68+69+70+71+72+73+74+75+76+77+78+79+80+81+82+83+84+85+86+87+88+89+90+91+92+93+94+95+96+97+98+99+100=5050
- 模拟多个卖票窗口出售车票
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int tickets=50;
void sale_tickets_job(void *arg) {
int id = *((int*)arg);
while(true){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(tickets>0){
printf("job window[%d] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: %d\n",id,--tickets);
}
else
break;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
printf("job window[%d] finished\n",id);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int num_jobs = 4;
int num_threads = 4;
threadpool thpool = thpool_init(num_threads);
thpool_pause(thpool);
int* work_id=new int[num_jobs];
for (int n=0; n1;
thpool_add_work(thpool, sale_tickets_job, (void*)&work_id[n]);
}
sleep(1);
printf("%d salling windows sale %d tickets>>>\n\n",num_jobs,tickets);
thpool_resume(thpool);
sleep(1);
thpool_wait(thpool);
thpool_destroy(thpool);
delete work_id;
printf("\nall tickets are saled out!\n");
return 0;
}
//输出结果:
4 salling windows sale 50 tickets>>>
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 49
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 48
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 47
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 46
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 45
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 44
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 43
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 42
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 41
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 40
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 39
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 38
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 37
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 36
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 35
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 34
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 33
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 32
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 31
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 30
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 29
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 28
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 27
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 26
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 25
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 24
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 23
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 22
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 21
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 20
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 19
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 18
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 17
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 16
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 15
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 14
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 13
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 12
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 11
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 10
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 9
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 8
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 7
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 6
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 5
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 4
job window[2] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 3
job window[3] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 2
job window[4] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 1
job window[1] sell one ticket,remain tickets num: 0
job window[2] finished
job window[1] finished
job window[4] finished
job window[3] finished
all tickets are saled out! 6. 参考文献【其他线程池实现方式】
Linux的多任务编程-线程池
高效线程池之无锁化实现(Linux C)
7. 开源代码下载
声明:
本文代码源自gitub上的开源代码,详见:C-Thread-Pool
本文着重对代码进行解读,加深对线程池原理和实现流程的理解。thpool.h
/**********************************
* @author Johan Hanssen Seferidis
* License: MIT
*
**********************************/
#ifndef _THPOOL_
#define _THPOOL_
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* =================================== API ======================================= */
typedef struct thpool_* threadpool;
/**
* @brief Initialize threadpool
*
* Initializes a threadpool. This function will not return untill all
* threads have initialized successfully.
*
* @example
*
* ..
* threadpool thpool; //First we declare a threadpool
* thpool = thpool_init(4); //then we initialize it to 4 threads
* ..
*
* @param num_threads number of threads to be created in the threadpool
* @return threadpool created threadpool on success,
* NULL on error
*/
threadpool thpool_init(int num_threads);
/**
* @brief Add work to the job queue
*
* Takes an action and its argument and adds it to the threadpool's job queue.
* If you want to add to work a function with more than one arguments then
* a way to implement this is by passing a pointer to a structure.
*
* NOTICE: You have to cast both the function and argument to not get warnings.
*
* @example
*
* void print_num(int num){
* printf("%d\n", num);
* }
*
* int main() {
* ..
* int a = 10;
* thpool_add_work(thpool, (void*)print_num, (void*)a);
* ..
* }
*
* @param threadpool threadpool to which the work will be added
* @param function_p pointer to function to add as work
* @param arg_p pointer to an argument
* @return 0 on successs, -1 otherwise.
*/
int thpool_add_work(threadpool, void (*function_p)(void*), void* arg_p);
/**
* @brief Wait for all queued jobs to finish
*
* Will wait for all jobs - both queued and currently running to finish.
* Once the queue is empty and all work has completed, the calling thread
* (probably the main program) will continue.
*
* Smart polling is used in wait. The polling is initially 0 - meaning that
* there is virtually no polling at all. If after 1 seconds the threads
* haven't finished, the polling interval starts growing exponentially
* untill it reaches max_secs seconds. Then it jumps down to a maximum polling
* interval assuming that heavy processing is being used in the threadpool.
*
* @example
*
* ..
* threadpool thpool = thpool_init(4);
* ..
* // Add a bunch of work
* ..
* thpool_wait(thpool);
* puts("All added work has finished");
* ..
*
* @param threadpool the threadpool to wait for
* @return nothing
*/
void thpool_wait(threadpool);
/**
* @brief Pauses all threads immediately
*
* The threads will be paused no matter if they are idle or working.
* The threads return to their previous states once thpool_resume
* is called.
*
* While the thread is being paused, new work can be added.
*
* @example
*
* threadpool thpool = thpool_init(4);
* thpool_pause(thpool);
* ..
* // Add a bunch of work
* ..
* thpool_resume(thpool); // Let the threads start their magic
*
* @param threadpool the threadpool where the threads should be paused
* @return nothing
*/
void thpool_pause(threadpool);
/**
* @brief Unpauses all threads if they are paused
*
* @example
* ..
* thpool_pause(thpool);
* sleep(10); // Delay execution 10 seconds
* thpool_resume(thpool);
* ..
*
* @param threadpool the threadpool where the threads should be unpaused
* @return nothing
*/
void thpool_resume(threadpool);
/**
* @brief Destroy the threadpool
*
* This will wait for the currently active threads to finish and then 'kill'
* the whole threadpool to free up memory.
*
* @example
* int main() {
* threadpool thpool1 = thpool_init(2);
* threadpool thpool2 = thpool_init(2);
* ..
* thpool_destroy(thpool1);
* ..
* return 0;
* }
*
* @param threadpool the threadpool to destroy
* @return nothing
*/
void thpool_destroy(threadpool);
/**
* @brief Show currently working threads
*
* Working threads are the threads that are performing work (not idle).
*
* @example
* int main() {
* threadpool thpool1 = thpool_init(2);
* threadpool thpool2 = thpool_init(2);
* ..
* printf("Working threads: %d\n", thpool_num_threads_working(thpool1));
* ..
* return 0;
* }
*
* @param threadpool the threadpool of interest
* @return integer number of threads working
*/
int thpool_num_threads_working(threadpool);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif- thpool.c
/* ********************************
* Author: Johan Hanssen Seferidis
* License: MIT
* Description: Library providing a threading pool where you can add
* work. For usage, check the thpool.h file or README.md
*
*//** @file thpool.h *//*
*
********************************/
#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 200809L
#include threads[n], n);
#if THPOOL_DEBUG
printf("THPOOL_DEBUG: Created thread %d in pool \n", n);
#endif
}
/* Wait for threads to initialize */
while (thpool_p->num_threads_alive != num_threads) {}
return thpool_p;
}
/* Add work to the thread pool */
int thpool_add_work(thpool_* thpool_p, void (*function_p)(void*), void* arg_p){
job* newjob;
newjob=(struct job*)malloc(sizeof(struct job));
if (newjob==NULL){
err("thpool_add_work(): Could not allocate memory for new job\n");
return -1;
}
/* add function and argument */
newjob->function=function_p;
newjob->arg=arg_p;
/* add job to queue */
jobqueue_push(&thpool_p->jobqueue, newjob);
return 0;
}
/* Wait until all jobs have finished */
void thpool_wait(thpool_* thpool_p){
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
while (thpool_p->jobqueue.len || thpool_p->num_threads_working) {
pthread_cond_wait(&thpool_p->threads_all_idle, &thpool_p->thcount_lock);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
}
/* Destroy the threadpool */
void thpool_destroy(thpool_* thpool_p){
/* No need to destory if it's NULL */
if (thpool_p == NULL) return ;
volatile int threads_total = thpool_p->num_threads_alive;
/* End each thread 's infinite loop */
threads_keepalive = 0;
/* Give one second to kill idle threads */
double TIMEOUT = 1.0;
time_t start, end;
double tpassed = 0.0;
time (&start);
while (tpassed < TIMEOUT && thpool_p->num_threads_alive){
bsem_post_all(thpool_p->jobqueue.has_jobs);
time (&end);
tpassed = difftime(end,start);
}
/* Poll remaining threads */
while (thpool_p->num_threads_alive){
bsem_post_all(thpool_p->jobqueue.has_jobs);
sleep(1);
}
/* Job queue cleanup */
jobqueue_destroy(&thpool_p->jobqueue);
/* Deallocs */
int n;
for (n=0; n < threads_total; n++){
thread_destroy(thpool_p->threads[n]);
}
free(thpool_p->threads);
free(thpool_p);
}
/* Pause all threads in threadpool */
void thpool_pause(thpool_* thpool_p) {
int n;
for (n=0; n < thpool_p->num_threads_alive; n++){
pthread_kill(thpool_p->threads[n]->pthread, SIGUSR1);
}
}
/* Resume all threads in threadpool */
void thpool_resume(thpool_* thpool_p) {
// resuming a single threadpool hasn't been
// implemented yet, meanwhile this supresses
// the warnings
(void)thpool_p;
threads_on_hold = 0;
}
int thpool_num_threads_working(thpool_* thpool_p){
return thpool_p->num_threads_working;
}
/* ============================ THREAD ============================== */
/* Initialize a thread in the thread pool
*
* @param thread address to the pointer of the thread to be created
* @param id id to be given to the thread
* @return 0 on success, -1 otherwise.
*/
static int thread_init (thpool_* thpool_p, struct thread** thread_p, int id){
*thread_p = (struct thread*)malloc(sizeof(struct thread));
if (thread_p == NULL){
err("thread_init(): Could not allocate memory for thread\n");
return -1;
}
(*thread_p)->thpool_p = thpool_p;
(*thread_p)->id = id;
pthread_create(&(*thread_p)->pthread, NULL, (void *)thread_do, (*thread_p));
pthread_detach((*thread_p)->pthread);
return 0;
}
/* Sets the calling thread on hold */
static void thread_hold(int sig_id) {
(void)sig_id;
threads_on_hold = 1;
while (threads_on_hold){
sleep(1);
}
}
/* What each thread is doing
*
* In principle this is an endless loop. The only time this loop gets interuppted is once
* thpool_destroy() is invoked or the program exits.
*
* @param thread thread that will run this function
* @return nothing
*/
static void* thread_do(struct thread* thread_p){
/* Set thread name for profiling and debuging */
char thread_name[128] = {0};
sprintf(thread_name, "thread-pool-%d", thread_p->id);
#if defined(__linux__)
/* Use prctl instead to prevent using _GNU_SOURCE flag and implicit declaration */
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, thread_name);
#elif defined(__APPLE__) && defined(__MACH__)
pthread_setname_np(thread_name);
#else
err("thread_do(): pthread_setname_np is not supported on this system");
#endif
/* Assure all threads have been created before starting serving */
thpool_* thpool_p = thread_p->thpool_p;
/* Register signal handler */
struct sigaction act;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
act.sa_handler = thread_hold;
if (sigaction(SIGUSR1, &act, NULL) == -1) {
err("thread_do(): cannot handle SIGUSR1");
}
/* Mark thread as alive (initialized) */
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
thpool_p->num_threads_alive += 1;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
//线程一直死循环运行,有任务就执行任务,无任务就处于阻塞状态(直到有新任务唤醒);直到调用thpool_destroy(),销毁线程池,退出循环。
while(threads_keepalive){
//一直阻塞,直到工作任务队列中有需要执行的任务。
bsem_wait(thpool_p->jobqueue.has_jobs);
if (threads_keepalive){
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
thpool_p->num_threads_working++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
/* Read job from queue and execute it */
void (*func_buff)(void*);
void* arg_buff;
job* job_p = jobqueue_pull(&thpool_p->jobqueue);
if (job_p) {
func_buff = job_p->function;
arg_buff = job_p->arg;
func_buff(arg_buff);
//afer the job is executed, we should remove the resource it owned.
free(job_p);
}
//--afer one job is executed, the total working trheads num decrease 1
//when num_threads_working=0,triger a sigal that indicates that all threads are idle.
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
thpool_p->num_threads_working--;
if (!thpool_p->num_threads_working) {
pthread_cond_signal(&thpool_p->threads_all_idle);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
}
}
//当调用thpool_destroy()时,threads_keepalive=0,退出该线程,故线程总数减1
pthread_mutex_lock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
thpool_p->num_threads_alive --;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&thpool_p->thcount_lock);
return NULL;
}
/* Frees a thread */
static void thread_destroy (thread* thread_p){
free(thread_p);
}
/* ============================ JOB QUEUE =========================== */
/* Initialize queue */
static int jobqueue_init(jobqueue* jobqueue_p){
jobqueue_p->len = 0;
jobqueue_p->front = NULL;
jobqueue_p->rear = NULL;
jobqueue_p->has_jobs = (struct bsem*)malloc(sizeof(struct bsem));
if (jobqueue_p->has_jobs == NULL){
return -1;
}
pthread_mutex_init(&(jobqueue_p->rwmutex), NULL);
bsem_init(jobqueue_p->has_jobs, 0);
return 0;
}
/* Clear the queue */
static void jobqueue_clear(jobqueue* jobqueue_p){
while(jobqueue_p->len){
free(jobqueue_pull(jobqueue_p));
}
jobqueue_p->front = NULL;
jobqueue_p->rear = NULL;
bsem_reset(jobqueue_p->has_jobs);
jobqueue_p->len = 0;
}
/* Add (allocated) job to queue
*/
static void jobqueue_push(jobqueue* jobqueue_p, struct job* newjob){
pthread_mutex_lock(&jobqueue_p->rwmutex);
newjob->prev = NULL;
switch(jobqueue_p->len){
case 0: /* if no jobs in queue */
jobqueue_p->front = newjob;
jobqueue_p->rear = newjob;
break;
default: /* if jobs in queue */
jobqueue_p->rear->prev = newjob;
jobqueue_p->rear = newjob;
}
jobqueue_p->len++;
bsem_post(jobqueue_p->has_jobs);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&jobqueue_p->rwmutex);
}
/* Get first job from queue(removes it from queue)
<<<<<<< HEAD
*
* Notice: Caller MUST hold a mutex
=======
>>>>>>> da2c0fe45e43ce0937f272c8cd2704bdc0afb490
*/
static struct job* jobqueue_pull(jobqueue* jobqueue_p){
pthread_mutex_lock(&jobqueue_p->rwmutex);
job* job_p = jobqueue_p->front;
switch(jobqueue_p->len){
case 0: /* if no jobs in queue */
break;
case 1: /* if one job in queue */
jobqueue_p->front = NULL;
jobqueue_p->rear = NULL;
jobqueue_p->len = 0;
break;
default: /* if >1 jobs in queue */
jobqueue_p->front = job_p->prev;
jobqueue_p->len--;
/* more than one job in queue -> post it */
bsem_post(jobqueue_p->has_jobs);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&jobqueue_p->rwmutex);
return job_p;
}
/* Free all queue resources back to the system */
static void jobqueue_destroy(jobqueue* jobqueue_p){
jobqueue_clear(jobqueue_p);
free(jobqueue_p->has_jobs);
}
/* ======================== SYNCHRONISATION ========================= */
/* Init semaphore to 1 or 0 */
static void bsem_init(bsem *bsem_p, int value) {
if (value < 0 || value > 1) {
err("bsem_init(): Binary semaphore can take only values 1 or 0");
exit(1);
}
pthread_mutex_init(&(bsem_p->mutex), NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&(bsem_p->cond), NULL);
bsem_p->v = value;
}
/* Reset semaphore to 0 */
static void bsem_reset(bsem *bsem_p) {
bsem_init(bsem_p, 0);
}
/* Post to at least one thread */
//给条件变量发送信号-----------
static void bsem_post(bsem *bsem_p) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&bsem_p->mutex);
bsem_p->v = 1;
pthread_cond_signal(&bsem_p->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&bsem_p->mutex);
}
/* Post to all threads */
static void bsem_post_all(bsem *bsem_p) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&bsem_p->mutex);
bsem_p->v = 1;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&bsem_p->cond); //广播形式发送信号
pthread_mutex_unlock(&bsem_p->mutex);
}
/* Wait on semaphore until semaphore has value 0 */
static void bsem_wait(bsem* bsem_p) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&bsem_p->mutex);
while (bsem_p->v != 1) {
pthread_cond_wait(&bsem_p->cond, &bsem_p->mutex);
}
bsem_p->v = 0;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&bsem_p->mutex);
}