四则运算生成器
文章目录
- 1 任务描述
- 1.1 概述
- 1.2 基本要求
- 1.3 附加功能要求
- 2 项目地址
- 3 项目源代码
- 4 更新版本
- 4.1 源代码 2.0
- 4.2 源代码 3.0
- 4.3 源代码 4.0
- 4.4 代码 5.0
- 5 演示图片
- 6 个人软件过程 PSP
- 6.1 代码1.0 PSP
- 6.1.1 已实现功能
- 6.1.2 未完成功能
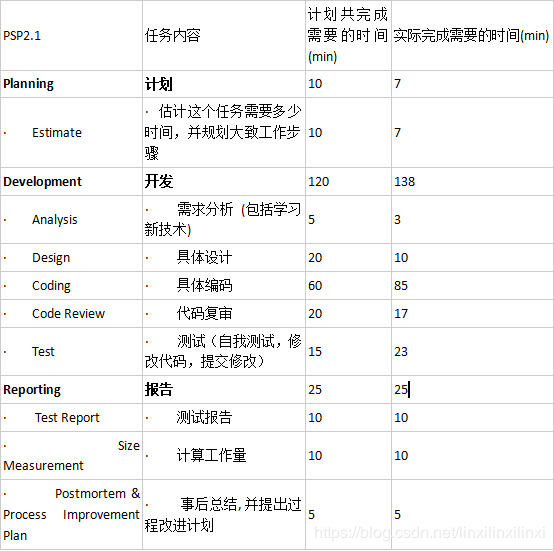
- 6.1.3 PSP表格
- 6.2 代码2.0 PSP
- 6.2.1
- 6.2.1 更新内容
- 6.2.2 PSP表格
- 6.3 代码3.0 PSP
- 6.3.1 更新内容
- 6.3.2 PSP表格
- 6.4 代码4.0 PSP
- 6.4.1 更新内容
- 6.4.2 PSP表格
- 6.5 代码5.0 PSP
- 6.5.1 更新内容
- 6.5.2 PSP表格
1 任务描述
1.1 概述
使用java或C/C++编程语言,独立完成一个3到5个运算符的四则运算练习的软件
1.2 基本要求
-
1 程序可接收一个输入参数n,然后随机产生n道加减乘除(分别使用符号±*÷来表示)练习题,每个数字在 0 和 100 之间,运算符在3个到5个之间。
-
2 每个练习题至少要包含2种运算符。同时,由于小学生没有分数与负数的概念,你所出的练习题在运算过程中不得出现负数与非整数,比如不能出 3÷5+2=2.6,2-5+10=7等算式。
-
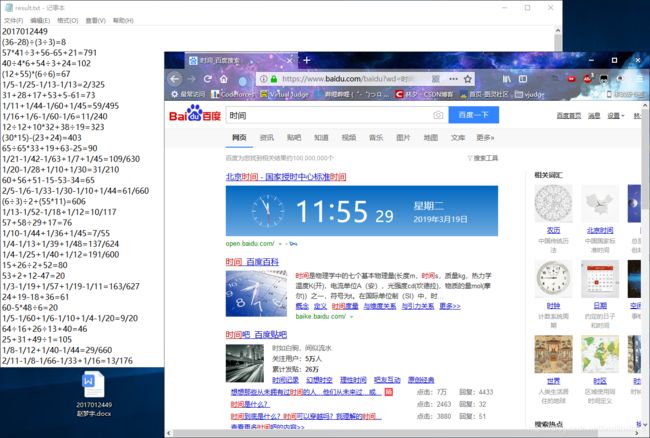
3 练习题生成好后,将你的学号与生成的n道练习题及其对应的正确答案输出到文件“result.txt”中,不要输出额外信息,文件目录与程序目录一致。
-
4 当程序接收的参数为4时,以下为一个输出文件示例。
2018010203 13+17-1=29 11*15-5=160 3+10+4-16=1 15÷5+3-2=4
1.3 附加功能要求
-
1 支持有括号的运算式,包括出题与求解正确答案。注意,算式中存在的括号数必须大于2对,且不得超过运算符的个数。
-
2 扩展程序功能支持真分数的出题与运算(只需要涵盖加减法即可),例如:1/6 + 1/8 + 2/3= 23/24。注意在实现本功能时,需支持运算时分数的自动化简,比如 1/2+1/6=2/3,而非4/6,且计算过程中与结果都须为真分数。
2 项目地址
个人博客
https://linxi99.gitee.io/
https://linxi99.gitee.io/20190319/Arithmetic-Device/
https://blog.csdn.net/linxilinxilinxi
https://blog.csdn.net/linxilinxilinxi/article/details/88548481
项目地址
https://gitee.com/linxi99/four_operational_generators
3 项目源代码
#include 4 更新版本
4.1 源代码 2.0
#include 4.2 源代码 3.0
#include 4.3 源代码 4.0
#include 4.4 代码 5.0
#include 5 演示图片
6 个人软件过程 PSP
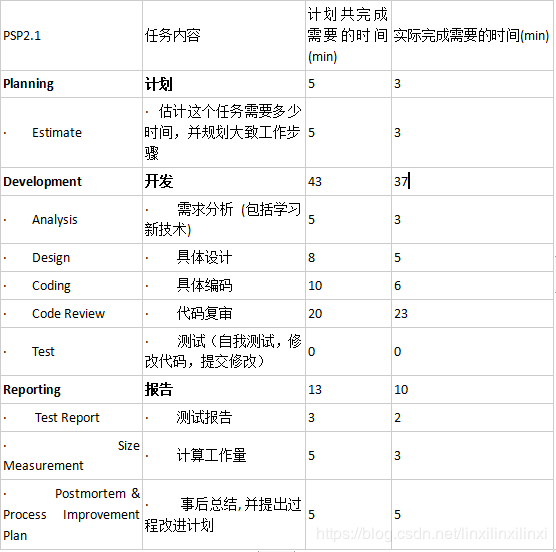
6.1 代码1.0 PSP
6.1.1 已实现功能
-
1 生成n道数字在 0~100 之间的算术题
-
2 运算过程中不出现分数与负数
-
3 运行 .exe 生成 result.txt
-
4 支持有括号的运算
6.1.2 未完成功能
- 1 支持真分数的出题与运算
6.1.3 PSP表格
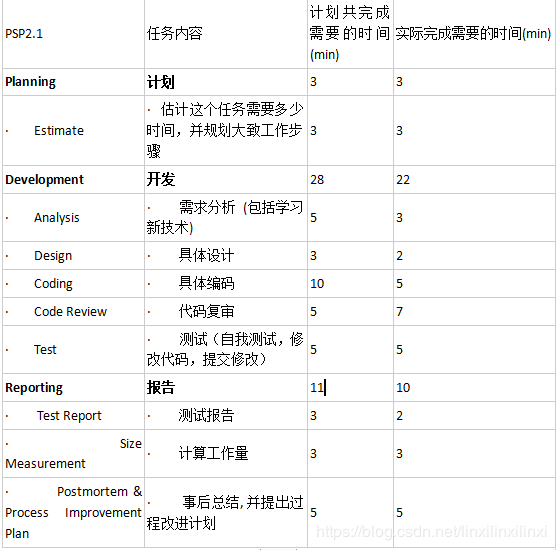
6.2 代码2.0 PSP
6.2.1
6.2.1 更新内容
-
重新复审了代码
-
优化了代码格式
-
分段加入了注释
-
修复了一些小BUG
6.2.2 PSP表格
6.3 代码3.0 PSP
6.3.1 更新内容
解决了被除数可能会大于100的问题
6.3.2 PSP表格
6.4 代码4.0 PSP
6.4.1 更新内容
成功生成真分数运算式
6.4.2 PSP表格
6.5 代码5.0 PSP
6.5.1 更新内容
-
封装了随机数生成函数
-
随机生成无括号运算式