springboot源码分析系列(三)--@EnableAutoConfiguration自动配置加载过程
为什么需要自动化配置
在常规的spring应用程序中,充斥着大量的配置文件,我们需要手动去配置这些文件,如配置组件扫描、视图解析器、http编码等等。常规的配置让开发人员将更多的经历耗费在了配置文件上。而这些配置都是一些固定模式的配置方式,甚至很多都是模板代码。那既然是这样一种情况,有没有一种可能性,让spring自动完成这些模板配置工作呢?答案是肯定的,这就是SpringBoot AutoConfiguration产生的初衷。将开发人员从繁重的配置工作中解放出来,把这些繁琐的配置交由SpringBoot完成,如果我们需要自己配置参数,只需要覆盖自动配置的参数即可。
SpringBoot自动化配置的核心原理
在之前的文章中,我们看过了SpringBoot的核心注解@SpringBootApplication注解的源码。其中有三个注解:@SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan。真正起自动化配置作用的是@EnableAutoConfiguration。以前我们需要配置的东西,SpringBoot帮我们自动配置,@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能,这样自动配置才能生效
下面我们来分析一下@EnableAutoConfiguration这个注解的加载过程
Target(ElementType.TYPE)
Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
由源码可知,@EnableAutoConfiguration是一个组合注解,由@AutoConfigurationPackage,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)这两个注解组成。
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@AutoConfigurationPackage的主要作用是自动配置包
/**
* Indicates that the package containing the annotated class should be registered with
* {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.3.0
* @see AutoConfigurationPackages
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
Spring底层注解@Import,给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class
将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包以及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器。
AutoConfigurationImportSelector的作用是导入哪些组件的选择器。将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回,这些组件就会被添加到容器中;也会给容器导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration),就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件。
有了自动配置类,免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作
具体的工作流程如下:
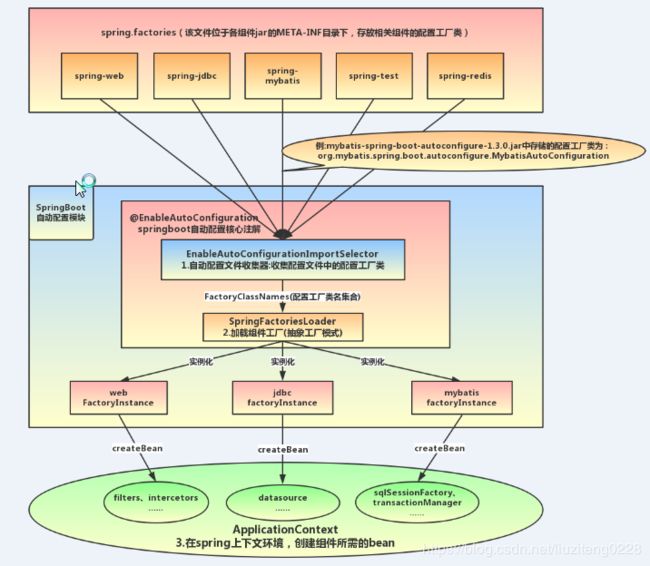
@EnableAutoConfiguration加载过程
自动配置主要由AutoConfigurationImportSelector实现的,我们主要从这个类开始讲起。AutoConfigurationImportSelector是@EnableAutoConfiguration“@Import”的DeferredImportSelector实现类,由于DeferredImportSelector作为ImportSelector的子接口,所以组件自动配置逻辑均在selectImports(AnnotationMetadata)方法中实现
自动配置加载过程主要分为以下几个步骤:
- 1.判断是否开启自动配置
- 2.从META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties文件中载入属性配置
- 3.获取所有的配置列表
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
//1.是否开启自动配置,默认开启
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
//2.从META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties文件中载入属性配置(有一些有默认值),获取注解信息
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
//3.获取所有的配置列表
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata,
annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
1.是否开启自动配置,默认开启
protected boolean isEnabled(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
if (getClass() == AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) {
return getEnvironment().getProperty(EnableAutoConfiguration.ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY, Boolean.class, true);
}
return true;
}
2.从META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties文件中载入属性配置
//文件为需要加载的配置类的类路径
protected static final String PATH = "META-INF/" + "spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties";
public static AutoConfigurationMetadata loadMetadata(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return loadMetadata(classLoader, PATH);
}
static AutoConfigurationMetadata loadMetadata(ClassLoader classLoader, String path) {
try {
//1.读取spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.6.RELEASE.jar包中pring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties的信息生成urls枚举对象
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null) ? classLoader.getResources(path)
: ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path);
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2.解析urls枚举对象中的信息封装成properties对象并加载
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
properties.putAll(PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(urls.nextElement())));
}
//3.根据封装好的properties对象生成AutoConfigurationMetadata对象返回
return loadMetadata(properties);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load @ConditionalOnClass location [" + path + "]", ex);
}
}
3.获取所有的配置列表
/**
* Return the {@link AutoConfigurationEntry} based on the {@link AnnotationMetadata}
* of the importing {@link Configuration @Configuration} class.
* @param autoConfigurationMetadata the auto-configuration metadata
* @param annotationMetadata the annotation metadata of the configuration class
* @return the auto-configurations that should be imported
*/
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
//1.将注解元信息封装成注解属性对象
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
//2.获取到配置类的全路径字符串集合
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
//需要排除的自动装配类(springboot的主类上 @SpringBootApplication(exclude = {com.demo.XXX.class})指定的排除的自动装配类)
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
//将需要排除的类从 configurations remove掉
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
//过滤掉不需要装配的类。过滤的逻辑有很多,比如我们常用的@ConditionXXX注解
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
3.1将注解元信息封装成注解属性对象
/**
* Return the appropriate {@link AnnotationAttributes} from the
* {@link AnnotationMetadata}. By default this method will return attributes for
* {@link #getAnnotationClass()}.
* @param metadata the annotation metadata
* @return annotation attributes
*/
protected AnnotationAttributes getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
String name = getAnnotationClass().getName();
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(name, true));
Assert.notNull(attributes, () -> "No auto-configuration attributes found. Is " + metadata.getClassName()
+ " annotated with " + ClassUtils.getShortName(name) + "?");
return attributes;
}
3.2获取到配置类的全路径字符串集合
getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);这个方法中有一个重要方法loadFactoryNames,这个方法是让SpringFactoryLoader去加载一些组件的名字
/**
* Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default
* this method will load candidates using {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with
* {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return a list of candidate configurations
*/
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
/**
* 这个方法需要传入两个参数getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()和getBeanClassLoader()
* getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()这个方法返回的是EnableAutoConfiguration.class
* getBeanClassLoader()这个方法返回的是beanClassLoader(类加载器)
*/
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
/**
* Return the class used by {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} to load configuration
* candidates.
* @return the factory class
*/
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
protected ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader() {
return this.beanClassLoader;
}
下面来看下loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),getBeanClassLoader());这个方法
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//factoryClassName为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
//该方法返回的是所有spring.factories文件中key为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的类路径
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if(result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
//如果类加载器不为null,则加载类路径下spring.factories文件,将其中设置的配置类的全路径信息封装 为Enumeration类对象
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null?classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories"):ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
//循环Enumeration类对象,根据相应的节点信息生成Properties对象,通过传入的键获取值,在将值切割为一个个小的字符串转化为Array,方法result集合中
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
//读取文件内容,properties类似于HashMap,包含了属性的key和value
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
//属性文件中可以用','分割多个value
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}
总结
springboot底层实现自动配置的步骤:
- 1.springboot应用启动
- 2.@SpringBootApplication起作用
- 3.@EnableAutoConfiguration
- 4.@AutoConfigurationPackage:这个组合注解主要是@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class),它通过将Registrar类导入到容器中,而Registrar类作用是扫描主配置类同级目录以及子包,并将相应的组件导入到springboot创建管理的容器中
- 5.@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):它通过将AutoConfigurationImportSelector类导入到容器中,AutoConfigurationImportSelector类作用是通过selectImports方法实现将配置类信息交给SpringFactory加载器进行一系列的容器创建过程,具体实现可查看上面的源码