Pytorch入门:数据的加载与处理
0. 写在前面
在深度学习的问题中处理数据都会占据比较大的时间,只有把数据处理好了才有可能对模型进行训练、测试等后续工作。
PyTorch提供了很多用于让数据加载变得更加方便的工具,接下来我们就来学习一下怎么样处理那些PyTorch没有提供直接接口的数据。
在学习这个之前,首先要保证电脑上已经安装了下面这两样东西:
- scikit-image:用于图像输入输出和转换
- pandas:用于更好的处理csv数据
这篇文章内容还是比较多的,但认真看完应该就可以掌握各种数据集的处理了。
1. 导入需要库
from __future__ import print_function, division
import os
import torch
import pandas as pd
from skimage import io, transform
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from torchvision import transforms, utils
# Ignore warnings
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
plt.ion() # interactive mode
2. 数据集介绍及下载
2.1 数据集介绍
接下来我们要处理的数据集是关于脸部姿势的,每张图片都会被注释成这样,每张脸上都会有68各不同的标记点:

2.2 数据集下载与展示
-
戳这里下载需要教程中用到的脸部数据集,跟数据集一起的还有一个注释文件
face_landmarks.csv。
直接打开如下图所示:
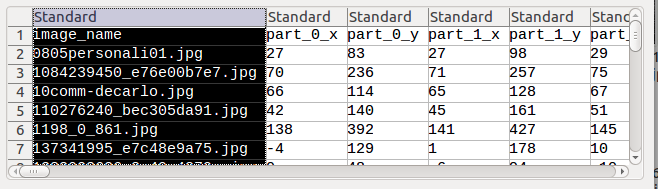
即每张图片都对应一个文件名和对应的N个脸部特征标记点。 -
在注释文件中的是N个坐标点,每个坐标点由两个横纵坐标组成。所以先用pandas工具把注释文件处理一下。
landmarks_frame = pd.read_csv('faces/face_landmarks.csv')
n = 65
img_name = landmarks_frame.iloc[n, 0]
landmarks = landmarks_frame.iloc[n, 1:].as_matrix()
landmarks = landmarks.astype('float').reshape(-1, 2)
print('Image name: {}'.format(img_name))
print('Landmarks shape: {}'.format(landmarks.shape))
print('First 4 Landmarks: {}'.format(landmarks[:4]))
3.将图像和对应的特征点标记出来展示。
def show_landmarks(image, landmarks):
"""Show image with landmarks"""
plt.imshow(image)
plt.scatter(landmarks[:, 0], landmarks[:, 1], s=10, marker='.', c='r')
plt.pause(0.001) # pause a bit so that plots are updated
plt.figure()
show_landmarks(io.imread(os.path.join('faces/', img_name)),
landmarks)
plt.show()
3. Dataset类介绍
3.1 原理介绍
torch.utils.data.Dataset是一个PyTorch用来表示数据集的抽象类。我们用这个类来处理自己的数据集的时候必须继承Dataset,然后重写下面的函数:
- __len__: 使得len(dataset)返回数据集的大小;
- __getitem__:使得支持dataset[i]能够返回第i个数据样本这样的下标操作。
3.2 创建脸部图像数据集
- 在类的
__init__函数中完成csv文件的读取工作; - 在类的
__getitem__函数中完成图片的读取工作。这样是为了减小内存开销,只要在需要用到的时候才将图片读入。 - 除此,数据集还会接收一个可以选择的参数
transform,用来对图像做一些改变,具体的会在下面进行介绍。 - 最终返回的样本数据是一个字典形式的,如下所示:
{‘image':image,'landmarks':landmarks}
那么现在我们就可以写出类的定义:
class FaceLandmarksDataset(Dataset):
"""Face Landmarks dataset."""
def __init__(self, csv_file, root_dir, transform=None):
"""
Args:
csv_file (string): Path to the csv file with annotations.
root_dir (string): Directory with all the images.
transform (callable, optional): Optional transform to be applied
on a sample.
"""
self.landmarks_frame = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
self.root_dir = root_dir
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.landmarks_frame)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img_name = os.path.join(self.root_dir,
self.landmarks_frame.iloc[idx, 0])
image = io.imread(img_name)
landmarks = self.landmarks_frame.iloc[idx, 1:].as_matrix()
landmarks = landmarks.astype('float').reshape(-1, 2)
sample = {'image': image, 'landmarks': landmarks}
if self.transform:
sample = self.transform(sample)
return sample
3.3 实例化类
接下来我们对上面定义好的类做实例化,然后在数据样本上进行迭代。我们会打印前4个样本图像及其对应的坐标点。
face_dataset = FaceLandmarksDataset(csv_file='faces/face_landmarks.csv',
root_dir='faces/')
fig = plt.figure()
for i in range(len(face_dataset)):
sample = face_dataset[i]
print(i, sample['image'].shape, sample['landmarks'].shape)
ax = plt.subplot(1, 4, i + 1)
plt.tight_layout()
ax.set_title('Sample #{}'.format(i))
ax.axis('off')
show_landmarks(**sample)
if i == 3:
plt.show()
break
4. Transforms
从上面显示的图片我们可以看到每张图片的大小都不一样,但往往我们在处理神经网络的输入图像的时候都希望它们有一个相对固定的大小。因此,我们需要一些对图像进行预处理的工作。
4.1 实现常用变换功能
我们试着写一下这三个常用的变换功能:
Rescale:重新调整图像大小;RandomCrop:随机从图像中截取一部分;ToTensor:将numpy类型表示的图像转换成torch表示的图像。
我们用类而不是函数来实现以上这三个功能,主要是考虑到如果用函数的话,每次都需要传入参数,但是用类就可以省掉很多麻烦。我们只需要实现每个类的__call__函数和__init__函数。
下面是对这三个功能的实现:
class Rescale(object):
"""Rescale the image in a sample to a given size.
Args:
output_size (tuple or int): Desired output size. If tuple, output is
matched to output_size. If int, smaller of image edges is matched
to output_size keeping aspect ratio the same.
"""
def __init__(self, output_size):
assert isinstance(output_size, (int, tuple))
self.output_size = output_size
def __call__(self, sample):
image, landmarks = sample['image'], sample['landmarks']
h, w = image.shape[:2]
if isinstance(self.output_size, int):
if h > w:
new_h, new_w = self.output_size * h / w, self.output_size
else:
new_h, new_w = self.output_size, self.output_size * w / h
else:
new_h, new_w = self.output_size
new_h, new_w = int(new_h), int(new_w)
img = transform.resize(image, (new_h, new_w))
# h and w are swapped for landmarks because for images,
# x and y axes are axis 1 and 0 respectively
landmarks = landmarks * [new_w / w, new_h / h]
return {'image': img, 'landmarks': landmarks}
class RandomCrop(object):
"""Crop randomly the image in a sample.
Args:
output_size (tuple or int): Desired output size. If int, square crop
is made.
"""
def __init__(self, output_size):
assert isinstance(output_size, (int, tuple))
if isinstance(output_size, int):
self.output_size = (output_size, output_size)
else:
assert len(output_size) == 2
self.output_size = output_size
def __call__(self, sample):
image, landmarks = sample['image'], sample['landmarks']
h, w = image.shape[:2]
new_h, new_w = self.output_size
top = np.random.randint(0, h - new_h)
left = np.random.randint(0, w - new_w)
image = image[top: top + new_h,
left: left + new_w]
landmarks = landmarks - [left, top]
return {'image': image, 'landmarks': landmarks}
class ToTensor(object):
"""Convert ndarrays in sample to Tensors."""
def __call__(self, sample):
image, landmarks = sample['image'], sample['landmarks']
# swap color axis because
# numpy image: H x W x C
# torch image: C X H X W
image = image.transpose((2, 0, 1))
return {'image': torch.from_numpy(image),
'landmarks': torch.from_numpy(landmarks)}
4.2 组合以上变换功能
假设我们现在需要将图像的较短边调整到256,然后从中随机截取224的正方形图像。我们就可以调用torchvision.transforms.Compose将以上的Rescale和RandomCrop两个变换组合起来。
以下的代码段展示了分开进行变换以及用Compose组合进行变换的结果图
scale = Rescale(256)
crop = RandomCrop(128)
composed = transforms.Compose([Rescale(256),
RandomCrop(224)])
# Apply each of the above transforms on sample.
fig = plt.figure()
sample = face_dataset[65]
for i, tsfrm in enumerate([scale, crop, composed]):
transformed_sample = tsfrm(sample)
ax = plt.subplot(1, 3, i + 1)
plt.tight_layout()
ax.set_title(type(tsfrm).__name__)
show_landmarks(**transformed_sample)
plt.show()
5. 合并dataset与transform、遍历数据集
简单回顾一下:
- 第3小节我们介绍了
dataset类; - 第4小节我们我们介绍了怎么样实现各个转换函数,然后将其组合起来。
如果你还记得的话,我们在之前定义dataset的时候是有一个transform参数的,但我们在第4节中是先取了样本数据,然后再进行变换操作,并没有将其作为参数传到dataset中。所以我们现在要做的工作就是将所有的内容集成到一起。每次抽取一个样本,都会有以下步骤:
- 从文件中读取图片;
- 将转换应用于读入的图片;
- 由于做了随机选取的操作,所以起到了数据增强的效果。
其实我们只要把Transform的部分作为形参传入dataset就可以了,其他的都不变。
然后用for循环来依次获得数据集样本。
transformed_dataset = FaceLandmarksDataset(csv_file='faces/face_landmarks.csv',
root_dir='faces/',
transform=transforms.Compose([
Rescale(256),
RandomCrop(224),
ToTensor()
]))
for i in range(len(transformed_dataset)):
sample = transformed_dataset[i]
print(i, sample['image'].size(), sample['landmarks'].size())
if i == 3:
break
6. DataLoader类
以上我们已经实现了dataset与transform的合并,也实现了用for循环来获取每一个样本数据,好像事情就已经结束了。
但等等,真的结束了吗?emmmm,我们好像还落了什么事情,是的没错:
- 按照batch_size获得批量数据;
- 打乱数据顺序;
- 用多线程multiprocessing来加载数据;
torch.utils.data.DataLoader这个类为我们解决了以上所有的问题,是不是很腻害~
只要按照要求设置DataLoader的参数即可:
- 第一个参数传入transformed_dataset,即已经用了transform的Dataset实例。
- 第二个参数传入batch_size,表示每个batch包含多少个数据。
- 第三个参数传入shuffle,布尔型变量,表示是否打乱。
- 第四个参数传入num_workers表示使用几个线程来加载数据。
如下所示即实现了DataLoader函数的使用,及批样本数据的展示。
dataloader = DataLoader(transformed_dataset, batch_size=4,
shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# Helper function to show a batch
def show_landmarks_batch(sample_batched):
"""Show image with landmarks for a batch of samples."""
images_batch, landmarks_batch = \
sample_batched['image'], sample_batched['landmarks']
batch_size = len(images_batch)
im_size = images_batch.size(2)
grid = utils.make_grid(images_batch)
plt.imshow(grid.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0)))
for i in range(batch_size):
plt.scatter(landmarks_batch[i, :, 0].numpy() + i * im_size,
landmarks_batch[i, :, 1].numpy(),
s=10, marker='.', c='r')
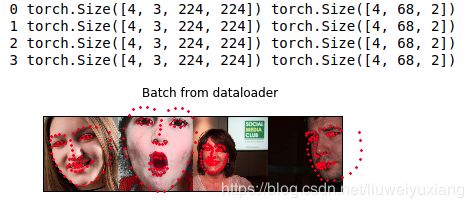
plt.title('Batch from dataloader')
for i_batch, sample_batched in enumerate(dataloader):
print(i_batch, sample_batched['image'].size(),
sample_batched['landmarks'].size())
# observe 4th batch and stop.
if i_batch == 3:
plt.figure()
show_landmarks_batch(sample_batched)
plt.axis('off')
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
break
7. torchvision
torchvision包提供了一些常用的数据集和转换函数。使用torchvision甚至不需要自己写处理函数。
在torchvision中最通用的数据集是ImageFolder,它假设数据结构为如下:
root/ants/xxx.png
root/ants/xxy.jpeg
root/ants/xxz.png
.
.
.
root/bees/123.jpg
root/bees/nsdf3.png
root/bees/asd932_.png
这里的root指代根目录,ants bees指的是不同的类标签,后面的是具体的图片名称。
当然它还提供了对PIL.Image的常用操作,包括RandomHorizontalFlip Scale等等。
以下为用torchvision实现的超简化版本的数据处理方法:
import torch
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomSizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
hymenoptera_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root='hymenoptera_data/train',
transform=data_transform)
dataset_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(hymenoptera_dataset,
batch_size=4, shuffle=True,
num_workers=4)
整理总结
我们来整理一下整个实现思路哦~
主要分以下三种情况:
1. 对于torchvision提供的数据集
- 这是最简单的一种情况。
- 对于这一类数据集,就是PyTorch已经帮我们做好了所有的事情,连数据源都不需要自己下载。
- Imagenet,CIFAR10,MNIST等等PyTorch都提供了数据加载的功能,所以可以先看看你要用的数据集是不是这种情况。
- 具体的使用方法详见之前的博客Pytorch入门学习(四)-training a classifier
2. 对于特定结构的数据集
- 这种情况就是不在上述PyTorch提供数据库之列,但是满足下面的形式:
root/ants/xxx.png
root/ants/xxy.jpeg
root/ants/xxz.png
.
.
.
root/bees/123.jpg
root/bees/nsdf3.png
root/bees/asd932_.png
- 那么就可以通过torchvision中的通用数据集ImageFolder来完成加载。
-具体使用方法见上文。
3. 对于最普通的数据集
- 最后一种情况是既不是自带数据集,又不满足ImageFolder,这种时候就自己进行处理。
- 首先,定义数据集的类(myDataset),这个类要继承dataset这个抽象类,并实现__len__以及__getitem__这两个函数,通常情况还包括初始函数__init__.
- 然后,实现用于特定图像预处理的功能,并封装成类。当然常用的一些变换可以在torchvision中找到。用torchvision.transforms.Compose将它们进行组合成(transform)
- transform作为上面myDataset类的参数传入,并得到实例化myDataset得到(transformed_dataset)对象。
- 最后,将transformed_dataset作为torch.utils.data.DataLoader类的形参,并根据需求设置自己是否需要打乱顺序,批大小…
- 具体见上文。
参考资料
Data Loading and Processing Tutorial
文章来源:
作者:与阳光共进早餐
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/6e22d21c84be
來源:简书
简书著作权归作者所有,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处。