MyLibco 协程网络库定时器的设计
时间戳类(基本摘自muduo)
//Timestamp.h
namespace Tattoo
{
class Timestamp
{
public:
Timestamp();
explicit Timestamp(int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch);
void swap(Timestamp &that)
{
std::swap(microSecondsSinceEpoch_, that.microSecondsSinceEpoch_);
}
std::string toString() const;
std::string toFormattedString() const;
//微妙大于0就是 valid 的
bool valid() const { return microSecondsSinceEpoch_ > 0; }
int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch() const { return microSecondsSinceEpoch_; }
//微秒转化为秒
time_t secondsSinceEpoch() const
{
return static_cast<time_t>(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
}
//得到现在的时间
static Timestamp now();
//获取一个无效时间,即时间等于0
static Timestamp invalid();
//一百万,一微秒等于百万分之一秒
static const int kMicroSecondsPerSecond = 1000 * 1000;
private:
int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch_;
};
// 这里重载 < 号,在下文的multimap 中就会用到
inline bool operator<(Timestamp lhs, Timestamp rhs)
{
return lhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch() < rhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
}
inline bool operator==(Timestamp lhs, Timestamp rhs)
{
return lhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch() == rhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
}
////将返回两个事件时间差的秒数,注意单位!
inline double timeDifference(Timestamp high, Timestamp low)
{
int64_t diff = high.microSecondsSinceEpoch() - low.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
return static_cast<double>(diff) / Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
}
//把秒转化为微秒,构造一个对象,再把它们的时间加起来,构造一个无名临时对象返回
inline Timestamp addTime(Timestamp timestamp, double seconds)
{
int64_t delta = static_cast<int64_t>(seconds * Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
return Timestamp(timestamp.microSecondsSinceEpoch() + delta);
}
} // namespace Tattoo
//Timestamp.cpp
using namespace Tattoo;
Timestamp::Timestamp()
: microSecondsSinceEpoch_(0)
{
}
Timestamp::Timestamp(int64_t microseconds)
: microSecondsSinceEpoch_(microseconds)
{
}
std::string Timestamp::toString() const
{
char buf[32] = {0};
int64_t seconds = microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
int64_t microseconds = microSecondsSinceEpoch_ % kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
//PRId64跨平台打印64位整数,因为int64_t用来表示64位整数,在32位系统中是long long int,64位系统中是long int
//所以打印64位是%ld或%lld,可移植性较差,不如统一同PRID64来打印。
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, "%" PRId64 ".%06" PRId64 "", seconds, microseconds);
return buf;
}
//把它转换成一个格式化字符串
std::string Timestamp::toFormattedString() const
{
char buf[32] = {0};
time_t seconds = static_cast<time_t>(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
int microseconds = static_cast<int>(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ % kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
struct tm tm_time;
gmtime_r(&seconds, &tm_time);
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%4d%02d%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%06d",
tm_time.tm_year + 1900, tm_time.tm_mon + 1, tm_time.tm_mday,
tm_time.tm_hour, tm_time.tm_min, tm_time.tm_sec,
microseconds);
return buf;
}
Timestamp Timestamp::now()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL); //获得当前时间,第二个参数是一个时区,当前不需要返回时区,就填空指针
int64_t seconds = tv.tv_sec; //取出秒数
return Timestamp(seconds * kMicroSecondsPerSecond + tv.tv_usec);
}
Timestamp Timestamp::invalid()
{
return Timestamp();
}
定时器
在这里,我是直接让协程在一段时间之后唤醒即可(runAfter),至于需不需要 repeat ,这个我也在思考当中,以后了解到了再加吧!!学习也就是一点一点积累的过程啦!!!
//Timer.h
/*定时器类*/
class Timer
{
public:
Timer(Timestamp when);
Timestamp expiration() const { return expire_; }
void run() const;
Timestamp expire_; //任务的超时时间
Routine_t *timer_rou_;
};
//Timer.cpp
Timer::Timer(Timestamp when)
: timer_rou_(get_curr_routine()), //一个定时器对应一个协程
expire_(when)
{
}
void Timer::run() const
{
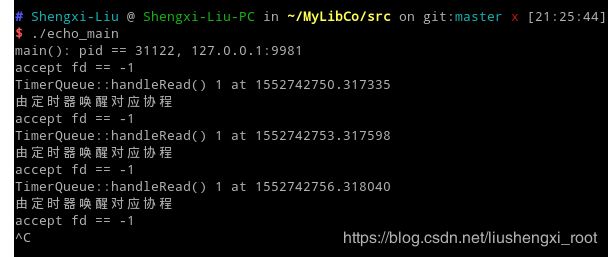
cout << "由定时器唤醒对应协程" << endl;
timer_rou_->Resume();
}
定时器容器
.h 文件
class TimeHeap
{
public:
TimeHeap(EventLoop *loop);
~TimeHeap();
Timer *addTimer(Timestamp when);
void delTimer(Timer *timer);
private:
typedef std::pair<Timestamp, Timer *> Entry;
typedef std::multimap<Timestamp, Timer *> TimerMap;
// 超时之后的可读回调
void handleRead();
std::vector<Entry> getExpired(Timestamp now);
/* 重置超时的定时器 */
void reset(const std::vector<Entry> &expired, Timestamp now);
bool insert(Timer *timer);
EventLoop *loop_;
const int timerfd_;
Channel timerfdChannel_;
TimerMap timers_;
};
.cpp 文件
namespace Tattoo
{
namespace detail
{
//创建 timerfd
int createTimerfd()
{
int timerfd = ::timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC,
TFD_NONBLOCK | TFD_CLOEXEC);
if (timerfd < 0)
{
std::cout << "Failed in timerfd_create" << std::endl;
}
return timerfd;
}
/* 计算超时时间与当前时间的时间差,并将参数转换为 api 接受的类型 */
struct timespec howMuchTimeFromNow(Timestamp when)
{
/* 微秒数 = 超时时刻微秒数 - 当前时刻微秒数 */
int64_t microseconds = when.microSecondsSinceEpoch() - Timestamp::now().microSecondsSinceEpoch();
if (microseconds < 100)
{
microseconds = 100;
}
struct timespec ts; // 转换成 struct timespec 结构返回
// tv_sec 秒
// tv_nsec 纳秒
ts.tv_sec = static_cast<time_t>(
microseconds / Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
ts.tv_nsec = static_cast<long>(
(microseconds % Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond) * 1000);
return ts;
}
/* 读timerfd,避免定时器事件一直触发 */
void readTimerfd(int timerfd, Timestamp now)
{
uint64_t howmany;
ssize_t n = ::read(timerfd, &howmany, sizeof(howmany));
std::cout << "TimerQueue::handleRead() " << howmany << " at " << now.toString() << std::endl;
if (n != sizeof howmany)
{
std::cout << "TimerQueue::handleRead() reads " << n << " bytes instead of 8" << std::endl;
}
}
/* 重置 timerfd 的超时时间 */
void resetTimerfd(int timerfd, Timestamp expiration)
{
struct itimerspec newValue;
struct itimerspec oldValue;
bzero(&newValue, sizeof newValue);
bzero(&oldValue, sizeof oldValue);
newValue.it_value = howMuchTimeFromNow(expiration);
//到这个时间后,会产生一个定时事件
int ret = ::timerfd_settime(timerfd, 0, &newValue, &oldValue);
if (ret)
{
std::cout << "timerfd_settime()" << std::endl;
}
}
} // namespace detail
} // namespace Tattoo
using namespace Tattoo;
using namespace Tattoo::detail;
TimeHeap::TimeHeap(EventLoop *loop)
: loop_(loop),
timerfd_(createTimerfd()),
timerfdChannel_(loop, timerfd_),
timers_()
{
// 设置自己独特的回调函数,并不是和普通的Channel 一样,直接唤醒了对应的协程
timerfdChannel_.setHandleCallback(
std::bind(&TimeHeap::handleRead, this));
timerfdChannel_.enableReading();
}
TimeHeap::~TimeHeap()
{
timerfdChannel_.disableAll();
::close(timerfd_);
for (auto it = timers_.begin();
it != timers_.end(); ++it)
{
delete it->second;
}
}
/* 添加一个定时器 ,返回定时器指针,会在 channel->addEpoll 函数中使用到,因为要删除对应的定时器*/
Timer *TimeHeap::addTimer(Timestamp when)
{
Timer *timer = new Timer(when);
////如果当前插入的定时器 比队列中的定时器都早 则返回真
bool earliestChanged = insert(timer);
//最早的超时时间改变了,就需要重置timerfd_的超时时间
if (earliestChanged)
{
//timerfd_ 重新设置超时时间,使得 timerfd 的定时事件始终是最小的
resetTimerfd(timerfd_, timer->expiration());
}
return timer;
}
/* 删除一个定时器 */
void TimeHeap::delTimer(Timer *timer)
{
auto it = timers_.find(timer->expire_);
if (it != timers_.end())
{
timers_.erase(it);
}
return;
}
//timerfd 可读 的回调
void TimeHeap::handleRead()
{
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());
//先读取
readTimerfd(timerfd_, now);
std::vector<Entry> expired = getExpired(now);
for (std::vector<Entry>::iterator it = expired.begin();
it != expired.end(); ++it)
{
it->second->run(); //run->Resume()
}
reset(expired, now); //这里主要是改变 timerfd 的定时最小值
}
//获取所有超时的定时器
std::vector<TimeHeap::Entry> TimeHeap::getExpired(Timestamp now)
{
std::vector<Entry> expired;
auto it = timers_.lower_bound(now);
assert(it == timers_.end() || now < it->first);
std::copy(timers_.begin(), it, back_inserter(expired));
timers_.erase(timers_.begin(), it);
return expired;
}
void TimeHeap::reset(const std::vector<Entry> &expired, Timestamp now)
{
Timestamp nextExpire;
for (std::vector<Entry>::const_iterator it = expired.begin();
it != expired.end(); ++it)
{
delete it->second;
}
if (!timers_.empty()) //timers_ 不为空
{
/*获取当前定时器集合中的最早定时器的时间戳,作为下次超时时间*/
nextExpire = timers_.begin()->second->expiration();
}
//如果取得的时间 >0就改变 timerfd 的定时
if (nextExpire.valid())
{
resetTimerfd(timerfd_, nextExpire);
}
}
bool TimeHeap::insert(Timer *timer)
{
bool earliestChanged = false;
Timestamp when = timer->expiration();
auto it = timers_.begin();
if (it == timers_.end() || when < it->first)
{
earliestChanged = true;
}
timers_.insert(std::make_pair(when, timer));
return earliestChanged;
}
OK,上面的就是具体的实现代码了,下面来说一下几个点:
1.如何添加定时器?
在我写的协程库中是这样实现的:
Channel::addEpoll()->loop_->runAfter(10)->timerHeap_->addTimer()
2.如何删除定时器?
loop_->cancel()->timerHeap_->delTimer()
3.如何将timerfd与Eventloop 统一起来?
首先来看一下eventloop:
.h
#include "Callbacks.h"
#include "Timestamp.h"
#include .cpp
#include 4.定时器的组织方式(和 muduo 差不多,他用的是set,我用的是 multimap)
muduo 定时器容器封装了 Timer.h 里面保存的是超时时间和回调函数, TimerQueue.h 使用set容器保存多个定时器, 然后在TimerQueue中使用timerfd_create创建一个timerfd句柄, 插入定时器A后先比较A的触发时间和TimerQueue的触发时间, 如果A的触发时间比其小就使用timerfd_settime重置TimerQueue的timerfd的触发时间, TimerQueue中的timerfd的触发时间永远与保存的定时器中触发时间最小的那个相同, 然后timerfd触发可读后, 遍历保存的多个定时器, 看看有没有同时到期的, 有执行回调函数
4.协程库中定时器的使用(与 libco 基本一样)
先行阅读:https://blog.csdn.net/liushengxi_root/article/details/88421955
主要函数(addEpoll):
void Channel::addEpoll()
{
//这里就设置的回调函数和 timerfd 设置的回调函数不一样哦
setHandleCallback(std::bind(&Channel::handleFun, this));
events_ |= kReadEvent;
events_ |= kWriteEvent;
update();
Timer *tmp = loop_->runAfter(10);
//退出当前协程
get_curr_routine()->Yield();
//删除加入的 epoll 信息和对应定时器
loop_->removeChannel(this);
loop_->cancel(tmp);
}
事件到来会唤醒对应的协程,时间超时时 也会唤醒对应的协程(不会让其一直阻塞下去)
主事件循环还是看上面的链接即可!!