leetcode | 72. Edit Distance
题目
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
Example 1:
Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
Output: 3
Explanation:
horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
rose -> ros (remove 'e')
Example 2:
Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
Output: 5
Explanation:
intention -> inention (remove 't')
inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
exection -> execution (insert 'u')
思路与解法
方法一
这道题目的意思是让我们寻找到一条可行的路径,将word1经过增、删、改三种操作变换为word2,找到最小的步骤数即可。
这是一道经典的动态规划的题目,最直观的想法是利用递归来实现,在递归过程中,当word1[0]!=word2[0]时,分别计算使用增、删、改三种方法将word1[0]转化为word2[0]表示的字符,并求得将剩余的word1Sub转化为word2Sub所需的代价(步骤数),并取得最小代价值+1(因为三种操作代价都为1)返回即可(直接上代码):
priceDelete := convert(word1[1:], word2) //delete
priceReplace := convert(word1[1:], word2[1:]) // replace
priceInsert := convert(word1, word2[1:]) // insert
删除的代价计算:convert(word1[1:], word2),由于word1需要删除第0位,所以接下来的代价便是从word1[1:]转化为word2所需的代价;
替换的代价计算:convert(word1[1:], word2[1:]),由于将word1的第0位替换为与word2的第0位相同的字符,所以剩下的代价即为word1[1:]转化为word2[1:]所需的代价;
插入的代价计算:convert(word1, word2[1:]),由于在word1的第0位插入了一个与word2的第0位相同的字符,所以剩下的代价即为word1转化为word2[1:]所需的代价。
代码实现
此算法我采用go语言实现:(注意:以下代码提交会超时,改进方法后续过程中介绍)
// 此函数为原题目提供函数,调用递归函数返回代价值
func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
return convert(word1, word2)
}
// 将word1Sub转化为word2Sub
func convert(word1Sub string, word2Sub string) int {
// 两个子串刚好匹配完全,即已经找到某个步骤使得word1转化为word2,剩余代价(步骤数)为0
if word1Sub == "" && word2Sub == "" {
return 0
}
// word1已经匹配完毕,但word2还有一部分,此时,需要付出len(word2Sub)个insert的代价
if word1Sub == "" {
return len(word2Sub)
}
// word2已经匹配完毕,但word1还有一部分,此时,需要付出len(word1Sub)个delete的代价
if word2Sub == "" {
return len(word1Sub)
}
// word1Sub与word2Sub首字母相等,则返回convert(word1Sub[1:], word2Sub[1:])即可
if word1Sub[0] == word2Sub[0] {
return convert(word1Sub[1:], word2Sub[1:])
} else {
// word1Sub与word2Sub首字母不等,计算三种方法后续的代价,并取最小值+1返回
priceDelete := convert(word1Sub[1:], word2Sub)
priceReplace := convert(word1Sub[1:], word2Sub[1:])
priceInsert := convert(word1Sub, word2Sub[1:])
priceMin := min(priceDelete, priceReplace, priceInsert)
return priceMin + 1
}
}
// golang中没有三目运算符,书写比较繁琐
// 返回priceDelete,priceReplace,priceInsert 中最小值
func min(priceDelete, priceReplace, priceInsert int) int {
var priceSmaller int
if priceDelete < priceReplace {
priceSmaller = priceDelete
} else {
priceSmaller = priceReplace
}
if priceSmaller < priceInsert {
return priceSmaller
} else {
return priceInsert
}
}
遇到的问题
从上述代码中,我们可以看到该算法的时间复杂度为指数级别,所以提交结果并未通过:
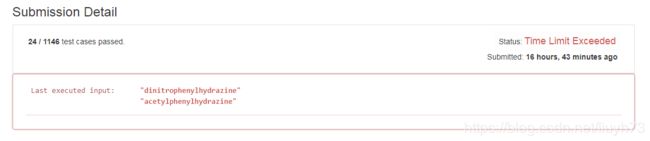
考虑这样的情况,假设源字符串分别为word1、word2,则:
- 若进行删除操作:则后续计算为convert(word1[1:], word2)
- 若进行删除操作:则后续计算为convert(word[2:], word2)
- 若进行替换操作:则后续计算为convert(word[2:], word2[1:])
- …… - 若进行替换操作:则后续计算为convert(word1[1:], word2[1:])
- …… - 若进行插入操作:则后续计算为convert(word1, word2[1:])
- ……
图示如下:

图中相同的颜色表示相同的转化,可知相同的转化在递归过程中被重复计算多次。
解决方法
由之前的分析可知,有很多重复的情况被多次计算代价,所以我们可以使用空间换时间的方法来提高效率:每次计算得到代价值,便存储当前的转化的两个字符串与该代价值的对应关系,在下次计算前,可以查询此时的两个字符串是否已经求得转化的代价值,若已经求过,则直接返回即可。具体实现如下:
var flag map[string][]map[string]int
func convert(word1Sub string, word2Sub string) int {
if len(flag[word1Sub]) > 0 {
for _, maps := range flag[word1Sub] {
if maps[word2Sub] != 0 {
return maps[word2Sub]
}
}
} else {
flag[word1Sub] = make([]map[string]int, 0) // 特别注意,需要首先make进行初始化
}
// ......
if word1Sub[0] == word2Sub[0] {
price := convert(word1Sub[1:], word2Sub[1:])
priceMap := make(map[string]int)
priceMap[word2Sub] = price
flag[word1Sub] = append(flag[word1Sub], priceMap)
return price
} else {
// ......
priceMin := min(priceDelete, priceReplace, priceInsert)
priceMap := make(map[string]int) // 特别注意,需要首先make进行初始化
priceMap[word2Sub] = priceMin + 1
flag[word1Sub] = append(flag[word1Sub], priceMap)
return priceMin + 1
}
}
func min(priceDelete, priceReplace, priceInsert int) int {
// ......
}
func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
flag = make(map[string][]map[string]int) // 特别注意,需要首先make进行初始化
return convert(word1, word2)
}
省略号附近的代码与之前保持一致,主要添加的是map[string][]map[string]int数据结构,即word1对应于可以转化到word2的一个切片,该切片的每个元素又是一个word2到代价值的一个映射。简单来说,就是每一组(word1,word2)对应一个代价值。
测试结果
方法二
此动态规划算法也可以使用递推来实现,使用dp[i][j]表示word1的前i个字符转化为word2的前j个字符所需的代价,则:
如果word1[i] == word2[j],则dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1];
否则,dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i][j-1]) + 1。
其中dp[i-1][j]、dp[i-1][j-1]、dp[i][j-1]分别表示删除、替换、增加所代表的代价。
代码实现
// 返回priceDelete, priceReplace, priceInsert中的最小值
func min(priceDelete, priceReplace, priceInsert int) int {
if priceDelete <= priceReplace && priceDelete <= priceInsert {
return priceDelete
} else if priceReplace <= priceDelete && priceReplace <= priceInsert {
return priceReplace
} else if priceInsert <= priceReplace && priceInsert <= priceDelete {
return priceInsert
}
return 0
}
func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
word1Len := len(word1)
word2Len := len(word2)
// 在字符串首部添加一个字符,便于计算dp[i][j](i=0或j=0)
word1 = "."+word1
word2 = "."+word2
// 初始化
dp := [][]int{}
for i:=0; i<=word1Len; i++ {
slice := make([]int, word2Len+1)
dp = append(dp, slice)
if i == 0 {
for j:=0; j<=word2Len; j++ {
dp[i][j] = j
}
}
dp[i][0] = i
}
// 递推
for i:=1; i<word1Len+1; i++ {
for j:=1; j<word2Len+1; j++ {
if word1[i] == word2[j] {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i][j-1]) + 1
}
}
}
return dp[word1Len][word2Len]
}
遇到的问题
dp数组的初始化十分重要,否则后续计算便不能得到正确的答案。此题目中,如果i等于0,则对于字符串word1,需要进行j次增加操作,dp[0][j]等于j;如果j等于0,则对于字符串word1,需要进行i次删除操作,dp[i][0]=i。

